Restoration methods and project results at Kis
Transcription
Restoration methods and project results at Kis
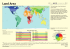
Restoration methods and project results at Kis-Balaton, Hungary. Máté, Magyari - Csaba, Megyer Location Kis-Balaton National protection levels Nature Conservation Area 1951 – 1.400 hectares Landscape Protection Area 1986 – 14.745 hectares National Park 1997 – 14.950 hectares Ramsar Site 1979 – 1.400 hectares 1993 – 14.745 hectares Natura 2000 site HUBF30003 (SPA, SCI) 2004 – 13.344 hectares IBA (Important Bird Area) 2002 – 12.072 hectares Water Protection System Phase I: 1981-1985, 1800 hectares, 21 million m3, average depth – 1,16 m Phase II: 1984-1993- 2014, 5100 hectares, 64 million m3, average depth – 1,25 m Embankment: 124 km, Water retention time: 60 days Problems Water quality: Phase I. = algic lake Rhapsodic nutrient circulation Vegetation changing, lack of macrophytes. Lack of water facilities (for example fish ladders) Decay of the reedbed in the Ingó-grave: - Too high water-level - Flow conditions - Lack of opportunities for flexible operation - Lack of the spawning areas - Lack of natural zonation Nature Conservation Vascular plants: Protected at national level 60 species Strictly protected at national level 1 species Community interest - Habitat Directive 2 species Invertebrates: Protected at national level 64 species Strictly protected at national level Ophrys insectifera Community interest - Habitat Directive 15 species Fishes: Protected at national level 4 species Strictly protected at national level 1 species Community interest - Habitat Directive 5 species Cucujus cinnabarinus Ophrys insectifera Natural values Amphibians & reptiles: Protected at national level 20 species Strictly protected at national level Community interest - Habitat Directive 16 species Birds: Protected at national level Strictly protected at national level Community interest - Bird Directive 196 species 51 species 80 species Mammals: Protected at national level 25 species Strictly protected at national level 4 species Community interest - Habitat Directive 20 species Water body types & habitats - river - canals - water reservoir - fens - marshland - swampland - other wetland types - open water surfaces - tangle vegetation - reed & bulrush beds - marsh & swamp vegetation - tussock & non-tussock sedge beds - wet meadows & hay meadows - willow shrubs & swamp woodlands AIMS: Water quality protection Nature reserve Flood-prevention What can we do…? Possible sources of conflict: contradiction between perceived and real professional interests for example. inland water, vegetation in the creek bed, hunting activity. Historical map by Ignác Müller, 1769 Habitat – restoration rehabilitation modification… Conservation requirements for utilization of wetlands Ensure the survival of the species to be protected Do not hauled into alien species Do not be harmful to the environment Adhere to the ethical standards Interventions aimed at protecting native fish species in protected areas Water movement for the vegetation growth Fish ladders establish temporary water covered areas invasive, non-native species displacement Realized version of Lake Kis-Balaton IngóiWater Management system Fenéki-tó berek Hídvégi-tó Fenéki-tó Külső tározótér Creating opportunities for flexible operation Continuous control during implementation and after… Target or source of danger? Circular dam ripping New wetlands Temporary water covered areas. Same aims? Creation of temporal water body Complex wetland Ingó water level decreasing. Unexpected situations, operational solutions. Tench Ingó 24T 2015.01.30. Ingó 24T 2015. 09. 17. Water management, potential and real problems. Different possibilities! Management 2 organization: Water Management Directorate Balaton-Uplands National Park Directorate Different aims – compromise 5 year test run Main aim: Well-functioning system! Thank you for your attention! Thank you for your attention!