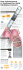Document 6530927
Transcription
Document 6530927
The Need for Repeat Ablation Following Pulmonary Vein Isolation With Both the First and Second Generation Arctic Front Cryoballoon: A Single Center Analysis Matt Brunson, MD, Kevin R. Wheelan, MD, Robert C. Kowal, MD/PhD, Alan Donsky, MD, Jay Franklin, MD, Cathy Headley, RN, David Michaels, B.A., Naveed Sarmast, MPH Introduction Methods Results • PVI using the first generation cryoballoon catheter(CB-Gen1) has been proven to be effective for patients with symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Single center, retrospective analysis. • The second generation cryoballoon catheter(CB-Gen2) has been developed providing more uniform cooling over the balloon surface area, thereby theoretically improving the efficacy of PVI. The first 303 cases were performed with CBGen1. The next 239 cases were performed with CB-Gen2. Objectives 542 consecutive patients with drug-refractory paroxysmal or early persistent AF underwent their first PVI with a cryoballoon catheter. The mean follow-up time was 271 days for CB-Gen1 and 264 days for CB-Gen2. Pulmonary Vein Reconnection Of the 303 patients treated with CBGen1, 18 (6%) underwent repeat ablation within the follow up period, and 16 (89%) of these had pulmonary vein reconnection. Of the 239 patients treated with CB-Gen2, 5 (2%) underwent repeat ablation within the follow up period, and 3 (60%) of these had pulmonary vein reconnection. Unadjusted analysis demonstrates a significantly lower voluntary rate of repeat AF ablation procedures when CBGen2 was used for the index PVI compared with CB-Gen1 (unadjusted Relative Risk=2.83; 95%CI: 1.06, 7.53). Isolated Pulmonary Veins LUPV LLPV RUPV RLPV Reconnected Pulmonary Veins LUPV LLPV Methods - Clinical Endpoint Repeat Ablations 1) To determine the need for repeat ablation for recurrent symptomatic atrial fibrillation (AF) after pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) with CB-Gen1 vs CBGen2. 2) To determine the incidence of pulmonary vein reconnection (PVR) at the time of repeat ablation for recurrent AF. 1) The number of repeat ablations performed due to recurrent symptomatic AF. 2) The incidence of PVR at repeat ablation. Repeat procedures were performed at the discretion of each patient and their physician. Catheter Number of Mean Incidence of Cases Follow-up Repeat Ablation CB-Gen1 303 271 days 6% (18 pt’s) CB-Gen2 239 264 days 2% (5 pt’s) Catheter Incidence of Pulmonary Vein Reconnection at Repeat Ablation CB-Gen1 89% (16 pt’s) CB-Gen 60% (3 pt’s) Conclusions In our single center analysis, the use of CB-Gen2 was associated with a lower incidence of repeat ablation for AF among patients undergoing cryoballoon-based PVI. Disclosures M. Brunson: None. K.R. Wheelan: Speakers Bureau, Significant, Medtronic; Ownership Interest, Significant, Medtronic; Consultant/Advisory Board, Significant, Medtronic. R.C. Kowal: Consultant/Advisory Board, Significant, Medtronic. J Franklin: Medtronic Speakers Bureau. Alan Donsky: None. C Headley: None. D Michaels: None. N Sarmast: None
Similar documents
Varicose Vein Procedure Guideline (0100‐GL‐DEPT‐0022‐HS) Prior authorization does not guarantee payment. Coverage of services is based on member eligibility and member’s benefits per the medical certificate of coverage at the time services are rendered.

Right diaphragmatic paralysis following endocardial cryothermal ablation of inappropriate sinus tachycardia

Global Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation System Market
 Ablation is the process of removal of undesired organs, abnormal growths or harmful substances from the human body. Ablation is the destruction of a nerve conduction pathway by the means of high frequency alternating currents, delivered by a bipolar or unipolar catheters. Radiofrequency (RF) ablation is a non-surgical procedure which utilizes radio waves or electric currents to interfere with the nerve conduction for a period of around six to nine months. Heat is generated from medium frequency alternating current in the range of 350-500 kHz. During radiofrequency ablation, a guiding needle reaches the desired tissue with the help of image guidance device such as a CT scan.
Ablation is the process of removal of undesired organs, abnormal growths or harmful substances from the human body. Ablation is the destruction of a nerve conduction pathway by the means of high frequency alternating currents, delivered by a bipolar or unipolar catheters. Radiofrequency (RF) ablation is a non-surgical procedure which utilizes radio waves or electric currents to interfere with the nerve conduction for a period of around six to nine months. Heat is generated from medium frequency alternating current in the range of 350-500 kHz. During radiofrequency ablation, a guiding needle reaches the desired tissue with the help of image guidance device such as a CT scan.