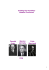DNA Song (Row, Row, Row your Boat)
Transcription
DNA Song (Row, Row, Row your Boat)
DNA Song (Row, Row, Row your Boat) I love DNA, made of nucleotides. Sugar, phosphate, and a base bonded down the sides. Adenine and Thymine make a lovely pair. Cytosine without Guanine would be very bare. **Grab a sheet of paper, and write down this song** DNA & RNA: The Genetic Codes DNA Song (Row, Row, Row your Boat) I love DNA, made of nucleotides. Sugar, phosphate, and a base bonded down the sides. Adenine and Thymine make a lovely pair. Cytosine without Guanine would be very bare Recite and Recall • What cell organelle is the “control center” of the cell? • Where is DNA found in the cell? • What is the function of DNA? Recite and Recall • What cell organelle is the “control center” of the cell? nucleus • Where is DNA found in the cell? Inside the chromosomes in the nucleus • What is the function of DNA? give instructions to cell What is DNA? • DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. (de – oxy – ri – bo – nucleic acid) • DNA is found in the chromosomes that are located within the nucleus of each cell • Chromosomes: rod-like structures that contain genetic material within the nucleus of a cell. What is DNA? Nucleus has Chromosomes made of Chromatin made of DNA History of DNA • In 1952, scientist Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is two chains of molecules in a spiral form. • By using an X-ray technique, Dr. Franklin showed that the large spiral was probably made up of two spirals. • In 1953, scientists James Watson and Francis Crick made a model of a DNA molecule. DNA Structure • DNA has 2 strands that form a double helix, or “twisted ladder” • DNA is made up of smaller unit called nucleotides. • A nucleotide is made up of 3 parts: – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate – Nitrogen base DNA is named deoxyribonucleic acid, because it is made of the sugar, deoxyribose! Nucleotide DNA Structure • The sides, “backbone” of DNA are made of the sugar, deoxyribose, and the phosphates. • Color the deoxyribose blue • Color the phosphates pink DNA Structure • The rungs in the middle of the DNA “twisted ladder” are made of the nitrogen bases. – Adenine, (A) ALWAYS pair up! – Thymine (T) – Guanine (G) ALWAYS pair up! – Cytosine (C) • The bases are bonded together by hydrogen bonds. Color the DNA Structure. DNA Structure Match the bases with their pairs. • • • • • • • • A G C G T T A C Match the bases with their pairs. • • • • • • • • A G C G T T A C • T •C •G •C •A •A • T •G Questions 1. Why is the nucleus called the “control center” of the cell? 3. Where in the cell are chromosomes located? 4. DNA can be found in what organelles? 5. What two scientists established the structure of DNA? Questions 1. Why is the nucleus called the “control center” of the cell? It tells the cell what to do 3. Where in the cell are chromosomes located? nucleus 4. DNA can be found in what organelles? mitochondria, chloroplasts 5. What two scientists established the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick Questions 7. What are the sides of the DNA ladder made of? 8. What 3 parts make up a single nucleotide: 9. What are the 4 bases that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder? 10. What sugar is found in DNA? 11. How do the bases bond together? A bonds with ______ G bonds with______ Questions 7. What are the sides of the DNA ladder made of? Sugar and phosphates 8. What 3 parts make up a single nucleotide: sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base 9. What are the 4 bases that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder? Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine 10. What sugar is found in DNA? deoxyribose 11. How do the bases bond together? A bonds with __T__ G bonds with__C___ RNA Structure • RNA is known as ribonucleic acid, a singlestranded nucleic acid. • RNA is made of nucleotides: – Ribose sugar – Phosphate – Nitrogen base (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil) Color the RNA Structure. Compare DNA Vs. RNA Deoxribose sugar Nucleic acid Adenine Double stranded Guanine Phosphate Ribose sugar Single stranded Cytosine Uracil Thymine RNA Structure • There are 3 types of RNA: – mRNA (messenger RNA) – tRNA (transfer RNA) – rRNA (ribosomal RNA) 3 Types of RNA • mRNA, is the RNA strand that is coded directly from a DNA strand. • Its job is to travel out of the nucleus to the ribosome (rRNA) in the cytoplasm. • There it gets decoded so that tRNA can bring amino acids to the ribosome to build a protein • This process is known as PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. How does DNA & the nucleus tell the cell what to do? • DNA is condensed into threadlike structures called chromatin. • The chromatin is condensed into rodlike structures called chromosomes. • Chromosomes are composed of genes, segments of DNA that code for amino acids. – These amino acids build proteins that express certain traits such as blue eyes, or baldness. • Genes can only be expressed when they have been turned into a protein. From DNA – RNA - Protein • The process of a DNA strand being coded into a RNA, and then coded into a protein is known as protein synthesis. – Step 1: Copy DNA strand (replication) – Step 2: Turn DNA strand into RNA strand – Step 3: mRNA carries RNA strand to ribosome – Step 4: tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome – Step 5: proteins are made in ribosome Step 1: DNA copies itself (Replication) • DNA unzips to form 2 separate strands • Nitrogen bases pair up to form new strands • DNA the zips back together. – Have one old strand and one new strand together. – This process is called semi-conservative, because DNA “saves” one old strand and copies one new strand. •Color old strand RED •Color new strand GREEN DNA Replication Color the old strand (including its base) red. Color the new strand (including its base) green. DNA Replication Color: Phosphate Sugar Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Step 2: DNA strand gets coded into RNA • DNA unzips • One side of DNA stranded gets coded for a mRNA strand – A to U – G to C • DNA the zips back together. • mRNA travels out of the nucleus. Step 3: mRNA leaves nucleus and travels to ribosome in the cytoplasm Step 4: tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome Step 5: Amino acids link to build a protein Questions 2. What is a gene? 6. Replication is called “semi-conservative” because half of the original strand is ______? 10. What sugar is found in RNA? 11. Why is RNA necessary to act as a messenger? Questions 2. What is a gene? section of DNA, codes for a trait 6. Replication is called “semi-conservative” because half of the original strand is saved. 10. What sugar is found in RNA? ribose 11. Why is RNA necessary to act as a messenger? DNA does not leave the nucleus; Double stranded DNA to big to fit through nuclear pores. Questions 13. Proteins are made where in the cell? 14. How is RNA different from DNA? ( 3 things) 15. The process of copying DNA is called _____? 16. What is the shape of DNA? Questions 13. Proteins are made where in the cell? ribosomes in the cytoplasm 14. How is RNA different from DNA? ( 3 things) single-stranded, uracil nitrogen base, ribose sugar 15. The process of copying DNA is called replication. 16. What is the shape of DNA? Double helix, “twisted ladder” Questions 17. How does one cell become a brain cell and another a skin cell? 18. Why is DNA called the “Blueprint of Life”? Questions 17. How does one cell become a brain cell and another a skin cell? only some genes are turned on 18. Why is DNA called the “Blueprint of Life”? DNA gives instructions for building an organism. DNA Helpful websites • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/ • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/tr anscribe/ • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/# • http://www.dnalc.org/view/15890-Ribosome-gameinteractive-2D-animation.html • http://www.mochigames.com/game/proteinsynthesis-race/ • http://www.wisconline.com/Objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP1302