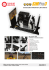Simulation Experience
Transcription
Simulation Experience
Simulation Experience Cynthia Cummings, RN, MSN, EdD M. A. (Bonnie) Holder, PhD, ARNP History at UNF First HFPS obtained in 2007 Sparsely used/Not to full potential Health Assessment only Lack of training for faculty No IT support In 2010 new faculty assigned to Simulation Initially Self taught training School paid for Laderal to provide training for 6 faculty Two faculty actively involved in simulation, others starting Part time IT support Simulation Equipment 3 G Laderal mannequin Video recording equipment 2 current cameras Simulation area No facility modification for special rooms or gas Three rooms with central “control” area Hospital Room set up for undergraduate Hospital bed Pseudo suction and oxygen headboard IV pumps/Medication cart/Supply “closet” Operating room with anesthesia machine for CRNA Equipment Equipment Funding Original funding for HFPS and equipment from a HRSA grant written by anesthesia Further funding for supplies and equipment from school operating budget. Teaching grant awarded this summer to further develop integration of simulation across the curriculum Faculty Involvement Rogers,E.M. (2003). Diffusion of Innovations, 5th ed. New York: Free Press. Relative Advantage Compatibility with staff Complexity Trialability Observability How do we make this happen? Faculty Innovation Become Change Agents Attended Laerdal SUN conference Practiced with equipment Worked with Computer assistant to develop scenarios POSITIVE about product Talked up the system to other faculty Allowed them to come watch our sessions Faculty Growth Our administration encourages the use of simulation and other technologies Encourage other courses to incorporate scenarios and work with them to develop their plan 5 Stages: Knowledge Persuasion Decision Implementation Confirmation We need to make it user friendly, so that they would be willing to try the simulations Faculty Benefits Biggest benefits is evaluation of student comprehension of: Techniques Medication administration Assessment techniques Evaluation of patient responses Safety factors Patient and family interaction SBAR and physician communication Interdisciplinary communication Critical thinking in a variety of situations Documentation Simulation Benefits Student learning takes place in a safe environment No harm to the patient can occur Students can practice skills, discuss medication processes Contact physicians and staff without reprimand Learn in real world scenarios and stressful events without actual consequences View the debrief sessions to understand their behaviors Putting the Plan to work Decided to change the adult health curriculum to incorporate simulations Studied other on-line systems, such as Evolve by Elsevier to look at scenarios and student involvement Agreed to have all adult health students attend two simulation sessions. Incorporated Pre and Post activities with the scenarios Simulation Scenarios Utilized the NLN scenarios and developed our own based on Evolve situations Used an evolve workbook to add trends and handlers Incorporated voices, xrays, labs, etc Scenario Development Started with the NLN off the shelf product Did own “voices” Then developed 6 Adult Health scenarios from class content Asthma- 33 yr old female admitted with acute attack Diabetes- 60 yr old homeless man with hyperglycemia and a foot ulcer Renal Failure- 82 yr old female with renal failure, breast cancer and medication needs Cardiac- 50 yr old male with chest pain and potential MI Abdominal mass- 60 yr old female with possible abdominal cancer requiring and NGT and pain medication Student Responsibilities Arrive 15 minutes prior to schedule Dressed in their clinical uniform bring appropriate equipment Required to go online and review the scenario prior to their session Complete the online Pre-simulation exercises and quiz Following the simulation Review their video and provide critique Complete on line Post simulation exercises and a quiz. Document their care and record their reflections These are evaluated for completeness and comprehension. The students are not assigned grade But incomplete assignments are documented under their clinical evaluation for the course Junior vs Senior Experiences Juniors were in the Adult Health Course and followed the previous slide requirements Assigned in groups of 2-3 students and were told of the scenario they were assigned in advance Seniors were in their final Professional Role Integration Course Not assigned scenarios in advance Simulation experience is done as a “solo” nurse provider Scenario chosen randomly from 10 possibilities Did not have a previous simulation experience Their performance was graded and was 20% of the course grade Senior Grading Rubric Introduction, explanation of events Assessment and ROS Plan & Communication with MD/Staff 10% 20% 15% Including utilization of SBAR and read-back Implementation of Interventions 25% Evaluation of actions and reassessment 10% Documentation 20% Using Cerner computer doc system Admission assessment SBAR form Plan of Care with priorities Simulation reflection Lessons Learned Senior Simulation Experiences Of 80 students, we found the following issues: 43 did not remember a medication usage, side effects or implications 26 did not read-back 22 incomplete ROS, missed allergies, meds at home and PMH 15 not know lab values on Chem 7 or ABG’s 12 not know the rhythm strip 12 not follow ABC’s, not correct priority 11 not follow correct procedure for IVP or IVPB 10 not follow correct procedure for resp. equipment 9 not perform assessment correctly (listened over pt. gown) 5 not follow medication rights 4 not follow universal precautions Student Responses Student responses were as follows: “overall I think I did well, I stayed calm and focused on my patient’s needs” “I forgot to read the orders back, the actual experience is intense!” “it is one of the best learning tools in the nursing program” “I need to work on my interview techniques, I missed some important questions and I didn’t know the medication side effects” “it was a good experience, I realized the importance of getting a history before calling the MD” “I felt like I was very slow and I didn’t know how to read the EKG, I thought I knew that?” Student Responses “I think I did really well, I’m actually feeling better about my abilities now” “I forgot some important things, like reassess the vital signs and I didn’t pick the best time for diabetic teaching” This was really helpful, I was completely independent, so it showed my strengths and weaknesses. Dr. Cummings really challenged me and refreshed my skills and memory.” “Boy, do I have room for improvement, I was surprised I could interpret lab findings, but I forgot to read back the orders and they went really fast.” “I was really nervous in the beginning, I missed some steps, but this is a great learning toll and I wish we could do more.” Faculty Responses Great tool for evaluation of student learning Reflects real world activities Incorporates other disciplines Allows for student critical thinking without faculty interaction Allows for student reflection and self-direction Great tool to see what areas need improvement, such as medication safety, SBAR, communication techniques Allows faculty to evaluate clinical learning experiences and see if any incorrect behaviors have been adopted Future Continue to work on scenario development Asked graduate students to assist in scenario planning Look at other online resources, actually using a different plan this fall Look at other equipment and supplies, obtained a research grant Continue to encourage other faculty to utilize the lab Presently we have: Adult Health Professional Integration Pediatrics/OB Psych/Rehab CRNA program