The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius
Transcription
The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius
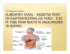
The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius Cavitas oris 1. Fill in the blanks in the following text. palate, salivary glands, incisors, ingestion, soft palate, mastication, molars, hard palate, oral, uvula, canines, saliva, Digestion begins in the mouth, also called the ________ cavity. The primary functions of the mouth are concerned with the intake or ____________ of food, with chewing or ______________ and swallowing. There are 32 teeth in a complete adult set, including ___________ and ___________ to bite food and _____________ for grinding. The ___________ is the roof of the mouth: the anterior portion (__________ ___________) is formed by bone and the posterior part (_____________ _____________) is made of soft tissue. The fleshy _____________, used in speech production, hangs from the soft palate. In the process of chewing the tongue, lips, cheeks, palate also help to break up the food and mix it with ___________, the digestive juice moistens the food and begins the digestion of starch. The ___________ _____________ secrete saliva into the mouth and are considered to be accessory organs of digestion. 2. Identify the parts of the oral cavity by a number from the picture. ͟ dens caninus ͟ dens incisivus primus (centralis) ͟ dens incisivus secundus (lateralis) ͟ dens molaris tertius (sapientiae) ͟ dentes molares (primus et secundus) ͟ dentes praemolares (primus et secundus) ͟ fauces ͟ gingiva ͟ labium inferius ͟ labium superius ͟ lingua ͟ palatum durum ͟ palatum molle ͟ tonsilla palatina ͟ uvula ͟ vestibulum oris 3. Fill in the blanks in the text with the given terms. foramen, dentin, pulp, crown, permanent, neck, cement, deciduous, roots, enamel, Each tooth consists of a ____________, which projects above the gum; one or more ___________ embedded in the alveolus; and a_______________, which stretches between the crown and the root. Each tooth also contains a cavity filled with ____________, richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves that enter the cavity through a small aperture or ______________ at the apex of each root. The solid inner part of the tooth consists of ______________, ___________ covers the exposed part of the crown, and ______________ covers the surface of the root. Two sets of teeth appear at different periods of life: the 20 primary or ____________ teeth appear during infancy, the 32 secondary or _____________ teeth during childhood and early adulthood. 4. Identify the parts of a tooth by a number from the picture. ͟ corona dentis ͟ cervix/collum dentis ͟ radix dentis ͟ enamelum ͟ dentinum ͟ cavitas dentis, pulpa dentis ͟ canalis radicis dentis ͟ gingiva ͟ periodontium ͟ cementum ͟ foramen apicis dentis Lingua 5. Fill in the blanks in the text with the given terms. mastication, dorsum, foliate, frenulum, tonsil,lingua, sulcus medianus, apex, papillae, filiform, fungiform, vallate, glossa, radix, sulcus terminalis, The tongue (L.,__________; Gk,____________), situated in the floor of the mouth. The tongue is important in taste,_____________ , swallowing, and speech. It is composed chiefly of skeletal muscle, is partly covered by mucous membrane, and presents a tip (________) and margin,__________ , inferior surface, and root (_____________). The tip, or apex, usually rests against the incisors and continues on each side into the margin. The dorsum extends from the oral cavity into the oropharynx. A V-shaped groove, the_________________, runs laterally and anteriorward from a small pit, the foramen cecum. The sulcus terminalis is the boundary between (1) the oral part, or anterior two thirds, and the pharyngeal part, or posterior third, of the tongue. The oral part of the dorsum may show a shallow median groove (_________________). The mucosa has numerous minute lingual ___________: the ___________ papillae, the narrowest and most numerous; (2) the ____________ papillae, with rounded heads (like mushrooms) and containing taste buds; (3) the _____________ papillae, about a dozen large projections arranged in a V-shaped row in front of the sulcus terminalis and containing numerous taste buds; and the __________ papillae, inconstant grooves and ridges at the margin posteriorly. Lymphatic follicles in the submucosa are collectively known as the lingual ____________. The inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the mouth by the __________. 6. Identify the parts of the tongue in the picture. ͟ apex linguae ͟ papillae foliatae ͟ sulcus medianus ͟ corpus linguae ͟ papillae fungiformes ͟ sulcus terminalis ͟ foramen caecum ͟ papillae vallatae ͟ tonsilla lingualis ͟ papillae filiformes ͟ radix linguae ͟ tonsilla palatina 7. Identify the parts of the digestive system in the picture. ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ ͟ anus ͟ ͟ appendix vermiformis ͟ ͟ caecum ͟ ͟ canalis analis ͟ ͟ cavitas oris propria 8. Fill in the blanks in each test with the given terms. cavitas oris colon ascendens colon descendens colon sigmoideum colon transversum duodenum gaster (ventriculus) glandula parotis glandula sublingualis glandula submandibularis glandulae salivariae majores hepar ileum intestinum crassum intestinum tenue jejunum oesophagus pancreas pars laryngea pharyngis pars oralis pharyngis pharynx ͟ rectum rima oris vesica biliaris (fellea) vestibulum oris From the mouth to the stomach peristalsis, pylorus, intestine,pharynx, esophagus, shincter, cardia, pepsin Portions of moistened food are moved from the oral cavity toward the ____________ where swallowing reflexes push it into the ____________. ______________moves the food through the esophagus and into the stomach. At its distal end, where it joins the stomach, the esophagus has muscle tissue that contracts to keep stomach contents from refluxing. This lower esophageal ___________(LES) is also called the cardiac sphincter‖ because it lies above the stomach‘s __________, the region around its upper opening. In the stomach food is further broken down as it is churned and mixed with secretions containing the enzyme ___________ and powerful hydrochloric acid (HCl), both of which break down proteins. The partially digested food then passes through the lower portion of the stomach, the ____________and then into the_________________. The Small Intestine jejunum, villi, duodenum, ileum, Food leaving the stomach enters the_______________, the first portion of the small intestine. Duodenum is from the Latin duodeni, meaning ―twelve each‖, referring to its length. As food continues through the ____________ and ______________, the remaining sections of the small intestine, digestion is completed. The digestive substances active in the small intestine include enzymes from the intestine itself and products from accessory organs that secrete into the duodenum. The digested nutrients, as well as water, minerals, and vitamins are absorbed into the circulation, aided by small projections in the lining of the small intestine called ___________. Each villus has blood capillaries to absorb nutrients into the blood stream and lymphatic capillaries, or lacteals, to absorb small molecules of digested fats into the lymph. The Large Intestine colon, sigmoid, rectum, ascending, transverse, descending, faeces, anus, cecum, appendix, Any food that has not been digested, along with water and digestive juices, passes into the large intestine. This part of the digestive tract begins in the lower right region of the abdomen with a small pouch, the ____________, to which the ____________is attached. The large intestine continues as the _____________, a name that is often used to mean the large intestine. The colon travels upward along the right side of the abdomen as the _____________ colon, crosses below the stomach as the _____________ colon, then continues down the left side of the abdomen as the _____________colon. As food is pushed through the colon, water is reabsorbed and stool or _____________is formed. This waste material passes into the S-shaped _____________colon and is stored in the ____________ until eliminated through the ___________. The Accessory Organs hepatic, liver, cholecyst, pancreas,salivary, bile, The _____________ glands, which secrete into the mouth, are the first accessory organs to act on food. They secrete an enzyme (salivary amylase) that begins the digestion of starch. The remainder of the accessory organs is in the abdomen and secrete into the duodenum. The_________ is a large gland with many functions. A major part of its activity is to process blood brought to it by a special circulatory pathway called the__________ portal system. The liver‘s role in digestion is the secretion of ____________, which emulsifies fats (breaks them down into smaller units). The gallbladder (______________) stores bile until it is needed in digestion. The common hepatic duct from the liver and the cystic duct from the gallbladder merge to form the common bile duct, which empties into the duodenum. The _______________ produces a mixture of digestive enzymes that is delivered into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. It also secretes large amounts of bicarbonate, which neutralizes the strong stomach acid. 9.Identify the parts in the picture. ͟ et v. lienalis (splenica) ͟ caput pancreatis ͟ cauda pancreatis ͟ corpus pancreatis ͟ diaphragma ͟ ductus choledochus (biliaris) ͟ ductus cysticus ͟ ductus hepaticus communis ͟ ductus pancreaticus ͟ duodenum ͟ lien (splen) ͟ lobus hepatis dexter ͟ pancreas ͟ vesica biliaris (fellea) Exercises 1. Give the latin term. 1st part of small intestine ___________________ lining of abdominal wall ___________________ membrane between small intestine ____________________ lymphoid tissue at the back of tongue ____________________ wavelike contraction of an organ’s walls ____________________ last part of large intestine ____________________ salivary gland under the lower jaw ____________________ gallbladder _____________________ the largest gland of the body _____________________ tiny projections of the wall of the small intestine _________________ stool ______________________ partaining to the lip ______________________ pertaining to the tongue ______________________ 2.Form adjectives. ileum __________________ hepar __________________ pancreas omentum __________________ mesenterium __________________ duodenum __________________ abdomen __________________ colon __________________ splen __________________ cysta __________________ lien __________________ peritoneum __________________ gaster __________________ appendix __________________ __________________ 3. Match the pairs. Latin omentum peritoneum mesenterium papilla ventriculus jejunum duodenum ileum colon cardia pylorus English Latin a) nipple-like projection b) 1st part of small intestine c) membrane hanging from stomach d) large intestine e) 3rd part of small intestine f) upper opening of stomach g) membrane lining abdominal wall h) 2nd part of small intestine i) lower opening of stomach j) membrane between small intestin k) stomach 5 caecum dens fel ductus bilifer glandula lingua rectum saliva uvula ventriculus vesica biliaris Greek a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) glossgastrodontsialstaphylcholecystcholangicholeproctadentyphl- 4.Name the inflammation of the parts. rectum ___________________ caecum pharynx ___________________ appendix vermiformis ___________________ ventriculus ___________________ vesica fellea ___________________ intestinum tenue ___________________ ductus bilifer ___________________ intestinum crassum ___________________ glandula salivaria ___________________ ___________________ 5. Fill in the blanks with the given terms nausea, vomitus, borborygmus, haematemesis, gastroenteritis, anaemia,diarrhoea, exsiccosis, dehydratatio, gastrorrhagia, perforatio, dyspnoea,melaena, anorexia, ulcus ventriculi, syncope, _______________ is a catchall term for infection or irritation of the digestive tract, particularly the stomach and intestine. Major symptoms include (feeling sick)__________ and (throwing up from the stomach) ______________, (loose and frequent stool)______________, and abdominal cramps. These symptoms are sometimes also accompanied by fever and overall weakness. Gastroenteritis typically lasts about three days. Adults usually recover without problem, but children, the elderly, and anyone with an underlying disease are more vulnerable to complications such as (loosing too much water) ___________________. Patients with _________________ (bleeding of stomach) often present with _______________ (vomiting blood), coffee ground vomiting, ______________ (black stool) , maroon stool, or hematochezia if the hemorrhage is severe. Patients may also present with complications of ____________ (low level of red cells), including chest pain, _______________ (loss of consciousness), fatigue and shortness of breath or ________________. 6. Match the pairs and tranlsate the suffixes. Term glossodynia sialadenectomia palatoschisis stenosis pylori hepatomegalia oesophagomalacia cholelithiasis cholecystectomia sigmoidoproctostomia duodenoscopia gastrorrhagia haematemesis diarrhoea oesophagectasia gastropexia paracentesis abdominalis cholecystorrhaphia Definition Suffixum a) enlargement of liver b) narrowing of lower opening of stomach c) endoscopy of the 1st part of small intestine d) bleeding of the stomach e) surgical removal of salivary gland f) loose and frequent stool g) fissure of the palate h) vomiting blood i) surgical suture of gall bladder j) pain in the tongue k) softening of the gullet l) stone formation in the gall bladder m) formation of a passage between sigmoid colon and rectum n) removal of gall bladder o) puncture of the abdominal cavity p) surgical fixation of the stomach -odynia -ectomia q) widening of the gullet -rrhaphia 6 -schisis -stenosis -megalia -malacia -lithiasis -ectomia -stomia -scopia -rrhagia -emesis -rrhoea -ectasia -pexia -centesis Meaning 7. What do these terms mean? gingivostomatitis ulcerosa ______________ rectoscopia ________________ cheilitis ______________ colitis ulcerosa ________________ odontolithiasis ______________ hepatopexia ________________ sialorrhoea ________________ resectio ventriculi ________________ pharyngospasmus ________________ herpes labialis _________________ oesophagectasia ________________ hypaciditas _________________ appendectomia ________________ anaciditas/achlorhydria __________________ 8.What are these drug types used for? antacidum ______________ emeticum ________________ antidiarrhoicum ______________ digestivum/stomachicum ________________ antiemeticum ______________ cholagogum ________________ laxativum ________________ obstipans ________________ 9. True-false? Duodenum is the middle part of small intestine. _____ ________________________ Ptyalismus is excess bile secretion. _____ ________________________ Icterus is jaundice in other terms. _____ ________________________ Ductus cysticus is the duct of the gall bladder. _____ ________________________ Colic is a crampy abdominal pain. _____ ________________________ 10. Odd one out. caput - fundus - corpus - cauda ______________________ diarrhoea - peristaltica - nausea - vomitus ______________________ caecum - colon - rectum - lien ______________________ pancreas - hepar - villi - glandulae salivariae ______________________ gingiva - pylorus - palatum - dens incisivus ______________________ 7 11. Match the pairs Latin flatus eructation foetor oris borborygmus pruritus regurgitation, reflux faeces chymus fistula diverticulum nausea melaena obstipation icterus cirrhosis diarrhoea meteorismus neoplasma English a) food mass in the intestine b) abnormal passage between two hollow organs c) itching d) bowel gas e) stool f) bad smell of the mouth g) liver disease in which liver becomes tawny and shrinks h) pouch in the abdominal wall i) abdominal gurgle j) burping k) backflow of digestive juice l) slow bowel movement m) jaundice n) tumour o) feeling that one is about to vomit p) black bloody stool q) frequent loose stool r) bloatednes 8 12. Case studies Case Study 1: Cholecystectomy G.L., a 42-year-old obese Caucasian woman, entered the hospital with nausea and vomiting, flatulence and eructatio n, a fever of 100.5°F, and continuous right upper quadrant and subscapular pain. Examination on admission showed rebound tenderness in the RUQ with a positive Murphy sign. Her skin, nails, and conjunctivae were yellowish, and she complained of frequent clay-colored stools. Her leukocyte count was 16,000. An ERCP and ultrasound of the abdomen suggested many small stones in her gallbladder and possibly the common bile duct. Her diagnosis was cholecystitis with cholelithiasis. A laparoscopic cholecystectomy was attempted, with an intraoperative cholangiogram and common bile duct exploration. Because of G.L.’s size and some unexpected bleeding, visualization was difficult and the procedure was converted to an open approach. Small stones and granular sludge were irrigated from her common duct, and the gallbladder was removed. She had a T-tube inserted into the duct for bile drainage; this tube was removed on the second postoperative day. She had an NG tube in place before and during the surgery, which was also removed on day two. She was discharged on the fifth postoperative day with a prescription for prn pain medication and a low-fat diet. Case Study 2: Colonoscopy With Biopsy S.M., a 24-year-old man, had a recent history of lower abdominal pain with frequent loose mucoid stools. He described symptoms of occasional dysphagia, dyspepsia, nausea, and aphthous ulcers of his tongue and buccal mucosa. A previous barium enema showed some irregularities in the sigmoid and rectal segments of his large bowel. Stool samples for culture, ova, and parasites were negative. His tentative diagnosis was irritable bowel syndrome. He followed a lactose-free, low-residue diet and took Imodium to reduce intestinal motility. His gastroenterologist recommended a colonoscopy. After a 2-day regimen of soft to clear liquid diet, laxatives, and an enema the morning of the procedure, he reported to the endoscopy unit. He was transported to the procedure room. ECG electrodes, a pulse oximeter sensor, and a blood pressure cuff were applied for monitoring, and an IV was inserted in S.M.’s right arm. An IV bolus of Demerol and a bolus of Versed were given, and S.M. was positioned on his left side. The colonoscope was gently inserted through the anal sphincter and advanced proximally. S.M. was instructed to take a deep breath when the scope approached the splenic flexure and the hepatic flexure to facilitate comfortable passage. The physician was able to advance past the ileocecal valve, examining the entire length of the colon. Ulcerated granulomatous lesions were seen throughout the colon, with a concentration in the sigmoid segment. Many biopsy specimens were taken. The mucosa of the distal ileum was normal. Pathology examination of the biopsy samples was expected to establish a diagnosis of IBD. 9 Vocabula Latin English Definition Clinical stem Example (circum)vallatus 3 vallate surrounded by a depression anus, i, m. anus an- anal apex of tongue lower opening of alimentary canal tip of the tongue apex linguae appendix vermiformis vermiform appendix end part of caecum appendic- appendicitis caecum, i, n. caecum 1st part of large intestine typhl- typhlectasia cardia, ae, f cardia upper opening of the stomach narrow, tail-like end of pancreas tail cavitas oris propria oral cavity proper inner part of oral cavity cavum/cavitas oris oral cavity stomat- stomatitis cementum, i, n. cement covering of the root cervix dentis cervix neck of teeth colon ascendens ascending colon upward part colon descendens descending colon downward part colon sigmoideum sigmoid colon S-like colon sigmoid- sigmoidostomia colon transversum transverse colon horizontal corona dentis corona crown corpus ventriculi corpus body of stomach dens caninus canine tooth eye tooth dens deciduus deciduous milk tooth dens incisivus incisor front teeth dens molaris molar back tooth dens permanens permanent teeth adult teeth dens praemolaris premolar before the molars odont- dentalis 2, odontologia cholangi- cholangiographi a cauda pancreatis cauda, ae, f. dens, dentis, m. tooth dorsum linguae dorsum upper part of tongue ductus bilifer bile duct ducts conveying bile ductus choledochus common bile duct ductus cysticus cystic duct ductus hepaticus hepatic duct ductus pancreaticus pamcreatic duct duodenum, i,n. 1st part of small intestine duoden- duodenoscopia fel, fellis n / bilis, is f bile chole- felleus 3, cholelith gingiv- gingivostomatitis filiformis 2 filiform thread-like foliatus 3 foliate leaf-like fundus ventriculi fundus base of the stomach fungiformis 2 fungiform mushroom-like gingiva, ae, f gingiva gum glandula parotidea parotid gland salivary gland near the ear glandula sublingualis sublingual gland salivary gland under the tongue 10 Latin English Definition glandula submandibularis glandula, ae, f submandibular gland under the mandible Clinical stem Example gland aden- adenomalacia glandulae salivariae salivary glands glands producing saliva sialaden- sialadenitis liver hepat- hepatomegalia 3rd part of small intestine ile- ileocaecalis 2 intestinum crassum/ colon, coli n intestinum tenue large intestine col-, colon- colitis small intestine enter- enteritis isthmus faucium narrow part of throat jejunum, i, n 2nd part of small intestine jejun- jejunostomia labium, ii, n. lip cheil- lingua, ae, f. tongue gloss- labialis 2, cheilitis glossitis lobus hepatis lobe of the liver mandibula, ae f lower jaw gnath-, geni- m. genioglossus maxilla, ae f upper jaw gnath- gnathoschisis membrane between small intestines gullet mesenteri- mesentericus 3 oesophag- oesophagitis oment- omentalis 2 palatum durum membrane hanging from the stomach hard palate palatum molle soft palate roof of the oral cavity palat- palatoschisis pancreas, -atis, n. accessory gland of digestion pancreat- pancreatitis papilla, ae f nipple-shaped protuberance peritone- peritonealis 2 pharyng- pharyngitis pylor(us)- transpyloricus proct- rectalis 2, proctitis sial- sialolith hepar, hepatis, n. ileum, i, n. ileum mesenterium, ii, n. mesentery oesophagus, i, m. oesophagus omentum omentum palatum, palati n palate pars laryngea pharyngis pars oralis pharyngis laryngopharynx laryngeal part of pharynx oropharynx oral part of pharynx peritoneum, i, n. peritoneum pharynx, pharyngis f pharynx membrane lining the abdominal cavity throat porta hepatis gate of liver pylorus, i, m lower opening of stomach radix linguae root of tongue rectum, i, n. last part of large intestine rima oris opening of mouth saliva, ae, f. spit tonsilla lingualis lingual tonsil tonsilla pharyngea pharyngeal tonsil uvula, ae f small extension of soft palate vena portae portal vein ventriculus, -i m stomach gastr- gastritis vesica fellea, vesica biliaris vestibulum oris gall bladder cholecyst- outer part of oral cavity vestibul- cholecystectomi a vestibularis 11 uvul-,staphyl- Clinical terms Latin term achalasia anorexia appendicitis ascites caries cholecystitis choledocholithiasis cholelithiasis cirrhosis diarrhoea diverticulosis dysenteria dyspepsia dysphagia enterocolitis eructation fistula flatulence flatus halitosis gastritis gastroptosis gastrorrhage hernia diaphragmatica inguinal hernia hypacidity acidity icterus ileus laparoscopia melaena nausea, ae f haemorrhoidal node constipation oesophagectasia oesophagospasmus pancreatitis, -itidis f perforation peritonitis pharyngospasmus ruptura lienis peptic ulcer vomitus, emesis Definition inability of the oesophageal sphincter to relax loss of apetite inflammation of the appendix collection of fluid in the abdominal cavity tooth decay inflammation of gall bladder stone formation in the common bile duct stone formation in the gall bladder liver disease in which the liver becomes tawni and shrinks frequent and loose stool formation of pouches in the abdominal wall infection of the intestine causing bloody diarrhoea digestion disorder difficulty in swallowing inflammation of the small and large intestines belching abnormal connection between two hollow organs having gas in the GI tract intestinal gas bad breath inflammation of the stomach downward displacement of the stomach bleeding of the stomach herniation of the diaphragm herniation of the groin low level of gastric acid excess gastric acid production jaundice obstruction of intestine endoscopic examination through the abdominal wall black bloody stool feeling that one is about to vomit piles, slow bowel movement dilation of the gullet cramp of the muscles of the gullet inflammation of the pancreas creation or development of a hole in an organ inflammation of the peritoneum cramp of the throat rupture of the spleen a lesion in the mucus membrane of the upper GI tract caused by gastric juice vomiting, throwing up from the stomach 12