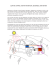A/C System Fundamentals - Arkansas Trucking Association
Transcription
A/C System Fundamentals - Arkansas Trucking Association
A/C System Fundamentals Steve Arnold – Truck Centers of Arkansas 1 Student Guide Page 1 A/C System Fundamentals Objectives: A. Explain the basic thermal laws that relate to HVAC system operation B. Identify, locate, and explain the functions of A/C system components C. Identify where and how thermal properties and processes affect operation of an A/C system D. Explain the refrigerant flow cycle Student Guide Page # How an Air Conditioner Works Principle # 1 - Heat energy will always move in the direction of “warmer” to “cooler” - Heat transfer occurs by Conduction, Convection, or Radiation Student Guide Page # How an Air Conditioner Works Principle # 2 - Heat transfer can occur as “Sensible” heat or “Latent” heat - Latent heat of Vaporization - Latent heat of Condensation 1 LB of Water Raise water temperature 1 degree Amount of heat = 1 BTU Student Guide Page # How an Air Conditioner Works Sensible Latent Sensible Subcooled Liquid Saturation Superheated Vapor (Saturation Pressure = 14.7 psia) Student Guide Page # How an Air Conditioner Works Principle # 3 - A change in pressure will cause a change in boiling point - R134a boils at -15.2 F @ sea level - By controlling pressure in an A/C system, we can control the temperature at which Latent Heat is absorbed or released Student Guide Page # Temperature/Pressure Table of Refrigerant R134a In a pure refrigerant (at saturation), temperature and pressure are directly related to each other 125 100 Vapor 75 50 Liquid 25 0 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125 Student Guide Page # 150 175 How an Air Conditioner Works Principle # 4 - When a vapor is compressed, temperature will increase even though heat has not been added - By controlling temperature, we can control the direction of heat transfer: (from air to refrigerant or refrigerant to air) Student Guide Page # System Components (TXV) Compressor Expansion Valve Condenser Evaporator Receiver/Drier Student Guide Page # Thermostatic Expansion Valve Charge of Refrigerant Low psi gas Low psi superheated gas From Evaporator To Compressor Low psi liquid Evaporator High psi subcooled liquid From Receiver-Drier Spring Student Guide Page # Thermal Laws and the A/C System Identify where and how thermal laws affect operation in an A/C system Heat always flows from “warmer” to “cooler” Latent heat transfer Sensible heat transfer A change in pressure will cause a change in boiling point When a vapor is compressed, temperature will increase even though heat hasn’t been added Student Guide Page # Refrigerant Flow in an Expansion valve System 4 Cold _____ Temperature Low _____ Pressure Gas _____ Refrigerant State Suction Side Hot _____ Temperature High _____ Pressure 1 Gas _____ Refrigerant State Discharge Side 86ºF (30ºC) 158ºF (70ºC) Discharge between Compressor and Condenser should be warmer than temp listed in PT chart Hot Cab Air Suction Line from Exp. Valve to Compressor should be warmer than temp listed in PT chart Compressor 86ºF (30ºC) Expansion Valve 41ºF (5ºC) Cold Cab Air Cold _____ Temperature Low _____ Pressure 3Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Ambient Ram Air and Fan Air 140ºF (60ºC) Plate And Fin Evaporator Line leaving Condenser should be cooler than temp listed in PT chart Warm _____ Temperature _____ Pressure 2 High Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Student Guide Page # Exercise 2.1 System Orientation 2 Now that we understand how the system works, we should be able to predict the Temperature, Pressure, and State (Gas or Liquid) of the refrigerant at various locations throughout the system: x x x x x x x x x x x Student Guide Page # x 2-15 Refrigerant Flow in a Fixed Orifice System 4 Cold _____ Temperature Low _____ Pressure Gas Refrigerant State _____ Suction Side 1 Discharge Side Hot Temperature _____ High _____ Pressure Gas Refrigerant State _____ 86ºF (30ºC) 158ºF (70ºC) Hot Cab Air Compressor 86ºF (30ºC) 41ºF (5ºC) Cold Cab Air Ambient Ram Air and Fan Air 140ºF (60ºC) Plate And Fin Evaporator Fixed Orifice Tube Cold _____ Temperature Low 3 _____ Pressure Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Warm _____ Temperature High 2 _____ Pressure Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Student Guide Page # Auxiliary A/C Systems During class discussion, enter notes and answer questions about the location and function of each component listed below. 4 Cold _____ Temperature Low _____ Pressure Gas _____ Refrigerant State Suction Side Discharge Side Hot _____ Temperature High 1 _____ Pressure Gas _____ Refrigerant State 158ºF (70ºC) 86ºF (30ºC) Hot Cab Air Compressor 2. Heater cores: __________________________ Independent, check control __________________________ valves or blend door operation 3. Blower motors: __________________________ Independent, check circuit, __________________________ airflow restriction Plate And Fin Evaporator 86ºF (30ºC) Expansion Valve Ambient Ram Air and Fan Air 41ºF (5ºC) Cold Cab Air Cold _____ Temperature Low 3 _____ Pressure Liquid _____ Refrigerant State 140ºF (60ºC) 1. Compressor, condenser, receiver/drier: __________________________ Common to both units, both __________________________ units will show problem __________________________ symptoms Warm _____ Temperature High 2 _____ Pressure Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Plate And Fin Evaporator Student Guide Page # Auxiliary A/C Systems 5. Controls: Independent, check CTC/ATC __________________________ controls and valves __________________________ 6. Evaporator temp switch: __________________________ Main unit only; may cause __________________________ freeze up or excessive clutch __________________________ cycling or no clutch cycling Suction Side Discharge Side Hot High _____ Pressure 1 Gas _____ Refrigerant State _____ Temperature 158ºF (70ºC) 86ºF (30ºC) Hot Cab Air Compressor Plate And Fin Evaporator 86ºF (30ºC) Expansion Valve 41ºF (5ºC) Cold Cab Air Cold _____ Temperature Low _____ Pressure 3Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Ambient Ram Air and Fan Air 140ºF (60ºC) 4. Evaporator/expansion valves (or evaporator/ fixed orifices): Independent, check line temps __________________________ and evaporator temps __________________________ Will likely not show up on __________________________ gauge readings __________________________ Cold _____ Temperature Low 4 _____ Pressure _____ Refrigerant State Gas Warm _____ Temperature High _____ Pressure 2Liquid _____ Refrigerant State Plate And Fin Evaporator 86F Student Guide Page # Ambient temp Leak Detection Blow out front of compressor and charge port cap areas with shop air. This clears any refrigerant that may be in the area that may cause false readings when it is time to check 0.25 oz/year or 0.50oz. per year depending on the component. Infrared Leak Detector Kent Moore J-39400 Robinair 22791 Student Guide Page # Leak Detection • Inject Dye as per tool manufacturers instructions Note: Many systems contain factory installed dye – If you are not sure, check service ports for evidence • More Dye IS NOT better! • May take up to 2 weeks for small leaks to appear Student Guide Page # Troubleshooting with Gauge Readings – All Systems • Low Refrigerant Charge • Low Side reads Lower than Normal • High Side reads Lower than Normal Student Guide Page # Troubleshooting with Gauge Readings – All Systems • Condenser Air Flow Restriction or System Overcharge • Low Side reads Higher than Normal • High Side reads Higher than Normal Student Guide Page # Troubleshooting with Gauge Readings – Day Cab • Expansion Valve Stuck Closed or Plugged • Low Side reads Lower than Normal or in a Vacuum • High Side reads Normal or Slightly High Student Guide Page # Troubleshooting with Gauge Readings – Day Cab • Expansion Valve Stuck Open • Low Side reads Higher than Normal • High Side reads Normal Student Guide Page # Troubleshooting with Gauge Readings – All Systems • Compressor Malfunction • Low Side reads Higher than Normal • High Side reads Lower than Normal Student Guide Page # Troubleshooting with Gauge Readings – O.T. Systems • Compressor Malfunction • Low Side reads Lower than Normal • High Side reads Lower than Normal Student Guide Page # Review Questions 1. In an A/C system, where does heat transfer occur? In the condenser and in the evaporator (from hot to cold) 2. Where is Latent Heat of Vaporization applied to the refrigerant? In the evaporator 3. Where is Latent Heat of Condensation removed from the refrigerant? In the condenser 4. Changing the pressure applied to refrigerant will change: a. Its boiling point b. Its condensation point c. Its temperature d. All of the above 5. What component prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor in a fixed orifice tube system? The accumulator Student Guide Page #