[KOTI Transport Session] Transjakarta Profile_Asia BRTS
Transcription
[KOTI Transport Session] Transjakarta Profile_Asia BRTS
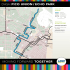
TRANSJAKARTA – BUSWAY BRT SYSTEM D.A.Rini – jakarta transportation council OUTLINES I. BACKGROUND II. INFRASTRUCTURE, OPERATIONAL, ORGANIZATIONAL, AND BUSINESS MODEL III. KEY PERFORMANCE FIGURES IV. FUTURE DEVELOPMENT Transport in Jakarta at glance • The number of motor vehicles in Jakarta currently stands at 6.7 million and increases by 11% per year; • 296 new four-wheeled motor vehicles are added daily to the city’s traffic; • A daily inflow of >700.000 motor vehicles from Jakarta’s surrounding cities, brings an estimated 1.6 million people; • The low ratio of public transportation vehicles to private vehicles (92.8); • Low capacity of public transport of 17 million trips daily, only 53% are taken by public transportation; • The poor condition of public transportation vehicles, which also gradually decrease in number. PUBLIC TRANSPORT DEMAND (trips/day) 847,750 1,078,663 1,465,912 5.302.194 7.384.939 9.445.808 Bekasi Tangerang 545,310 693,099 940,834 2002 7.3 Million Trips/day 2010 9.9 Million Trips/day 2020 13 Million Trips/day 620,702 791,295 1,148,528 Bogor & Depok WHY BRT IN JAKARTA? • Local government’s responsibility to provide good public transport system • Faster time of construction • Road infrastructure supports the system • Flexibility in determining the bus route • Suitable infrastructure for transition before the implementation of bigger system such as Subway • Efficient usage of road space • Success stories in other cities in the world TRANSJAKARTA BRT • In operation: − 1st corridor: 2004 − 2nd & 3rd corridor: 2006 − 4th & 7th corridor: 2007 − 8th corridor: 2009 − 9th & 10th corridor: 2011 − 11th corridor: 2012 • Closed trunk BRT system • Network-based System • Off-board fare collection • High platform-median BRT station • Public sector bus procurement and private sector bus operation • Flat Fare throughout the system TRANSJAKARTA SYSTEM NETWORK Length of Corridor: 191.25 km (11 corridors) Number of Stations: 206 shelters (spacing ± 1 km) Number of Routes: 21 routes Feeder Service: 3 routes Fleet Size: 544 buses (73 articulated) Fleet Fuel: CNG except 1st corridor Number of Operators: 9 operators Number of Bus Depots: 8 depots Employee: more than 5,500 Fare: IDR 3,500 (0.4 USD), free transfer Transjakarta Route Map With 11 corridors, the network is expanded up to 25 routes, minimizing transfer for Passenger TECHNOLOGY FEATURES IN TRANSJAKARTA 1. GPS-based vehicle tracking system 2. Onboard CCTV 3. Online CCTV system for BRT station – 203 CCTV cameras, 30 of which are shared through the website at www.transjakarta.co.id – 48 are also monitored live via Fibre Optic connection, the rest use on-site recording 4. e-Ticketing system – contactless smart card – 3 type of payment: JakCard, Single Trip, and Multi Trip – currently operational for 6th corridor, all corridor will be operational by the end of this year LEGAL AND INSTITUTIONAL FORM • Transjakarta is managed by BLU Transjakarta, a technical agency under supervision of Jakarta Transportation Agency • BLU Transjakarta is a government body with flexibility in some financial aspect such as: – Government agency that is allowed to sell its services to the public. – Revenues can be directly used for operation. NonBLU government agencies are not allowed to do this. – Also allowed to receive subsidy KEY PERFORMANCE FIGURES TRANSJAKARTA PERFORMANCE • Ridership (pax) per year : – 2004 : 15,942,423 – 2005 : 20,798,196 – 2006 : 38,828,039 – 2007 : 61,446,336 – 2008 : 74,619,995 – 2009 : 82,377,670 – 2010 : 86,937,287 – 2011 : 114,783,774 Highest one-day passenger record: 383,031 (July 2011) With 8 years in operation, Transjakarta passengers has increased almost 8 times since its opening year TRANSJAKARTA BUSWAY FINANCIAL FACTS • – – – – – – – – – Revenues : 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 (May) : Rp : Rp : Rp : Rp : Rp : Rp : Rp : Rp : Rp 39,063,108,475 55,831,672,900 130,783,673,000 205,779,781,500 248,339,552,000 274,517,532,000 288,757,425,500 379,457,500,500 155,175,402,500 Approximately (in current US$ rate): 2011: USD 39,526,822.97 2012: USD 16,164,104 (May) (@ US$1 = Rp. 9,600) • – – – – – – – Cost Recovery : 2004 : 89.91% 2005 : 97.51% 2006 : 75.18% 2007 : 59.37% 2008 : 60.94% 2009 : 61.30% 2010 : 62.56% OPERATIONAL CHALLENGES • Limited CNG supply – only 5 CNG station in Jakarta to serve all the Transjakarta fleet – causing loss of service time of the fleet • Mixed traffic and unsterilized lanes – encroachment by motorcycles and cars – substantial mixed traffic segment in almost all corridors • Insufficient fleet supply – highly increasing demand FUTURE DEVELOPMENT NETWORK EXPANSION • Construction of 12th, 13th, 14th, and 15th corridor as planned in the Jakarta Transportation Masterplan. • 12th corridor will be operational by the end of this year. • 13th – 15th corridor will be built elevated DIRECT-SERVICE IMPLEMENTATION • Based on Guangzhou BRT Senen P.20 Manggarai S.66 S.612 Kp Melayu Blok M KORIDOR 6 T.57 • Making Transjakarta an open system BRT S.612 Ps Minggu Lebak Bulus P.20 S.75 Ragunan Blk • Incorporating existing bus routes to support Transjakarta BRT service Kp Rambutan STATION EXPANSION • Implementation of multiple sub stops to accommodate direct-service with overtaking lane at every station. NEW STATION DESIGN • New station design to promote a better image of Transjakarta as an integral part to the life of Jakarta citizens. Thank You