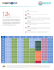
The BBC`s learning impact
Transcription
The BBC`s learning impact
The BBC’s learning impact Submission to the Independent Panel on Charter Review September 2004 Preface The BBC has been asked by the DCMS to write a submission covering our learning activities since the last licence fee settlement. It has been agreed with the DCMS that seven key questions should be covered: • What does the BBC aim to contribute to society in the field of learning? • Whom does the BBC serve through its contribution to learning? • What investment does the BBC make in learning and what does that investment deliver? • Through what outputs, activities and projects does the BBC deliver its learning contribution? • With whom does it work? • On whom does it have an impact, be it positive or negative? • How should the BBC’s learning contribution develop beyond the end of the current Charter period? The submission answers these questions through its analysis of the strategy, approach and performance of three areas in which the BBC contributes to learning. These are: • Formal learning output, which has specific curriculum-related learning objectives. This includes our programming for primary and secondary schools and for pre-school children. • Informal, targeted learning which aims to create immediate, informal learning opportunities for every citizen over the age of seven. • Wider programming from the BBC that has no formal learning objectives when commissioned but from which audiences nonetheless feel that they learn. 2 Contents Chapter 1 Overview.....................................................................................4 Chapter 2 Formal learning...........................................................................9 Chapter 3 Informal, targeted learning ........................................................29 Chapter 4 Informal learning from general programming ............................54 Chapter 5 Future strategy..........................................................................66 Appendix A The BBC’s commercial role in learning .....................................71 Appendix B Financial summary and list of learning output...........................75 3 Chapter 1 Overview The BBC aims to create public value by engaging every UK citizen in learning from the cradle to the grave. We hope that our programming and output helps create a better educated, more flexible and dynamic population that engages passionately with new challenges and ideas. The BBC creates a range of learning output because it aims to reach everybody and to engage them in active learning. This includes: • Services for pre-school children and their parents • Support for teachers, students and parents throughout primary and secondary school • Help for the millions who struggled at school and are learning basic skills • Integrated cross-media learning experiences that convert viewers and listeners of major factual programming into active learners • Programming that introduces millions of viewers and listeners to new interests and encourages them to go further and learn more. In addition, each year the BBC broadcasts 9,900 hours of general, factual programming on network television and radio from which audiences find out about the world around them1. This plays an important role in helping to create a well informed citizenship. The services that we provide constantly evolve. By tracking changes in consumer behaviour, attitudes and interests, exploring the opportunities opened up by technological innovation and noting changes in market dynamics, we keep our learning services fresh and relevant. We do not concentrate solely on the well motivated minority who naturally engage with learning. This is why we integrate our informal learning services closely into mainstream programming and use cross-media resources to make the first steps into learning as clear and simple as possible. This is just one of the distinctive aspects of the BBC’s learning services. In addition: • The BBC has created CBeebies and CBBC, which broadcast high proportions of UK-originated content making them distinct from other children’s channels. • We have brought a fusion of broadcast and interactive media expertise to basic skills, an area of considerable objective need, through Skillswise and our broadcast campaigns. • Our factual landmarks and social action campaigns have pioneered the use of media across different platforms to maximise learning impact. We have created integrated learning experiences that bind together television, 1 BARB analysis / BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 4 radio, the internet, interactive television and mobile media to involve more people in active learning experiences than the BBC has ever achieved before. • The BBC is an important innovator in learning. We are already successfully using mobile media to deliver revision support to GCSE students and will continue to find ways to harness new media for learning impact. The BBC invested £142m in services with specific formal and informal learning objectives during 2003/04. Of this, £29.4m went into formal learning output and the remaining £112.6m into informal output. A further £371.4m was invested in broad factual programming2. The BBC spends these licence fee revenues carefully to maximise their learning impact. We invest the vast majority to satisfy carefully identified audience needs, leaving a small proportion for leading-edge innovation. In schools we undertake a full review of output each year to understand the evolving needs of teachers and students and the impact of our previous spending. We learn from discussions with partner organisations and other learning providers across the UK (including Channel 4’s 4Learning), from our own advisory committees, from comprehensive annual quantitative research and from specific qualitative work. We have recently completed an analysis of the country’s social needs as we reassess our strategy for future social action output and we will continue to do this on an annual basis. Partnerships are important both in defining and implementing our strategy. They are already an important part of our learning campaigns and events and will become more important still as we seek to increase the reach of our activities to communities across the country. Successful collaborations with partners have demonstrated vividly how valuable our external relationships can be, how they can add critical mass and how much we can learn from them. The BBC as a whole recognises that more effective partnerships can increase public value. Learning will be at the forefront of this. We will invest more time and effort in building long-term partnerships - as we have done with the Open University - and involve partners earlier in the development of major future learning services. The BBC recognises the need to be increasingly sensitive to the market, particularly as media convergence and the proliferation of digital services create areas where the boundaries between public and commercial activities are unmarked. We are working closely with the commercial sector on major projects such as the Digital Curriculum and believe this sort of co-operation will be crucial in the future. We will ensure that the public value for the individual citizen and for society is always far greater than any negative commercial impact. 2 Consists of Factual and Learning, Music and Arts, Current Affairs, and Children’s. Excludes programming with no obvious learning objectives. 5 We assess the performance of our learning services in terms of reach, impact and effectiveness and carry out analysis and specific audience survey work following each major campaign. Learning services tend to be more expensive than the average BBC programme since they are often targeting more specific groups. Generally we achieve solid reach, impact and value for money through our major services (see Table 1). Table 1 Service Reach Value for money CBeebies channel 35-40% of under 5s3 2.6p per viewer hour4 CBeebies online 1.1m users per month on average5 3.3p per user CBBC channel 18% of 7-12s6 54.6p per viewer hour7 Television for schools 61% primary teachers 67% secondary teachers8 5p per student viewing experience9 Radio for schools 52% primary teachers10 Less than 1p per student listening experience11 GCSE Bitesize online 698,000 users per month on average12 23.4p per user Skillswise (basic skills online resource) 70,000 users per month on average13 £4.40 per user Landmark programming 14–36% adult population14 4–20p per first run viewer hour Enduring online factual services 6,519,000 users per month on average 7.1p per user Social action campaigns Up to 41% adults15 From 8p per viewer hour16 A third of television viewers and an average of 44% of listeners to the BBC’s five network radio stations say they have learnt directly from these services during the previous three months17. We have, however, relied too heavily on 3 BARB does not record the viewing of the under-4s. 68% of 4 and 5/6 year olds have access to CBeebies (Review of CBeebies against Conditions and Commitments, submission to DCMS, March 2004). CBeebies reaches 35-40% of them – assuming reach amongst 0-3 year olds (not recorded) is at least as high as reach amongst 4-5 year olds (38.2% 30 minute non-consecutive weekly reach). 4 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 5 “Unique users” refers to individual computers (identified through ‘cookies’) – the actual number of pupils will be higher since several people typically use one computer. Average per month across 2003/04; increasing since launch (March 2004, 1.47m users). 6 BARB analysis. 7 BARB / BBC Finance. 8 BBC/NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. 9 BBC Finance / BBC / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. 10 BBC / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. 11 BBC Finance / BBC / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. 12 Average per month across 2003/04; peaked at 1.8m in May 2004 13 Average per month across 2003/04; peaked at 130,000 in March 2004 14 BARB analysis. 15 BARB / Human Capital analysis. 16 BARB / BBC Finance. 17 BBC Omnibus survey. 6 traditional broadcast and online measurement techniques to assess the impact and cost-effectiveness of our learning activities. Consistent measurement of learning outcomes will become more important as we seek to create greater longevity through our learning activities on the ground. This is an important area in which we must improve our measurement in order to track and continue to improve our performance. When viewers are asked to place a value on learning services, they respond positively. Audiences place a value of £240m on CBeebies18, for example, whereas the service costs £7.9m and the negative market impact is estimated to be £2m19. Educational programming is ranked highly as a genre in terms of the value it creates for society – out of the 38 genres to choose from, education is ranked sixth, with only national and regional news, wildlife programming, current affairs and soaps ranked more highly20. There are four themes to our future strategy. These will maximise learning impact by satisfying identified needs more effectively. They will do this by capitalising on technological innovation and building on lessons learnt during the current Charter period. 1. We will continue to develop leading interactive learning resources. The Digital Curriculum, a broadband, interactive multimedia resource for every child in the UK, will be introduced in 2006. It will become the backbone of our future schools service. The Creative Archive will open up the television and radio archives of the BBC for use by the public for non-commercial purposes. The long-term aim is to create a national resource including public and commercial audiovisual resources. 2. We will build on the success of existing digital services such as CBeebies and Skillswise. The CBeebies website reaches 1.5 million unique users each month. We will add greater depth and structure to the learning resources for these important early years. We will introduce Skillswise, the service for adult learners, directly into workplaces in collaboration with employers and industry bodies. 3. We will create bigger campaigns with greater impact. These will be about social action and subjects people are passionate about and will be anchored in peak-time BBC One. They will involve hundreds of thousands of people in active learning. 4. Partners will be increasingly integral to the delivery of these campaigns and the maximisation of public value through learning. By creating stronger, longer-term and more wide-reaching partnerships, we will take learning into communities across the country and create the enduring impact to which both the BBC and its partners aspire. 18 Human Capital/Martin Hamblin GfK, A study measuring the value of the BBC, 2004. Oliver and Ohlbaum Market Impact Study, March 2004. 20 Human Capital/Martin Hamblin GfK, A study measuring the value of the BBC, 2004. 19 7 The contribution made by each of these future projects will be analysed through the public value test and their progress measured in terms of reach, learning impact and value for money. 8 Chapter 2 Formal learning 2.1 What are the BBC’s formal learning services? Analysis of the BBC’s learning services is broken into the three areas in which we operate: formal learning; informal, targeted learning; and general output with learning impact. This is the first of these sections. Our formal learning services are defined by their intent – all are closely linked to achieving a particular, defined learning objective or qualification and are often related to nationally set educational goals. The BBC spent £29.4m in 2003/04 on formal educational activities. The core services are: • CBeebies - the dedicated pre-school channel and branded zones on BBC One and BBC Two which encourage under-5s to learn through play, both on their own and with their parents. More than half of the channel’s programmes have learning objectives when they are commissioned, and these closely follow national early learning goals. • BBC services for schools - providing a backbone of high quality content and resources for teachers and students in both primary and secondary schools across the curriculum. Television and radio programmes for use by teachers in class have been the core of this service for a long time. Now the programmes have dedicated online resources to help teachers maximise classroom impact. There are also stand-alone online services. Bitesize, launched in 1998, has become a central plank of the schools service. Originally designed as a mixed television and online exam revision service for 14-16 year olds and their teachers, the online service was the first in the market and rapidly took off. The original service was so popular among teachers and students that it was expanded to cover 7-17 year olds21. Last year, 69% of GCSE year 11 pupils and 64% of teachers used GCSE Bitesize22. • BBC essential skills services - comprising Skillswise, a pioneering online service designed for the approximately 24,000 tutors23 teaching basic skills and their students, and WebWise, which aims to help the 15 million UK people who have never tried the internet24 to go online for the first time. 21 The original Bitesize service has expanded into services for 14-17 year olds (GCSE Bitesize in England, Wales, NI; Bitesize Standard Grade and Bitesize Higher in Scotland), 11-14 year olds (under the name Key Stage 3 Bitesize), and 7-11 year olds (equivalent to Key Stage 2; under the name Revisewise). See case study on p20 for more information. 22 BBC Educational Tools, July - August 2003 (BMRB International). When asked, And which [revision aids], if any, have you used? (prompted) 69% of year 11 students mentioned GCSE Bitesize. 90% of GCSE students have used Bitesize in some form. 23 Estimates vary between 20,000 and 28,000 (DfES). This is an average. 24 DfES/Basic Skills Agency 9 • We are also experimenting to find new ways of delivering learning to hardto-reach groups. We have developed outreach services consisting of seven Learning Centres and twelve Learning Buses to help deliver skills and other learning-related services. 2.2 The BBC’s formal learning strategy Creating media to support formal education has been an important part of the BBC’s commitment to learning since the first schools broadcasts in 1924. Six themes have driven the BBC’s formal learning strategy during the current Charter period. All have created public value by maximising learning impact. We have: • Responded rapidly to the changing needs of teachers, students and parents • Worked closely with our partners • Invested heavily in pre-school learning • Maintained a long-term commitment to investment in schools television and radio • Innovated in the use of digital media, breaking new ground to encourage increased take-up and usage and drive a digital UK • Integrated media across multiple platforms to maximise the learning impact of both new and existing content. Pre-school and services for schools have been a major focus for investment, reflecting increasing parental concern, new pressures on teachers as a result of a compulsory curriculum and the growing importance of exam success. Figure 1: "I am concerned about the quality of education available to my children” % 100 ABC1 Parents 79 80 60 40 C2DE Parents 68 52 69 47 28 20 0 1975 1985 1995 Source: BBC Education Strategic Market Plan, 1997 Parental concern about the education of their children has increased over the past 30 years across all social groups, as Figure 1 shows25. The BBC’s own research showed that this concern was growing from the earliest, pre-school 25 Note: This data is only collected every ten years, but the trend is clear and more recent research suggests that it is continuing. 10 years through to GCSE/Standard Grade exams – and in CBeebies and Bitesize we have invested to create leading services to support parents and their children. Wide consultation, consumer research with students, teachers and parents and co-ordination with Channel 4’s schools team define our schools content development strategy. Each year we review the full range of schools output to define gaps in our coverage, understand the impact of shifts in educational policy and the changing needs of students, parents and teachers. New programming and content are also piloted in schools before being broadcast. We consult with a wide range of organisations as part of our commitment to keeping our content fresh and relevant. • Senior members of the BBC Schools team regularly meet educationalists from across the UK. In the last year we have discussed strategy and content development with o Local Education Authorities o BECTA o The QCA and equivalents for the nations o BBC Educational Broadcasting Councils (in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland) and specialist advisory committees of primary and secondary head teachers • We use annual quantitative research surveys to track trends Massive changes in the school curriculum across the UK, starting with the introduction of the National Curriculum in England and Wales 16 years ago, have triggered a revolution in the classroom and placed enormous pressures on teachers. The BBC rapidly developed programming and online services to support them with the new curriculum, both online and through fresh television programming for schools. Schools television and radio have remained central. We have continued to invest in new programming throughout the Charter period, focusing spend on areas where there is a particular classroom need for which television or radio is the medium best suited. The increasing emphasis on public exams and national tests also placed more pressure on students. Our research into the experiences, concerns and needs of GCSE students led directly to the student resource sections of Bitesize which have proved so popular. We continue to drive this innovation by experimenting with the delivery of Bitesize revision through interactive television and mobile devices. Our new formal learning content for home, schools and colleges is now mostly multi-platform, using, where appropriate, television, radio, online, mobile 11 media and interactive television in close combination to make our learning resources deeper, more flexible and cost-effective. Interactive learning resources are extremely effective in supporting learning and we believe that digital resources will fundamentally change the way that school and college learning takes place. By creating resources such as Bitesize and the Digital Curriculum, the BBC helps bring school, home and community learning closer together. We hope that the range and quality of the BBC’s digital learning content encourage both schools and homes to go digital. Educational content for young children has helped persuade a new wave of former digital TV rejecters to take the plunge26. Free BBC online teaching resources should help to persuade more teachers to use online content more actively in the classroom. The Digital Curriculum will help take this to the next stage. We have also worked to improve the broader population’s digital literacy by helping those fearful of computers and the internet to go online for the first time through WebWise. As broadband becomes more widely accessible, particularly in schools and colleges, our investment in pure television and radio resources is beginning to be reduced. This trend will continue. In the future we will create a limited amount of original television/radio-based content where it is the most suitable medium, but we will be focusing our resources on the rich fusion of audiovisual content and interactive learning that is possible through broadband. Our experimental community projects in Hull and Merseyside are finding innovative ways of reaching new audiences with learning content. The projects are small-scale at the moment but make us well prepared to drive the future growth of community learning as broadband access multiplies. The BBC is committed to avoiding digital exclusion and in Hull – a city with a high quality broadband network – we have used interactive broadband content to create shared learning experiences for families in the community and in schools. 26 BBC Research into the motivations of Freeview digital adopters. 12 2.3 CBeebies – learning for the under-5s The pre-school years are perhaps the most critical for a child’s development. There is compelling evidence demonstrating that experiences during these years have more influence on a person’s success and general well-being during school and beyond than at any other period during their lives27. CBeebies is a digital channel that was launched in February 2002. Its launch has boosted the volume of BBC programming and interactive services produced for under-5s since the new content has been additional to programming on the mainstream television channels. The number of hours broadcast on mainstream channels has increased slightly since the launch of CBeebies28. Since about 70% of homes with children under 5 now have multichannel television29, the majority of families can now access far more dedicated learning programming for under-5s. The digital channel delivers 67%30 of total viewing to BBC pre-school programming. At the heart of CBeebies – and the pre-school programming broadcast on BBC One and BBC Two in the CBeebies Zones – is “learning through play”. The concept is to engage pre-school children with all six elements of the national pre-school curriculum – maths, language, literacy and personal, social and emotional development – by entertaining them with high quality, original UK programming.31 Learning through play was chosen because it is equally relevant to all children whatever their background. 2.3.1 CBeebies on television Since launch, CBeebies has become the most watched children’s channel in the UK among 4 and 5 year olds, reaching between 35-40% of them32 (Figures 3 and 4) for at least half an hour each week. 27 For Head Start research, see the Basic Skills Agency in the UK and the Advisory Committee on Head Start Research and Evaluation, US Department of Health & Human Services. In 2003, the National Audit Office commissioned a literature review of the impact of early years provision on young children from Birkbeck College’s Institute for the Study of Children, Families & Social Issues. It concluded that, while the 200+ studies of Head Start provide mixed results, there is evidence that Head Start is associated with improved health, education, crime and employment outcomes. 28 BARB analysis. 29 Review of CBeebies against Conditions and Commitments, submission to DCMS, March 2004. 30 BARB analysis, Jan-June 2004. 31 91% UK content – see Figure 4. 32 BARB does not record the viewing of the under-4s. 68% of 4 and 5 year olds have access to CBeebies (Review of Cbeebies against Conditions and Commitments, submission to DCMS, March 2004). CBeebies reaches 35-40% of them – assuming reach amongst 0-3 year olds (not recorded) is at least as high as reach amongst 4-5 year olds (38.2% 30 min non-consecutive weekly reach). 13 Figure 3: CBeebies reach 4 & 5 year olds Figure 2: Children’s channels reach to 4 & 5 year olds 0 10 20 30 Reach % Source: BARB, 30 min non consecutive weekly reach 38.2 Half Hour Weekly Reach (Non-consecutive) % Cbeebies Nick JR 22.1 Boomerang 20.6 Cartoon Network 12.5 Fox Kids 9.6 Fox Kids +1 9 CBBC 7.4 Cartoon Network Plus 6.8 Nicktoons 6.4 Nickelodeon 5.9 The Disney Channel +1 5.5 The Disney Channel 5.5 Toon Disney 5.2 Playhouse Disney 4.9 Discovery Kids 4.3 Nickelodeon Replay 4.1 Toonami 3.1 Trouble 1.3 Trouble Reload 0.6 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 40 Feb Jun Oct Feb Jun Oct Feb Jun 02 02 02 03 03 03 04 04 Source: BARB, 30 min non consecutive weekly reach CBeebies costs £7.9m each year. Budgets for originated programming stand at £60,500 per hour33 but the channel still achieves good value for money by running a high repeat rate. This can be sustained because pre-school children have a high tolerance for repetition. In fact they positively demand it. The cost per hour viewed of CBeebies is 2.6p. This is lower than the mainstream channels, BBC One and BBC Two, which cost 5.5p and 4.5p per hour viewed34. CBeebies, we believe, has a powerful role in creating public value. In research, audiences place a value of £240m on CBeebies. This is made up of £48m of value to society as a whole and £192m of value to the individual35. The negative impact on the industry is estimated to be approximately £2m36. There are clear and simple reasons to explain why CBeebies creates public value:37 • The lack of adverts and perceived quality of the programmes • The embedded trust in BBC programming – parents enjoy and benefit from BBC programmes and want their children to do so too • Parents feel there is more learning-related programming on CBeebies and they are right – over 60% is commissioned with learning objectives in mind 33 BBC Annual Report 2003-4. BARB, Human Capital analysis, and BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 35 Human Capital/Martin Hamblin GfK, A study measuring the value of the BBC, 2004. 36 Oliver and Ohlbaum Market Impact Study, March 2004. 37 Qualitative research amongst parents of children who watch CBeebies. 34 14 • The programming is (almost entirely) originated in the UK (see Figure 4) and focused entirely on the needs and experiences of UK children. The presenters, voices and cultural references are from the UK too Figure 4: UK Pre-school Thematic Channel Output by Region of Origin % 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 6 3 91 Cbeebies 24 16 Rest Of World 42 US 42 UK 67 10 Disney Nick Jr Playhouse Source: BARB, DGA, O&O analysis 2.3.2 CBeebies online CBeebies is a multi-platform service – the website is an integral part, designed to take the learning further. Interactive learning is woven into the programming but the internet is inherently interactive enabling parents and children to learn together. Young children often engage more easily with learning material when it is closely linked to programmes they have seen on television. So the CBeebies website offers a wide range of stories and games designed to build on the themes within the programming, encouraging basic maths, literacy, language and computer skills. Almost 1.5 million people now use the service in a month (see Figure 5). The site’s cost per user is 3.3p and the cost per page impression is just 0.06p (ie 17 page impressions still cost less than a single penny). Figure 5: Users & page impressions to CBeebies website Users (000's) 3,000 Users (000's) Page impressions (m) 2,500 2,000 1,500 1,000 57.4 48.9 39.9 43.2 857 930 908 Apr 2003 May Jun 37.4 46.3 77.1 76.9 61.9 43.0 1,055 941 976 Jul Aug Sep 86.2 1,102 1,115 1,153 1,253 Oct Nov Dec Jan 2004 1,372 500 0 Source: BBC server logs 15 Feb Page impressions (m) 100 86.9 90 80 70 60 1,474 50 40 30 20 10 0 Mar 2.3.3 The distinctiveness of CBeebies Because of the BBC’s unique funding mechanism, CBeebies offers a programme mix that is different from any other channel. The programming on CBeebies comes from a range of genres and, unlike other channels, most of it is made in the UK. Core CBeebies programming includes well-known children’s brands such as the Fimbles, Teletubbies and Tweenies. These character-based programmes are popular with children but are also carefully structured to achieve learning goals. The channel broadcasts innovative and distinctive programming. Something Special is an award-winning series38 that uses a fusion of video, images, spoken English, sign language and written text. It was designed from the outset to be as inclusive as possible, developing language for all sorts of children. The first four programmes were commissioned by BBC Schools but CBeebies has commissioned a further 16. CBeebies can reflect the whole of the UK through its programming. The Bobinogs, made in Wales, is broadcast in both Welsh and English language versions. Balamory is a major strand produced and set in Scotland. 2.3.4 CBeebies: summary CBeebies is a distinctive channel with clear learning objectives. It creates considerable consumer value for its target audience of parents and under-5s. In the long term, the channel aims to create considerable citizen value by exposing young viewers to a wide mix of high quality, educational programming. “ I wouldn’t let him watch Cartoon Network – its just too American, too awful, too crazy, too busy, we don’t like at all – we like a nice, easy pace … I know that everything is completely safe and there’s no violence. ” “ We would choose to watch CBeebies over everything else. It has higher educational value because it’s well researched – delivers what pre-schoolers need. It’s about having fun as well, it’s about learning through fun. 38 39 ” 39 RTS Education Award for Pre-School Programming 2004. Review of Cbeebies against Conditions and Commitments, submission to DCMS, March 2004 16 2.4 BBC services for schools The BBC has had a long commitment to schools through the provision of radio and television programming for teachers - the first schools radio and television programmes were broadcast in 1924 and 1957 respectively. The BBC makes a wide range of programmes to support teachers across most of the subjects taught at most of the different primary and secondary levels. During 2003/04, the BBC broadcast 1,335 hours of schools television programming40 and made available 224 hours of schools radio programming41. Our programmes range from the geography of Mexico for 5-7 year olds to writing skills for 11-14 year olds, from primary phonics to biology for 14-16 year olds. We also create content for children with different ability levels and for those with special needs. During the current Charter period, we have developed online services to complement our television and radio programming and launched a new revision service, Bitesize. We have innovated in the use of mobile and integrated cross-platform content to maximise learning impact. The BBC now provides approximately 25,000 web pages of material that specifically supports teachers or is for direct use in the classroom alongside other BBC resources. Bitesize provides a further 8,000 web pages of content that is relevant to students, teachers and parents. Last year we invested £11.7m to sustain the BBC schools service. The BBC has built an important position in educational media for schools through the scale and longevity of its commitment. The BBC has deep inhouse expertise, insight into teachers’ and pupils’ needs, and is one of the most trusted brands. Its links with schools, teachers, educationalists and agencies across the nations and regions go back decades. 2.4.1 Television and radio schools services During the late 1990s, usage of all schools television, including BBC programmes, declined. Nonetheless, in 2003, 61% of primary teachers and 67% of secondary teachers were still using these resources in the classroom (Figures 7 and 8)42. When the frequency of use has been factored in, we can derive a cost per use of £1.3043. If we assume around 30 in a class, this comes to less than 5p per student. 40 BBC programme schedules. BBC Annual Report 2003-4. 42 NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. 43 BBC Finance / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003 / Human Capital analysis. 41 17 Figure 6: Primary Teacher Usage of Schools Television Figure 7: Secondary Teacher Usage of Schools Television Source: BBC/ORB/NOP Annual Schools Survey Source: BBC/ORB/NOP Annual Schools Survey % C4 Schools TV BBC Schools TV 100 90 71 80 70 57 57 56 60 51 51 43 50 37 34 31 40 30 20 10 0 2003 1999 2000 2001 2002 % C4 Schools TV BBC Schools TV 100 88 90 77 80 65 70 62 61 58 54 60 50 43 42 42 40 30 20 10 0 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Radio for schools costs £1.38m. It is mainly used in primary schools where teachers have used evolving versions of programming such as Music and Movement for decades. More than half of all primary school teachers use BBC schools radio, compared with less than one in ten secondary school teachers. The cost per teacher use of radio is similar to that of online at 28p44. Amortised over a class of 30 children, cost per student experience is less than a penny. BBC schools television and radio programming will be used in classrooms for many years to come. However, we will be concentrating new television and radio production in targeted areas where it is most effective - areas such as PSHE (Personal, Social & Health Education) on television or acts of worship on radio - as overall there will be a more compelling need for resources in interactive media. This is already underway, with a larger proportion of funding being invested into complementary online resources to create cross-platform services. 2.4.2 Online schools services Approximately half of primary and secondary school teachers now use the BBC Schools website (Figures 9 and 10). This usage rose by 50% among primary school teachers and 64% among secondary school teachers between 2001 and 200345. Teachers are finding online content an increasingly important part of their teaching mix and integrating it into their long-term lesson planning. BBC Schools online resources are used each week by more than a quarter of teachers, and one in ten uses them daily46. This frequency pushes the cost per computer down to 27p47. Since, on average, several students use each computer, the cost per student is much lower than this and is likely to fall further as more teachers integrate ICT into their lessons. 44 BBC Finance / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003 / Human Capital analysis. Ibid. 46 NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. 47 BBC Finance / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003 / Human Capital analysis. 45 18 Figure 8: Use of BBC Primary Resources, 2003 BBC Schools Videos 77 BBC Teacher Notes BBC CD-ROM 67 BBC Schools TV 67 BBC Schools TV BBC Schools Radio/Audio Tapes BBCi Schools Website BBC Pupil Books Figure 9: Use of BBC Secondary Resources, 2003 61 56 50 BBC Schools Videos 48 BBCi Schools Website 46 BBC Teacher Resource Packs 35 BBC CD-ROM 31 0 20 40 60 80 100 % Source: BBC/NOP Annual Schools Survey 27 12 0 20 40 60 80 100 % Source: BBC/NOP Annual Schools Survey Bitesize has been a dramatic success story, as can be seen from the case study. This year’s early research results suggest 2004 will be another recordbreaking year. 19 Case Study: Bitesize Audience Need The introduction of school league tables and national testing placed new pressures on students and teachers alike. Our research showed that many students who were borderline pass/fail and those achieving low pass grades could improve their performance by a grade with structured support in key areas of the curriculum. We believed that a new service could motivate students and help them enjoy revision more and achieve the higher grades which they had not thought possible. Approach Bitesize was launched in 1998 as a combination of television programmes and online. It was the first revision service to make the internet a core part of its proposition. The internet rapidly became the preferred way of using the service for the vast majority of teachers and pupils. It became the service’s central plank, supported by books, interactive TV and, most recently, mobile phone applications. The internet was the natural home for Bitesize since it matched the sectionalised, highly interactive nature of the service. The service is now easily accessible by almost all students: More than 99% of schools now have internet access1, and 68% of schoolchildren have internet access at home2. Since the revision was as interactive as possible, including interactive games and a great deal of self-testing, the target students found the revision process far more involving than usual. Less confident students could see their scores rising steadily as they improved at their own pace and without the competitive issues that many find intimidating in school. Research showed that there was a clear desire from younger students to be able to access similar resources for their national tests, and teachers, who had been critical in endorsing Bitesize at GCSE level, were equally positive. So in 1999 the Bitesize service was expanded to cover Key Stage 3 (11-14 year olds) and, in 2000, Revisewise was established to cover Key Stage 2 (7-11 year olds). The services for 14-17 year olds are now under the name GCSE Bitesize (in England, Wales and Northern Ireland) and Bitesize Standard Grade and Bitesize Higher (in Scotland). The Key Stage services are still growing. ReviseWise usage is particularly high among teachers (Figure 11).The widest possible range of resources is available to support these services, including DVD, video, schools radio and CD-ROMs, as well as the online service. _______________________ 1 DfES, Survey of Information and Communication Technology in Schools 2003 2 DfES, Young People and ICT 2002, Fig. 5.5 20 Benefits GCSE Bitesize, the original and still most heavily used part of Bitesize, is accessed by around two thirds of both teachers and students48. The week before GCSEs began last year, GCSE Bitesize received 44 million page impressions. In May 2004, 1,790,000 unique users visited the site49. The service is, naturally, very seasonal, with a huge surge from February onwards as students begin revision in earnest. Figure 11: GCSE Bitesize website traffic levels Figure 10: Usage of Revisewise/Bitesize, 2003 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Teachers Pupils 67% 64% Page Impressions (millions) 50 69% 40 39% 38% 30 20 20% 10 Key Stage 2 Key ReviseWise Stage 3 0 GCSE Bitesize Aug Oct Dec 03 03 03 Monthly totals Source: BBC server logs Source: BBC/NOP Annual Schools Survey Apr 03 Jun 03 Feb 04 When asked about GCSE Bitesize50, the students give good reviews. They say that it … • Makes revision more varied and enjoyable • Builds confidence through steadily improving test scores • Helps users familiarise themselves with examination instructions • Reassures, since students understand that GCSE Bitesize covers all the elements that they can expect in the exam Is an ideal way to fill gaps in knowledge or take on areas where they feel less sure • • Helps provide structure to their revision51. Because of the limited size of the GCSE student and teacher market, the cost per user of GCSE Bitesize is around 24p, but each page impression costs just 1.7p. The Bitesize service as a whole becomes steadily better value for money as the number of users grows. Bitesize has also spawned a highly successful site to support students going through the stresses of schoolwork and exams. In May 2004, 229,319 unique users logged onto Onion Street to talk to people their own age, read and watch interviews with experts and get advice on revision techniques and dealing with school stress. 48 BBC / NOP Annual Schools Survey 2003. Ibid. 50 Qualitative research amongst 14-16 year olds on behalf of the BBC. 51 BBC Marketing Communications & Audiences Consumer Research. Revision Services Learning Impact, Oct 2003. 49 21 2.4.3 The distinctiveness of BBC schools services BBC Schools does not just provide programming in areas that are going to be the most cost-effective. We respond directly to the needs of teachers in subjects that they find challenging to deliver. Citizenship and PSHE have become compulsory parts of the school curriculum recently and are a challenge for many teachers, as our consultation and research show. So we have created dramas such as Child52 that make it far easier for students to relate constructively to issues that can be difficult to handle in the classroom. This builds on a long tradition of BBC Schools programme-making. Since it was created in the 1960s, the award-winning series, Scene, has always used drama to help teachers engage their students in important social issues. This is an area of programme-making that we plan to sustain since it is the most effective way of satisfying this important teacher and pupil need. A new focus on primary languages put pressure on teachers who are not specialist linguists. It is hard to plan structured language lessons when you teach across the whole curriculum and have limited expertise. The BBC identified this need and created websites with extensive support, designed for nonspecialist teachers, with printable resources to consolidate learning objectives and rich spoken language sections to give learners good models. We also respond directly to the needs of the nations. In Northern Ireland, we have created themed content around the curriculum subject of Education for Mutual Understanding, challenging pupils to question their attitudes and beliefs through an interactive tour of an interfaith area in Belfast or by creating balanced news reports online. Other content, catering for specific national needs, includes our Celtic history site, which is in both English and Welsh, and interactive games created to teach Scottish children about their history, geography, and wildlife. 2.4.4 Schools services: summary All of our schools services are high quality, free to all at the point of use and deliver solid value for money. We are constantly innovating to deliver learning in new ways. Our digital services help to take the digital revolution into schools across the UK and to convert teachers to the use of interactive resources as part of their teaching armoury. The Digital Curriculum, when it is launched in 2006, will take our substantial commitment into its ninth decade – the truly interactive decade. 52 An examination of the lives of children with HIV/AIDS in London and Rwanda. It was an important story that stimulated debate for upper secondary PSHE and Citizenship. 22 2.5 Essential skills services Skillswise and WebWise address the most important skills issues facing the UK – limited literacy, numeracy and IT skills. The BBC has regularly returned to these areas. In the late 1980s there was On the Move, starring Bob Hoskins, and in the 1990s there were major campaigns such as Read and Write Together and Computers Don’t Bite. Skillswise and WebWise emerged from these initiatives. Although the services have been successful, they have been far weaker without television programming support. We have learnt from this and, as is described in the next chapter, a new generation of peak-time social action campaigns will drive these services in the future. More than seven million adults in the UK cannot read or write at the level expected of an eleven year old53. One and a quarter million have reading and writing skills less effective than those of an eight year old54. This is not an issue that is going away: 145,000 people leave school each year with literacy levels at or below the age of eleven55. Numeracy problems are easier to get around in everyday life through the use of calculators but have an even greater impact on the country’s economic health56. More than seven million people have limited numeracy skills and over two million find simple calculations impossible57. More than a third of adults are yet to go on the internet for the first time and computer-phobia still blocks more than six million adults from taking even the first steps58. Skillswise and WebWise were created to address these issues head-on. 2.5.1 Skillswise – improving literacy and numeracy Those who have chosen to improve their skills are the end-users of Skillswise. The crucial intermediaries are the 24,000 or so adult basic skills tutors59. Skillswise was launched in April 2002 and the BBC team worked with 30 tutors from around the country to create the service they needed. Resources were created that fit flexibly into lessons, provide ways into difficult learning areas and reinforce learning objectives. The service is continuously evolving 53 Basic Skills Agency. DfES/Basic Skills Agency. 55 The Prince’s Trust. 56 Moser Report (A Fresh Start), 1998, DfES. 57 Basic Skills Agency. 58 DfES. 59 Estimates vary between 20,000 and 28,000 (DfES). We have taken an average. 54 23 as a result of feedback from our weekly newsletter that is sent out to over 9,000 subscribers60. The service has proved very popular. During 2003/04 there were approximately 130,000 unique users (ie unique computers accessing the service), but since Skillswise is primarily used in FE Colleges where several students use an individual computer during a week, the actual number of users is likely to be higher. In fact, Skillswise receives more than 4.2 million page impressions each month. “ Just to say brilliant, thank you, well done, smashing, lovely! I am an online tutor and your resources are absolutely brilliant for adult learners. ” “ Fantastic site, well worth the licence fee for this alone! ” Tutor 61 2.5.2 Webwise – helping get more people online The 15 million who are yet to go online for the first time62 are the focus of WebWise, the BBC’s beginner’s guide to the internet. Since its launch in 1999, over one million people have used WebWise63. The service consists of three elements: • The WebWise CD-ROM provides a two-hour internet taster • Becoming WebWise is the 10 hour beginner’s online course that helps learners gain confidence and practical skills in using the web. Learners take a final hour-long accredited test, developed in partnership with awarding bodies and FE colleges, at a ‘Becoming WebWise’ centre • The bbc.co.uk/webwise site – an informal environment in which users can find out more about the internet and have their questions answered. In all, 1,700 FE colleges and other post-16 learning centres deliver the WebWise course. Over 41,000 people have completed the ten-hour course since it began in April 2000, and many more have started or dipped into it.64 The WebWise site attracts 220,000 unique users each month. 60 BBC Skillswise database. Comments made on the Skillswise website. 62 DfES. 63 Because the WebWise CD-ROM has been used in so many venues, by over 5,000 partners for over 5 years, we have only broad estimates based on samples of usage in particular locations that suggest over a million learners have used the CD-ROM sampler. 64 Data collected from partners, BBC WebWise. 61 24 WebWise and Skillswise together cost £774,000. Over the last three years, they have increased their impact through external funding (used for outreach activity) - £271,000 from the Learning and Skills Council and £385,000 from the European Social Fund. When all the costs, including the marketing costs but excluding the cost of training tutors, are taken into account, we estimate the cost per user to be between 2p and 3p for these services. 2.6 Community initiatives The BBC has wanted to take learning directly into communities for many years. Traditionally we have relied on partners to do this but since 2000 we have been carrying out experimental pilots to see how we can deliver learning support directly to communities. The BBC’s skills have traditionally been as a broadcaster – a ‘one-to-many’ model. The internet has the flexibility to be more personal. These projects are experimenting with the most personal approach of all – a one-to-one model. There are twelve BBC buses and seven BBC open centres. The open centres are in Hull, Stoke, Blackburn, Sheffield, Merseyside, Wrexham and Newport. The buses are located in Cumbria, Derby, Devon, Greater Manchester, Humberside, Lancashire, Lincolnshire, Liverpool, Belfast, South Yorkshire, Tees Tyne & Wear and mid-Wales. A mixture of BBC staff and tutors or information and guidance professionals, from local partner organisations, staff each bus or open centre. With 180,000 visitors to learning centres and buses each year, the average cost per visitor is £8.56 for the buses and £2.20 for the open centres65, reflecting the high set-up costs. This will fall over time, but the cost of one-to-one contact will always be high when compared to the oneto-many economics of broadcasting. At the moment, this approach is experimental and the BBC is looking at ways to scale up the buses and open centres. The learning offered ranges from basic skills through to the more advanced creative skills of digital storytelling. The type of skills training on offer responds directly to local learner needs. It is delivered in close collaboration with local lifelong learning providers and aims to attract new learners whom more formal environments and organisations often struggle to reach. In addition, we have worked with a range of local and national partner organisations to pilot an innovative programme of e-learning activity at a BBC learning centre in central London – 21CC. Since opening in autumn 2002, we have organised events for over 7,000 people – children, teenagers, teachers and family groups, with many activities geared towards children with special needs and those from socially disadvantaged areas. 65 BBC Learning, based on analysis of Quarter 2, 2004 surveys. 25 2.7 Market impact The BBC’s formal television and radio services have traditionally been complementary with only a limited impact on the commercial market. BBC Schools was for a long time the only provider of television and radio programming for schools, a market with only one notable alternative provider to this day - Channel 4, another public service broadcaster. When Bitesize was launched as a cross-platform television and online service, there was no service with similar scale or ambition. The BBC was creating a new type of service at a time when online take-up was still relatively low. The objective was to create public value by helping to raise educational achievement levels. At the same time, Bitesize helped stimulate a growing demand for revision services. It is convergence that is leading to significant market impact issues in schools media. Digital, interactive learning resources fusing television, written and interactive learning resources that are accessible in school, at home or any other location are the future. The BBC’s Digital Curriculum – to be launched in 2006 - will contribute to Curriculum Online, the Department for Education and Skills’ initiative to encourage the development and use of digital educational resources. Substantial research into the likely market impact was carried out before the Digital Curriculum was given the go-ahead by the DCMS66. The structure of the service is designed to provide a strong backbone of resources while minimising the impact on the commercial market. Its impact will be reviewed again by the DCMS two years after the launch – in 2008. In the meantime the BBC Digital Curriculum team and commercial companies are meeting on a regular basis to ensure that the project team is aware of the concerns of commercial learning companies. CBeebies was also the focus of market impact analysis prior to its launch. The most recent analysis suggests that the channel’s negative impact on the advertising market has been less than £1.4m per year, since its approach is distinctive in the market67. The report also confirms that there have been strong positive effects on digital take-up and the UK production base. 66 67 Price Waterhouse. Oliver and Ohlbaum Market Impact Study, March 2004. 26 2.8 The future We have clear plans for the future in formal learning: • Innovation will continue to be central to our approach. We will develop learning across new platforms such as mobile, and integrate learning across platforms in new ways. • In 2006, we will launch the Digital Curriculum in collaboration with the commercial sector. The service will help to bring a new standard in broadband interactive learning to every child and every school in the country. Our aim is through our reputation, history, reach and quality of content to make interactive resources integral to every child’s learning and to the teaching practices of more and more teachers at all levels. This service is a huge investment - £150m – and will be the backbone of our future schools services, both primary and secondary. As part of broader national investment plans, we believe that it will help to improve educational standards and increase media literacy amongst schoolchildren. • The CBeebies website is already a huge success but we plan to take it further, adding more depth and structure to the learning resources we provide to under-5s and their parents during those crucial years. • We will develop a new skills service for those leaving school with few or no qualifications. • Literacy and numeracy will be an enduring theme of our social action work in the coming years as described in the next section. Skillswise will not only be a part of that but will be developed in new ways to make access easier for individual learners and to drive usage of the service by employers in key industries with low skills levels among employees. • The ‘digital revolution’ has been more evolutionary than some imagined, but we know from our experiences in Project Hull that community learning built around broadband infrastructures can have considerable impact and drive the uptake of digital. Hull’s educational performance is affected by deprivation, but projects involving children, teachers and parents across citizenship, literacy, numeracy, science, languages and geography have had considerable success, as have family language learning pilots and creative projects such as short films about citizenship in the CITZN-H project. The knowledge we have gained will inform national community projects as digital penetration increases. 27 “ What has been really satisfying, especially for the students that have worked with me on the films is when they are used in the classroom - when groups of students see their friends, know that they have been involved in the process and see familiar names and places it adds a far greater relevance to the subject matter … Another result has been the massive uptake in the use of digital media in the school, which now has its own TV channel - and to think...it all started with a 10 minute film on Homelessness in Hull. ” Deputy Head, Kingswood High School, Hull (CITZN-H) 68 68 BBC Learning Community Projects report. 28 Chapter 3 Informal, targeted learning 3.1 What are the BBC’s informal, targeted learning services? This is the second type of learning output that the BBC produces. The BBC’s informal, targeted learning services aim to provide relevant, engaging learning opportunities to every citizen over the age of seven. These opportunities are not connected to formal or course-related learning. Informal targeted learning accounted for a total spend of £112.6m in 2003/04. The biggest elements of this are CBBC (£46.7m), factual landmarks (£48.6m) and social action (£11.1m)69. Delivering learning across a range of easily accessible platforms is a major theme. We use online, interactive television and events on the ground in close coordination with television and radio programming to maximise our learning impact. • Our factual landmark programmes include series ranging from Pompeii to How to Be a Gardener. They are designed to attract large audiences to factual programming and then take them on to closely linked interactive learning experiences. • Enduring online factual services are linked to our factual landmarks but are also sustained services in their own right, often attracting hundreds of thousands of users each month. These services cover history, science and nature, religion and ethics, arts and lifestyle. • Social action programming and campaigns engage audiences with important social issues such as basic skills, domestic violence, personal finance and obesity. The campaigns join together partners, national and regional television, national and local radio and interactive media to raise awareness and encourage the audience to take action. BBC Radio is committed to social action programming across its networks and especially on Radio 1 and Radio 2. • 69 Our continuing learning services include Sport Academy, OneMusic and BBC Languages. £46.7m is the cost of the learning component of CBBC, not the total cost for the channel. 29 Sport Academy and OneMusic encourage active involvement in sport and music, building on the popularity of BBC Sport and Radio 1 among hardto-reach audiences. BBC Languages is a range of multimedia courses designed for learners at different levels. • CBBC is a digital channel and branded terrestrial zone for 7-12 year olds. The concept of ‘learning through fun’ is at the channel’s heart, inspiring children to find out more about their interests and the wider world. Informal learning is the objective of most non-Schools programming on the channel. 3.2 The BBC’s informal learning strategy The BBC creates public value through the breadth and depth of softer learning opportunities that it produces each year. These aim to reach all members of the audience either one way or another. By drawing every group in the population into learning experiences, the BBC is helping to create a more flexible, dynamic, learning society that enjoys taking on new challenges. We create maximum learning impact by using several platforms to engage and motivate our audience – not just broadcast television and radio, but also online, interactive television and live events. There are six million highly motivated adults with broad and varied interests whom we find relatively easy to engage with learning opportunities, but they are a minority70. The BBC has always created programming and resources to feed their curiosity, and always will do so. They are dramatically skewed towards better educated, more affluent groups. This is reflected by patterns of national involvement in learning (see Figures 13 and 14). It is what NIACE71 calls the ‘learning divide’. The BBC’s strategy is to reach out beyond the six million who are easiest to involve to the 21 million who are engaged by particular types of learning and beyond them to the 17 million who range from those who are resistant to learning to those who are outright rejecters72. 70 The Audience & Learning, Human Capital, Feb 1997. The Learning Divide Revisited, 2000. NIACE, the National Institute for Adult and Continuing Education. 72 The Audience & Learning, Human Capital, Feb 1997. 71 30 Figure 12: Currently Engaged In Learning By Socio-Economic Group % 35 32 Figure 13: Current/Recent Participation In Learning By Age % 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 32 30 25 20 17 15 12 10 5 0 AB C1 C2 86 65 48 43 36 25 19 15 17- 20- 25- 35- 45- 55- 65- 75+ 19 24 34 44 54 64 74 Source: NIACE DE Source: NIACE During the current Charter period, we have taken four clear approaches to achieve this strategy: 1. Using our unique reach to encourage the whole audience to learn. BBC One and BBC Two’s share of viewing may have fallen, but the weekly reach of BBC One is still 84.3% and BBC Two 67.1%73. We have attracted audiences as high as 10 million to programming with learning embedded in its core74. The radio networks also have considerable reach – Radio 2 reaches 24.5% of the population each week75 and Radio 1 reaches 48.7% of 15-24s76. 2. Combining media across platforms means major social action and landmark events reach up to two-thirds of the adult population and hit consumers from several different angles. The BBC brings together national and local radio, network and regional television, online and interactive television to turn learning and social action campaigns into national events. 3. Ensuring the viewer’s first steps from television into more active learning are clearer and simpler than ever before. The BBC has become expert in bridging the gap through closely integrated interactive television and online content. 4. Making our partnerships more integral to our projects. Partners have become more important as we find new ways to create citizen value on the ground in local communities. Partners are an essential part of projects ranging from The Big Read, commissioned in partnership with the Open University, to social action campaigns addressing domestic violence. The BBC helps brings a multiplier effect to the creation of public value through learning. The range of BBC services is one element; the other is the catalytic role the BBC plays in bringing together public service and commercial partners to achieve common learning goals. The resulting impact is far greater than could be achieved by the individual parts working separately. 73 BARB, June 2004 average weekly 3 minute consecutive reach. Pompeii with 10.1m viewers (BARB). 75 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 76 RAJAR. 74 31 The Big Read is a model for how our major projects can have a multiplier effect when we work closely with our partners. This is a key plank or our current and future strategy. Case Study: Partnerships and the impact of The Big Read Audience Need This series, co-commissioned with our long-term partners, the Open University, focused on objective as well as expressed needs. Reading is one of the most popular pursuits and we wanted to celebrate and encourage this. But there was also an objective need – to engage those who do not read or only rarely read and to encourage them to try out a book. Approach The aim was to create an event that would make trying a new book the thing to do, whoever you are. A wide network of partnerships was integral to this campaign and included, amongst others, libraries, LearnDirect, the Reading Agency, the National Literacy Trust, Booktrust, bookshops and schools. The aim was to create an event that had direct impact on the ground, by stimulating reading groups, by making libraries a place to go to find out more and by involving bookshops on every high street across the country. Viewers could walk in, find the books from the programme, start reading immediately and make a more informed vote as a result. Benefits Eighty-seven per cent of the population was aware of The Big Read77 and 17.6 million people watched the programme for 30 minutes or more78. Library loans of the top 21 books went up 56%; sales of the top 21 books up 575%; the number of non-readers fell from 27% to 23% during the series79. Our partners played a critical role in taking the campaign into the community: there were 40,000 visits to the LearnDirect database and 10,000 calls; 75% of libraries carried Big Read displays and 33% ran events; 65% of library visitors (60,000 people) took part in a Big Read event; 114,000 people downloaded a reading group starter pack and 2,150 reading groups were registered; there were 45,000 downloads of national curriculum related teaching resources and 65% of schools ran a Big Read event80. The BBC is also at the forefront of promoting media literacy and many BBC services and activities build public value in this respect. Apart from the formal learning examples of encouraging new users to the internet through Webwise and developing digital technology skills through our community initiatives (both described in Chapter 2), there are various other projects which aim to encourage media literacy in more informal ways. 77 BBC Omnibus survey after broadcast. BARB analysis. 79 BBC research for The Big Read 80 Ibid. 78 32 BBC Blast targets 13-19 year-olds who have a passion for dance, filmmaking, art, writing or digital creativity – but who need help in translating their ideas into action. It has collaborated with over 400 youth and arts organisations across the UK to deliver taster sessions, skills workshops and masterclasses, involving over 12,000 young people. Some of their resulting work has been broadcast on BBC Television or featured on the BBC’s local Where I Live sites. In addition, CBBC encourages a discerning approach to the media among 712 year-olds by getting them to enjoy and expect a mixture of high quality, mixed-genre programming supported by online activity. And the BBC is taking new, older audiences online – often for the first time – through resources ranging from BBC Languages to BBC Gardening to People’s War, all of which tap into the interests and passions of the retirement generation. 3.3 Factual landmarks The BBC has often created landmarks that bring large, mainstream audiences to factual programming on television and create a wave of public interest in new subjects. The arrival of new media has allowed us to harness that interest more immediately and dynamically than before. Our partners have allowed us to create outreach projects taking related learning opportunities into communities, making the learning a two-way experience. Together they make the BBC’s factual output a more powerful force involving new waves of viewers in deeper learning experiences. Our factual landmarks are particularly powerful in creating public value because: • They attract substantial audiences for factual programming. The reach of most landmarks is greater than a quarter of the adult population (see Figures 15 and 16). • Across our range of factual programming, we reach almost every group in the audience across age, socio-economic group and ethnic background (see Figures 17-20). Programmes such as Walking with Cavemen and Human Senses achieve strong reach to all social and ethnic groups. They also achieve strong reach to all age-groups bar the elusive 16-24s. • We are increasingly successful in taking people from television and radio into interactive online learning experiences. Both The Human Mind and The Big Read attracted over 300,000 users to the BBC’s linked websites. • Once experienced, users return to our enduring online factual services again and again. 33 Figure 14: Average Audience For Major Factual Programmes With Linked Learning Resources 5.7 2.2 10.1 10.0 20.0 Reach (millions) Source: BARB, 15 minute non-consecutive reach Ind Ind ividu ivid a Ind ual ls ivid s A In d u a B l i Ind vidua s C1 ivid ls C Ad uals 2 ul D Ad t s 1 6 E - 24 ult Ad s 2 5 u -3 Ad lts 35 4 ult - 44 s Ad ult 45-5 s 4 Ad 55-6 Eth ults 4 6 n Eth ic - W 5+ Eth nic - hite nic Bla - A ck sia n Source: BARB, 15 minute non-consecutive reach Figure 18: D-Day 12 10 12.5 11.2 8 6 Figure 19: Human Senses 6.0 5.7 6.4 5.5 6.2 4.0 7.0 6.2 6.3 8.1 8.4 6.1 9.7 6.2 Reach % 20.1 25.6 4 4.4 12.1 13.6 12.4 11.1 11.4 4.3 7.2 10.2 13.0 5 6.8 9.6 9.3 9.2 9.5 10.1 23.8 29.1 32.8 19.5 24.7 16.3 18.2 9.1 14.4 18.4 In Ind divid ivid uals Ind ual s iv Ind idua AB ivid ls C In d u a 1 ivid ls C Ad uals 2 u D Ad lts 16 E ult 2 Ad s 25 4 ult 3 Ad s 35 4 ult - 44 s Ad ult 45-5 s 4 Ad 55-6 Eth ults 4 65 n Et h i c - W + nic h Eth - B ite nic lack -A sia n 19.3 22.2 20.0 17.2 Figure 17: Walking with Cavemen Reach % 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Source: BARB, 15 minute non-consecutive reach 25 6.7 0 Figure 16: Pompeii 30 14.7 D-Day 4.4 Source: BARB 10 12.6 Great Britons 0 4.0 8.0 12.0 Average Audience (millions) 15 15.0 Human Senses 2.6 D-Day 20 10.1 Restoration 3.8 Human Senses Pompeii, the last day Great Britons Reach % Big Read 2.7 13.4 9.8 11.3 11.9 11.1 10.0 9.7 11.3 Restoration 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 10.5 1.4 Big Read Reach % Walking with cavemen Human Mind 5.7 Walking with Cavemen Human Mind Figure 15: Reach For Major Factual Programmes With Linked Learning Resources 2 0 In Ind dividu ivid al Ind uals s ivid A Ind uals B ivi C Ind duals 1 ivid C2 Ad uals D ults E 1 Ad ults 6-24 2 Ad ul 5-34 Ad ts 35ult 44 Ad s 45ults 54 Ad 55-6 Eth ults 4 65+ nic Et h - W h nic it Eth - Bla e nic c -A k sia n In Ind divi ivi dua Ind dua ls i l Ind vidu s AB ivi als d Ind u C1 iv als Ad idua C2 u ls Ad lts 1 DE 6 u Ad lts 2 -24 ult 5-3 Ad s 3 4 5 u Ad lts 4 -44 ult 5-5 A s 55 4 Et dults -64 hn 6 Et ic - 5+ hn W Et ic - hite hn Bl a ic - A ck sia n 0 Source: BARB, 15 minute non-consecutive reach Source: BARB, 15 minute non-consecutive reach 3.3.1 Landmark events on television The BBC’s commitment to landmark factual television is demonstrated by the wide range of subjects covered in just the last 18 months: Great Britons, Restoration, Pyramid, Pompeii, Coliseum, The Big Read, Walking with Cavemen, Human Senses, How to Be A Gardener, Child of Our Time and the Second World War / D-Day commemorations. The Open University is an 34 important partner, co-commissioning programmes including The Big Read and Child of Our Time. Our landmarks aim to be carefully crafted, high-budget productions. As a result, although they reach large audiences, they usually cost more than the BBC average per viewer hour. The BBC average is 4.7p81 whereas the average cost of our landmarks is around twice this (Figure 21). Figure 20: Cost (Pence) Per Viewer Hour (First Run Only) Elephant: Spy in the Herd Pompeii Leonardo The Abyss Intensive Scares Wild in your garden Child of Our Time Seven Industrial Wonders Jungle Human Mind Animal Camera War at Sea Colosseum Wild Down Under/ Australasia Big Read Top 100 Restoration Born to win Walking with Cavemen St Paul Byron Big Read 0 BBC Average 4.70 4.04 4.05 4.27 4.94 5.75 6.74 6.80 7.40 8.91 10.26 10.54 10.72 10.75 12.06 12.37 13.28 14.14 5 10 15 15.95 16.74 19.02 20.18 20 25 Pence per viewer hour Source: BARB, BBC Finance 3.3.2 Landmark events and interactive learning A critical part of our landmarks is the ease with which the audience can move from being passive viewers to active learners. The way viewers were guided from watching Robert Winston’s series about human beings (The Human Body, Human Instinct, Human Mind and Human Senses) to engaging in interactive learning illustrates how effectively the BBC’s cross-platform approach can work when we get it right. On-screen, Robert Winston demonstrated interactive online links and encouraged viewers to explore these for themselves. More than 300,000 extra people visited the BBC Science site in the month The Human Mind was broadcast. Continued cross-promotion meant that over two million page impressions were received each week, as viewers learnt more by exploring a virtual human body, its mind and senses (Figure 22). These interactive learning experiences reinforced the key messages in the series. 81 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 35 Page Impressions (millions) Figure 21: Human Body Website Traffic Levels Before, During and After Human Senses 3.5 Programme: 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.0 7 3.0 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.2 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.0 0.7 0.5 0.2 0 w/c w/c w/c w/c w/c w/c w/c Week 28th 5th 12th 19th 26th 2nd 9th after Jun Jul Jul Jul Jul Aug Aug series Source: BBC server logs Learners do not simply stop visiting after the programme ends; once they have been introduced to interactive learning experiences, they keep coming back. The BBC Science site now achieves over five million page impressions each week and 2.5 million unique users over an average month, regardless of television support. Table 2 shows how effectively different landmark programmes have converted viewers into interactive learners across four different series. Performance does vary, as does cost per extra user, ranging from 15p to 50p. Table 2. Factual Landmarks – Online Reach and Value For Money Landmark factual website Cost Number of extra users82 Cost per extra user Human Mind £48,000 310,000 15.5p Walking With Cavemen £68,000 190,000 35.8p Wild In Your Garden £43,000 95,000 45.3p £156,000 310,000 during finals Oct 2003; 210,000 during nominations Apr 2003 From 50.3p (during finals) The Big Read We are experimenting with interactive television as a learning medium. At times, the cost of reaching a user through interactive television is high, since we are still learning what works and what does not – this is the cost of innovation. Dunkirk, the most expensive of the interactive projects, targeted older viewers, encouraging them to try interactive television. It had some success but was expensive. We expect these figures to fall as we learn how to use the medium more effectively, as penetration increases and as people become more familiar with the technology. 82 ‘Extra users’ is an estimate based on difference between baseline number of users for that site (average for preceding months) and the peaks seen during and immediately after the landmark programme is broadcast. 36 Table 3. Factual Landmarks – Interactive Television Reach and Value for Money83 Interactive TV Service Total Cost £m Users Millions Cost per user pence Walking With Cavemen 0.18 1.0 17.8 Human Senses 0.14 0.9 15.0 Abyss Live II 0.15 0.6 25.2 Death in Rome 0.22 0.5 44.8 Dunkirk 0.35 0.3 115.3 As the People’s War case study shows, our ambition is to use the driving force of broadcast to encourage viewers to learn more both through interactive media and events that take our factual landmarks into communities across the country. 83 Indicative figures represent the absolute number of users (monthly average across 2003/04). Science and Nature have been combined. 37 Case Study: People’s War Audience Need There are over 9.3 million people in the UK who are old enough to have strong memories of the Second World War84. The BBC felt there was a need not just to commemorate the events that went on during those years but also to involve that generation in recording its memories and to open up those memories to the generations that followed. The BBC saw this as an opportunity to use its programming to encourage older people to go online, often for the first time. The stories could be then be used to bring communities together around shared history and the resource created could underpin further community learning for the younger generations. Approach People’s War is the over-arching concept behind the BBC’s Second World War, Dunkirk and D-Day commemorations and lasts for three years. Dramas, documentaries and live coverage of commemorative events were all used to promote the concept. It aims to bring the older generation to digital technology, recording their stories as part of an online, national archive of wartime memories. In partnership with Culture Online, we are working with a network of 2,500 associate centres across the UK to help the less confident go online and play their part. The stories of veterans have been integrated into local radio programming across the country. The next stage will involve veterans going into schools to share their experiences, as well as exhibitions and archive events supported by the Big Lottery Fund. In partnership with Culture Online, the project will also reach out to often disenfranchised groups, such as those who are housebound or disabled. Benefits There have been more than 20,000 contributions to date from individuals describing their personal wartime experiences. The service has achieved this at a cost per user of 17p. This is just the start. As the archive is used in schools and communities, it brings the reality of the war home to the generations that have followed. It will leave an enduring resource for the nation. 3.3.3 Factual landmarks: summary During the current Charter period, we have integrated interactive learning into major factual events, involving millions of people in related learning. Our events are a wonderful opportunity to draw into learning people who often would not otherwise consider it. The next step will be to create bigger campaigns with more impact that involve hundreds of thousands of people in 84 UK Census 2001. Number of people born 1939 or earlier. 38 active learning experiences in their communities as well as introducing them to ever richer interactive, digital learning experiences. 3.4 Enduring online factual services Every month approximately 4.6 million people visit one of the online sites that make up the BBC’s enduring online factual services. These are ongoing services that have built up loyal and often substantial groups of users. As a result, their costs per user are competitive at between 8 and 12p (Table 3). Table 3. Factual Genres – Online Value For Money Factual website Cost Number of users Cost per user £1,447,000 1,211,000 10.0p History £790,000 795,000 8.3p Religion & Ethics £170,000 122,000 11.7p Arts £210,000 218,000 8.3p £2,170,000 2,300,00085 7.9p Science & Nature Lifestyle The sites are linked directly to current programming but also exist as enduring services that have been built up around long-running series or created originally for landmarks and other special events. So, while the Science and Nature site directly supports programmes such as Countryfile, Horizon and The Sky at Night, it also has enduring content about animals, genes, space and prehistoric life, thereby bringing in a new and often younger user. The history site has naturally put considerable emphasis on World War Two in recent months but visitors attracted by this topic may also be tempted to explore site sub-categories such as archaeology, ancient history, and wars and conflicts. They may, too, be interested in looking at the section on history for children, to support their children’s or grandchildren’s studies at school. The aim is a simple one. Users are likely to come to the site for a specific, programme-linked reason the first time. However, we encourage them to explore other related areas at the same time, and give them good reasons to return to the site again and again to pursue their interests further. 85 Includes some staff who work across teams. 39 3.5 Social action Our social action programming has two objectives: to make the audience aware of important social issues and to encourage those affected to take action. The BBC has created considerable public value through its long commitment to social action, particularly in areas such as literacy, numeracy and computer skills. During the 1990s, we moved spending entirely into online resources through continuing services - Skillswise and WebWise. While these services have been successful, we made a mistake by leaving them unsupported by broadcast output. This will be reversed next year when skills campaigns will return to the heart of BBC One peak time. Our approach to social action is a fusion of the analytical and the creative. We track the major social issues facing society and seek to spot new issues as they emerge, both through analysis and our relationships with partners and other organisations. We then carry out research and set briefs that focus the effort of creative teams as they work to develop ways in which media can be used effectively. Not all issues are ones that broadcasters are well equipped to deal with, but the BBC can be more inventive and flexible in its approach than most other providers since we are not dependent on advertising. 3.5.1 Social action campaigns built around television We maximise the impact of our larger campaigns by working across several platforms and co-ordinating them closely. Television is at the heart of the largest campaigns but national and local radio, the internet, interactive television, and events organised in close co-operation with our partners are equally important in transforming programming into an event which genuinely drives people to take action. During the last 18 months, there have been two major awareness-raising social action campaigns on BBC television: Hitting Home about domestic violence and Taking Care about children in care. Since these campaigns are spread across so many media, precise value for money analysis is difficult. People often experienced the campaign on different platforms and certain spend was targeted at the needs of very precise groups, such as those suffering from domestic abuse. The cost per viewer hour for such campaigns comes out between 8p and 10p, around twice the BBC average of 4.7p86. This expenditure enables us to bring important social issues to a mass audience. 86 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 40 Case Study: Hitting Home Audience Need Between 6% and 10% of women suffer from domestic violence each year87. Domestic violence accounts for 18% of all violent crime in the UK88 and the police receive 570,000 calls each year as a direct result89. On average a woman will suffer 35 assaults before calling the police90. And domestic violence is chronically under-reported91. The impact is not just felt in the short term. Children of violent parents are particularly likely to be abused and are more likely to grow into violent adults. Approach The Hitting Home season raised awareness of domestic violence as an issue and provided immediate freephone support for those affected who wanted help and advice. The season combined drama, documentary, news investigation, feature film and discussion programming across BBC One, BBC Two, CBBC, the national radio networks and many local radio stations. There were also supporting story lines in soaps such as EastEnders. Radio trailed the campaign heavily and addressed the issues directly in programmes ranging from The Jeremy Vine Show on Radio 2 to Fi Glover’s show on Radio Five Live. Hitting Home worked with more than fifty related organisations92 to create a support network around the season, details of which were provided online as well as over the phone. Benefits Hitting Home reached 41% of the adult population with 15 minutes or more of television programming93, while 35% heard four or more messages related to Hitting Home across the BBC radio networks94. There were 17,135 calls in total to the helpline. Of these, 2,485 were answered in person. The rest were answered with a telephone message and many were repeat calls that received personal advice in the end. The website received 9,000 page impressions per day during the campaign and partner organisations received many more calls –as much as 40% more among partners who keep records of call volumes95. 87 Women’s Aid Domestic Violence Statistical Factsheet 2002. British Crime Survey 2002-3. 89 Women’s Aid Domestic Violence Statistical Factsheet 2002. 90 Women’s Aid Domestic Violence Statistical Factsheet August 2001. 91 Women’s Aid and Refuge. 92 BBC Hitting Home team. 93 BARB / Human Capital analysis. 94 BBC Factual & Learning Strategy. 95 Data collected from partners. 88 41 There are important areas where we have made progress, but we have learnt that we can do better in the future. • The first way in which we can improve is through working more closely with our expert partners from the earliest stages and being more open to their ideas. In social action, an expert understanding of the realities of the target audiences, their needs and experiences is essential. • The second way is through the provision of support alongside our social action programming. We provide immediate telephone support for a wide range of radio programmes and usually cope with the volume of calls successfully, but the Hitting Home case study shows how we can find it difficult to deal with the wave of calls that television can create. • Finally, we must also add greater longevity to our campaigns, giving them life beyond the programming. Our social action campaigns have considerable impact while they are supported by broadcast and in the immediate aftermath. We create wide awareness and immediate action but that impact is often quickly dissipated or alternatively the support network created is not organised to last as long as the demand that has been created. This is something that we are beginning to resolve by working in closer collaboration with our partners over longer periods of time. 3.5.2 Targeted social action campaigns on radio and television The BBC’s commitment to social action is not just about high profile campaigns but also targeted programming reaching defined audiences through a range of radio and television output. We have covered drugs, child abuse, domestic violence, crime, personal finance, delinquency, cancer, heart disease, fertility, childcare and many other subjects during the current Charter period. The cost of television programming is varied, depending on the subject and the network. The cost per viewer hour ranges from 5.1p for Money Spinners, the daytime finance show, only slightly above the BBC One average, up to £1.77 for Body Hits on BBC Three, which raised awareness of the effects of various forms of addiction on the body96. The BBC is committed to bringing social action to all its audiences across all its channels, which inevitably means that there will be higher costs per viewer hour on the developing digital channels. The cost of creating social action on radio is far lower since the content is often embedded within existing programmes. But BBC Radio provides substantial one-to-one helpline support that allows listeners to talk directly to someone about issues that are raised in programmes. This helpline answering service answered over 560,000 calls last year97, covering a very 96 97 Figure for Body Hits excludes repeats. BBC / Capita call centre data. 560,000 is the total for calls made in response to TV as well as radio. 42 wide range of issues. The cost per call is approximately £3.5698, which may sound high but is comparable to that of other bespoke telephone information services. Radio 1 has an ongoing commitment to providing impartial information on drugs, highlighting both the health dangers and the myths. As well as campaigns, Radio 1’s Sunday Surgery programme tackles problems faced by listeners, ranging from relationships to self-harm. Immediate telephone support is available, and the One Life website offers information, advice and next steps, taking users to a range of carefully vetted partner organisations. Radio 2 brings social action to the 24.5%99 of homes it reaches each week through the eight social action campaigns created each year. The impact of the network is clear from the volume of calls generated: this is sometimes higher than that created by major network television campaigns. Case Study: Talking Teenagers Audience Need Radio 2’s audience has a solid core of parents and grandparents. Almost a quarter of parents with teenage children are seriously concerned about their relationship with them100. Approach The campaign’s objective was simple - to help adults and teenagers to talk, listen and trust each other. The issues were addressed directly through the Talking Teenagers campaign, which integrated case studies, discussion, expert opinion and advice into a range of Radio 2’s output. Benefits Almost 34,000 people called Radio 2’s audience line in October 2003, as a result of the Talking Teenagers campaign101. Callers wanted advice on how effectively to communicate and build stronger relationships with their children or, often, stepchildren. Many callers wanted help dealing with issues affecting their relationships with their children, such as drugs, alcohol, sex, depression and eating disorders. Many were given advice and then directed onwards to partner organisations, Parentline Plus and the Parents’ Information Service. 98 BBC Finance / Capita call centre data. BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 100 NCH sponsored research. 101 BBC / Capita call centre data. 99 43 “ The strong partnership between the Department for Education and Skills and BBC Radio 2 has been extremely important in helping the Department to convey its messages to its target audiences. ” Tom Peel, Head of Broadcasting Unit, Department for Education and Skills 3.5.3 Social action: summary The BBC has had a long-term, unwavering commitment to social action on the radio networks and has renewed its commitment on television over the last three years. Our future strategy is to create direct action on a far larger scale, adding greater longevity to our future campaigns. Partners will be integral to our planning from the very beginning in order to enable tens or even hundreds of thousands of people to take long-term action, addressing issues that will improve their lives and those of others. With every one of our campaigns, we will try to ensure a lasting legacy. 3.6 Continuing learning services The BBC has three continuing learning services. Sport Academy and OneMusic target hard-to-reach audiences and have been created during the current Charter period. The third is the long-running BBC Languages service. 3.6.1 Sport Academy – getting young people into active sport Sport Academy has the broadest appeal, attracting over a million unique users in certain months (Figure 23). The service is online but is trailed during major sport broadcasts and was integral to Born to Win, a peak-time BBC One landmark series involving teenagers in competitive sport. The programme reached 13 million people102 and approximately 25,000 secondary school pupils took part in activities as a result103. 102 103 BARB analysis. 15 minute non-consecutive reach. BBC Sport estimate based on response rates by secondary schools. 44 Users (000's) 2500 Figure 22: Unique Users & Page Impressions to Sport Academy Website By Month Jan 03 - Mar 04 Users (000's) 8.1 2000 1500 1000 7.1 4.9 725 4.9 5.1 4.4 640 7.7 6.2 862 642 Page impressions (m) 10 Page impressions (m) 632 5.3 1070 1065 799 915 7.0 5.9 897 6.1 948 6 1130 4 500 2 0 Apr May 2003 Source: BBC server logs 8 0 Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan 2004 Feb Mar Sport Academy promotes the benefits of sport to 10-16 year olds and gets them involved in sport at a local level, using advice and endorsement from well-known figures such as Tim Henman and Jonny Wilkinson. More than 30 partnerships with sporting organisations across the country are critical to the service’s success104. 3.6.2 OneMusic – helping young people get into the music industry OneMusic was created because so many Radio 1 listeners want to enter the music industry. The site is a one-stop shop for this audience. It provides advice and information, explores professional opportunities in the music industry and allows budding professional musicians to get their work reviewed by experts and in some cases played on Radio 1. Record or management companies have signed several artistes as a result. OneMusic is a specialist service with a defined target audience. On average, 25,000 unique users visit the site each month, delivering approximately 150,000 page impressions. This figure has soared to over 400,000 when music created by OneMusic users is broadcast on Radio 1. Thirty-nine per cent of visitors to the site said that they had discovered new opportunities in music as a result of their visit105. The OneMusic service is not just trailed on-air. It has also become an integral part of Radio 1 Roadshows and OneLive events and has staged six events of its own around the country in Leeds, Plymouth, Londonderry, Bolton, Brighton and Stoke, attracting over 5,000 young people106. 104 BBC Sport. BBC Insite Survey March 2004. 106 BBC Radio 1 live events attendance data. 105 45 Figure 23: Users and Page Impressions to OneMusic Website Users (000s) 45 Users (000s) Page impressions (m) 38.6 40 0.18 30 25 0.14 28.1 20 15 0.27 0.25 0.22 35 27.8 0.11 0.25 0.21 0.20 27.2 Page impressions (m) 0.30 28.1 0.17 0.17 0.15 23.9 21.5 18.6 17.3 0.20 0.10 13.8 10 0.05 5 0 0 Sep 03 Oct 03 Nov 03 Dec 03 Jan 04 Feb 04 Mar 04 Apr 04 May 04 Jun 04 Source: BBC server logs 3.6.3 BBC Languages – a multimedia resource BBC Languages has a long history – the first programmes were broadcast back in 1924. The service has a wider target audience for its integrated multimedia resources - the 4.5 million people learning a language and the further 7.5 million others who are interested but yet to take the plunge107. Interactive, online learning resources are increasingly important as part of this integrated multimedia approach and will be the focus of an increasing proportion of our languages spending. New learners can go to online Steps beginners’ courses covering French, Spanish, German and Italian; there are further taster courses in Portuguese, Mandarin and Greek; and brief introductions and key phrases are available for 28 further European languages, plus Japanese and the UK languages (Welsh, Irish, and Scottish Gaelic). Over 300,000 users come to the site each month (see Figure 25). Figure 24: Users to BBC Languages Websites Users (m) 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 Jan Mar May Jul Sep Nov Jan Mar May 03 03 03 03 03 03 04 04 04 Source: BBC/ORB/NOP Annual Schools Survey 107 BMRB research for BBC Languages. 46 “ Vast, splendid, free and not at all po-faced. ” Sunday Times A new range of short courses (Talk …) has been created, supported by television series, print, audio and online resources, to respond to the needs of a new breed of potential learners. These people have clear, functional aims and less time for study than our previous courses demanded. Talk… courses guarantee learners will rapidly learn the language skills to achieve their goals. All our projects are developed in consultation with language professionals, both academics and teachers, who advise on course syllabus and content. We have regular contact with academic bodies such as the University of Cambridge Language Centre and CILT (the Centre for Information on Language Teaching and Research) and with the cultural arms of foreign embassies. The BBC will continue to support Adult and Further Education tutors. We have developed free tutor resources on the website and have held workshops across the country in collaboration with the Learning and Skills Council and Adult Learners’ Week. 3.7 CBBC The CBBC digital channel was launched in February 2002, offering a mix of genres for 7-12 year olds. This complements the 1 hour 50 minute branded segment on BBC One each weekday for the 28% of 7-12 year old children who do not have access to digital television108. Both services offer high quality programming in an advertising-free environment. The mix of genres and the soft learning intent of much of the programming make the channel distinctive in a marketplace where many children’s channels show mostly acquired, and often imported, programming. The philosophy underlying CBBC is 'learning through fun', inspiring children to find out more about their interests, introducing them to new ideas and placing them in the context of the wider world. Children not only participate in the channel’s live programming but 49% of all 7-14 year olds go online each month to find out more and that number is rising109. CBBC has steadily extended its reach since launch. At the beginning of 2002, CBBC’s half-hour weekly reach (the proportion of 7-12 year olds watching at least half an hour per week) was less than 3%, but has climbed to 18% today in digital households (Figure 26). This reach figure is higher than for any other children’s channel (Figure 27). 108 109 BARB analysis. BBC Quarterly Survey (BRMB, June 2004). 47 Figure 25: Half Hour Weekly Reach of 7 to 12 Year Olds CBBC Nickelodeon Cartoon Network Nicktoons Nickelodeon Replay Boomerang The Disney Channel Toon Disney The Disney Channel +1 Cartoon Network Plus Fox Kids Cbeebies Toonami Fox Kids +1 Trouble Nick JR Discovery Kids Playhouse Disney Trouble Reload Figure 26: CBBC Half Hour Weekly Reach of 7 to 12 Year Olds 0 4 Half Hour Weekly Reach (Non-consecutive) 18.0 17.3 14.7 13.7 12.4 10.4 10.2 9.0 8.4 8.2 7.9 7.4 6.1 5.5 5.4 3.5 2.4 2.0 1.8 8 12 16 20 % Source: BARB, 30 min non-consecutive weekly reach % 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Feb Jun Oct Feb Jun Oct Feb Jun 02 02 02 03 03 03 04 04 Source: BARB, 30 min non-consecutive weekly reach The cost of CBBC is higher than CBeebies (£46.7m vs. £7.9m)110, and has a smaller average audience of 18,700, compared to 60,000111. It is often hard to attract audiences to distinctive public service content such as factual and drama but we believe that it is important that we do. This is a competitive sector with several channels vying for the attention of 7-12 year olds and live factual and drama cost over ten times more than acquired animation, which achieves similar audiences. As a result, the channel is relatively more expensive. Research suggests a total public value of £220m. This breaks down into an individual value of £173m and a value to society of £48m112. The market impact is under £2m113. So, with a budget of £46.7m, CBBC is perceived by audiences to be a net generator of public value. CBBC’s programme mix is broad. It includes news, drama and factual (see Figure 28) including well known programmes such as Newsround and Blue Peter. 110 £46.7m is the cost of the learning component of CBBC programming only, not the total cost of the channel. 111 BARB analysis. 112 Human Capital/Martin Hamblin GfK, A study measuring the value of the BBC, 2004. 113 Oliver and Ohlbaum Market Impact Study, March 2004. 48 % 100 90 Figure 27: CBBC Genre Mix 1/4/02 – 31/3/03 2% 80 70 60 50 40 4% News Comedy 16% Drama 19% Entertainment 20% Animation 35% Factual, including schools 30 20 10 0 Source: BARB Newsround has expanded to five live bulletins each weekday and three on Saturdays and Sundays. The programme is not just about current affairs but also takes on issues such as bullying and domestic violence, often as part of wider social action campaigns. The programme is also international in its view, reporting on issues of interest to 7-12 year olds from around the world – the programme has been broadcast live for a week from Africa, for example. Many viewers are interested in journalism. There are now over 40,000 Press Packers, young regional volunteers who contribute regional news online, writing their own reports about issues ranging from HIV to local concerts. We intend to develop this service to involve online modules which will allow Packers to gain a form of qualification. Xchange is broadcast live every day at 7.30am and 5.30pm, with a mix of factual, active, entertaining programming. The programme covers subjects from training for Sport Relief to UFOs, from the Ancient Egyptians to the best ways to customise your clothes, from inline skating to ballet. Children inspired by the programme are encouraged to go to the website where themes in the programme can be pursued further. Bamzooki is our latest show demonstrating how CBBC fuses learning and entertainment. It takes the values and approach of gaming but encourages children to build their own virtual creatures on the internet, developing their creative skills and their understanding of how creatures function. CBBC also makes dramas for children. The Story of Tracy Beaker mixes live action with short animated segments. The programme is built around life in a foster home and the storylines focus on issues such as the relationships between adults and parents, loyalty, integrity, but through tangible situations that the young audience can directly relate to. Drama is the most expensive children’s genre and only a public service broadcaster can support our degree of commitment to it. 49 3.8 Market impact Factual landmarks and social action are both focused on the creation of public value. Social action has no real market impact and our factual landmarks, although competitive in audience terms, are no more so than lower cost programming in other genres would be. Our factual television actually creates industry value: the commercial market for books and media related to our factual landmarks benefits directly from increased consumer interest. Our social action campaigns create considerable value for the individuals they help directly, for society in general and also for the charitable bodies with whom we work in partnership. Our continuing learning services, Sport Academy and OneMusic, also have only a positive public value and commercial market impact, attracting more young people into sport and helping new talent into the music industry. BBC Languages, however, does clearly affect the commercial market since successful commercial products are closely linked to the public service programming and websites. The BBC aims to grow the overall market by attracting new learners. The other service with an impact on a commercial market is CBBC. The channel was launched to target the needs of 7-12 year olds who were already being targeted by other digital channels - Nickelodeon, Cartoon Network and Disney. Figure 28: Thematic Children’s Channels Genre Mix – May 2003 Makeover Sketch Show Behind The Scenes % Investigation 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 6 12 33 37 3 12 5% 3 10 17 CBBC 9 10 Chart Show Challenge Sit-com Series Drama 22 13 Studio Based Demonstrations 5% 5 4 3 24 Reality Format Magazine 21 20 0 4 17 4 48 41 Comedy/Drama Comedy Model/Puppet 21 Animation/Cartoon Discovery Kids Nickelodeon Source: BARB, DGA, O&O analysis 50 The Disney Channel Animation/Adventure The channel has a distinctive mix of programming in the market (see Figure 28). A recent study 114suggests that the revenue lost by the commercial sector each year is between £1m and £2.4m and that the most direct commercial impact has been on the ITV network rather than on the niche, digital channels. The analysis shows that the channel is distinctive from the commercial market and has had a medium/high impact on driving digital television penetration, particularly through the Freeview platform, which is now in almost 4 million homes115. 3.9 The future We have learnt many lessons during the current Charter period. As a result we have significant plans for the future which will take informal learning to the next level: 1. Building on social action successes During this Charter period, the BBC has made a renewed commitment to major social action campaigns on television. We have succeeded in creating awareness but believe that these campaigns can be far more powerful if we work with our partners more closely, give them greater focus and a more compelling call to action. Each year the BBC will create a blockbuster social action campaign that will sit at the heart of the BBC One peak-time schedule. The explicit aim of our campaigns will be to encourage action. Our partners will be integral to the planning and delivery of these campaigns and we in the BBC will be open to supporting and developing ideas created by our partners. The result will be to encourage hundreds of thousands of people into learning activities related to important social issues. Basic literacy and numeracy skills campaigns will be the first in this new breed of partnership. 2. Landmarks The BBC’s commitment to landmark, television-based factual programming with learning at its heart will remain unchanged. We will continue to explore ways of increasing the learning impact of our programmes for individuals, communities and society as a whole. Each year we will deliver one big ‘passion’ campaign that encourages people to take their interest further through participating in activities beyond the broadcast. We will look for subjects where the BBC‘s special skills or resources can be leveraged up in to huge connecting and celebratory events. 114 115 Oliver and Ohlbaum Market Impact Study, March 2004. BBC press release 17th June 2004. 51 3. Developing the Creative Archive The Creative Archive would aim to open up the television and radio archives of not just the BBC but also other organisations for use by the public for non-commercial purposes. Prior to launch, it would be subject to analysis through the public value test. We are developing this initiative in partnership with other major public and commercial audio-visual collections in the UK, including leading museums and libraries. Our ambition is to help establish a common resource that will extend public access while protecting the commercial rights of intellectual property owners. Whether a collector, enthusiast, artist, musician, student or teacher, users would be able to search for and use material for their own creative or teaching purposes. Our plan is to showcase exciting new works and products made from this material. 4. Working with partners to create action on the ground Partnerships have been an important and integral part of both social action campaigns and landmark factual events during the current Charter. We have learnt a great deal and know that we can do better, building partnerships for the long term and integrating our partners earlier into planning and development. This is already beginning to happen with projects such as the literacy campaign in autumn 2005 and has been an enduring feature of our relationship with the Open University. 52 Case Study: The Evolving Relationship Between the Open University and the BBC The BBC and the Open University have had a working partnership for 33 years. Shared aims of widening access to higher education and satisfying the needs of lifelong learners mean that this partnership is now under its fifth agreement. The relationship used to be focused on programming related to OU courses, broadcast overnight on the Learning Zone, but this has become less and less relevant as the internet has taken over and fewer students make use of television for course material . During the current Charter period, the OU-BBC relationship has been broadened and has entered new and valuable territory. The emphasis now is not so much on providing TV course material for OU students but on bringing a mainstream audience to learning informally. The OU has become a co-producer of peak-time series which offer lifelong learning opportunities to wide audiences – series such as Child of Our Time, The Human Mind, Leonardo and The Big Read. And we are working with the OU not only on BBC Two, but also on BBC Three, BBC Four, the radio networks and the World Service. The OU is an integral part of Child of our Time, which follows children born in 1999 to their 20th birthdays. It has provided activity packs to 50,000 parents who responded, developed online tests and for the next series is encouraging every primary school in the country to be involved, creating schools packs to make this possible. These activities will provide results that will be integrated into the series. The OU also offers a short course, Understanding Children, which received a large number of applications following the first series. The relationship between the OU and the BBC has evolved with the times and prospered as a result. We see this as a model for further long-term partnerships in the future. 53 Chapter 4 Informal learning from general programming 4.1 What are the BBC’s informal, targeted learning services? This is the third type of learning output produced by the BBC. It includes a wide range of factual, current affairs and drama programming that the audience learns from simply because it is good, informative programming. By definition, this is an extensive category, and in this chapter we aim to give an overview of it. This programming is important in helping to create a well-informed citizenship. The BBC creates public value by introducing the audience to new subjects, enhancing general knowledge and stimulating interest and engagement in domestic and world issues by broadcasting more than 9,900116 hours of factual programming each year across network television and radio alone. This figure excludes the output of the BBC’s local radio stations and the drama output from which audiences might also learn. This output is not commissioned with specific learning objectives in mind, but its overall learning impact is nonetheless considerable as we know from our programme research. What these programmes lack, when compared to those created as part of our learning strategy, is the rich, multi-platform learning content wrapped around them - content that offers clear steps to learning. The BBC is good at creating learning experiences from its broader output because: • Educating and informing our audience is central to the BBC’s programmemaking tradition • Our explicit aim is to make complex factual subjects accessible for a wide audience across television, radio, online and interactive television • The diversity and volume of the factual and factually based programming that we create each year means that there is something for everybody. The BBC broadcast over 3,700 hours of factual programming on BBC One and BBC Two in 2003/04 and a further 2,500 hours on BBC Three and BBC Four117. This is the equivalent of 260 days of continuous, 24 hour-a-day factual output. Factual programming is woven into many BBC Radio programmes across all the networks. There were 1,295 hours118 of factual 116 BARB and BBC Annual Report 2003/04; includes documentaries, arts, current affairs and hobbies and leisure programming. Excludes local radio and drama. 117 ibid. 118 BBC Radio analysis, BBC Annual Report 2003/04; does not include current affairs or arts programming. 54 programming on BBC Radio in 2003/4 and a further 721 hours of arts and 1,738 hours of current affairs119. The scale of the BBC’s factual programming combined with the BBC’s reach means that a high proportion of the population enjoys BBC factual programming each week. Forty-seven per cent of the population will watch more than half an hour of BBC factual television during an average week120. The average viewer watches more than two hours of factual television on BBC One and BBC Two each week, which is 52% of their total terrestrial channel factual viewing121. Figure 30: Hours of Factual Programming on BBC Radio 7 6 5 4 3 1.3 BBC Four 1.2 BBC Three 2.0 BBC Two 1.7 BBC One Total Hours Broadcast, 000s Total Hours Broadcast, 000s Figure 29: Hours of Facutal Programming on BBC TV 2 1 0 Factual Programming Source: BARB 03/04 Arts, Current Affairs, Documentaries and Hobbies and Leisure 4.2 1254 26 15 0 Radio 4 Radio 2 Radio Radio 1 3 0 Radio 5 Live Source: BBC Annual Report 03/04 Television A third of licence payers feel strongly they “learnt many things” from BBC television programming during the most recent quarter;19% feel that they have learnt specific new skills or developed existing ones122. This perception is based on the breadth and depth of the programming that the BBC produces, not just on specific ‘learning’ programming, as we know from our tracking of the most memorable shows123. The BBC has a commitment to factual programming in peak time when there are the largest potential audiences and the impact tends to be greater. On BBC One there has been a slight increase in peak time factual programming from 470 to 489 hours between 2001/02 and 2003/04. There has been an increase in the volume of hobby and leisure programming and a small fall in current affairs and documentaries (see Figure 31)124. But dig below the surface to the more detailed genres and you can see that the reduction in total current affairs is because of a fall in the volume of consumer current affairs. Political, economic and social current affairs programming has 119 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. BARB / Human Capital analysis. 121 ibid. 122 BBC, April – June 2004. 123 BBC PBTS. 124 BARB. 120 55 grown its share of peak time. There has also been a considerable increase in arts programming in peak time. The reductions in natural history and science programming, though not major, are disappointing and something we are working to address, using innovative approaches such as those in Live from the Abyss and Big Cat Week to provide attractive factual alternatives to soaps for pre-watershed family audiences. BBC Two is broadcasting substantially more factual programming in peaktime – up from 640 to 780 hours between 2001-2 and 2003-4. Documentaries and arts programmes have shown the largest leap (see Figure 32). Current affairs has also risen slightly. The major reduction has been in hobby and leisure programming. The increase in human interest documentaries includes programmes such as One Life and Would Like to Meet, alongside solid increases in documentaries about history, science and religion, such as What the Romans Did for Us and Space125. Inevitably the number of hours of specific types of programming changes each year but the BBC is sustaining its commitment to peak-time factual output. During this Charter period, BBC Three and BBC Four have also been launched, creating a further 1,180 hours of peak-time factual programming (368 on BBC Three and 812 on BBC Four)126. Figure 31: BBC One Factual Programming 2001/02 2003/04 2001/02 123 Hobbies & Leisure 209 522 Documentaries 228 138 146 Current Affairs 2003/04 149 165 Hobbies & Leisure 92 Documentaries Arts Figure 32: BBC Two Factual Programming Current Affairs 19 Arts 4 Hours Broadcast Source: BARB Source: BARB 361 80 74 29 8 Hours Broadcast A specific BBC objective is to increase public understanding of specialist subjects such as science, history, natural history, business, arts and religion. The BBC aims to bring these subjects to the widest possible audience and has increased spend in this area by nearly 10%127 over the last year. The BBC has maintained regular peak-time factual programme series such as Horizon and Timewatch, which draw in average audiences of 2.6m and 2.3m to science and history programming128. They cover a wide range of subjects from the impact of nanotechnology to the Great Storm of 1953. 125 BARB analysis. Applies to all numbers in this paragraph. BARB analysis. 127 This includes only history, science, natural history and business. Figures from TV Strategy, submitted to Ofcom. 128 BARB analysis. 126 56 We have increased our investment in arts programming in peak time from £18m in 2002 to nearly £20m in 2004129, continuing to increase the number of arts landmarks, strands and series across all channels. The audience reach of BBC One arts programmes has been increased by the extended range we are broadcasting - from family, tea time viewing like Rolf on Art to Sunday evening specials such as Leonardo (audiences of 3.6 - 4.2 million) and the new arts strand, Imagine (average audiences of 1.8 million)130. Case Study: Rolf On Art Need Arts programmes on all channels tend to appeal to ABC1, older audiences. Only rarely do arts programmes attract substantial younger or less well off audiences. The BBC was seeking a way to make arts subjects interesting and accessible to the whole audience. Approach Rolf Harris, a popular presenter, brought the lives and works of some of the world's best-loved artists to life on screen by exploring their methods and techniques, then painting his own pictures in their style. Benefits The reach of the first and second series was 11.9m and 11.2m respectively, each series achieving high appreciation indexes of 73131. Tracking of individual arts viewing behaviour shows that the series managed to engage both a more serious BBC Two arts audience and also a more populist BBC One audience successfully. Nearly eight out of 10 viewers, whether they were art connoisseurs or not, agreed they learned something new from watching Rolf on Art. Forty per cent of those previously uninterested in arts programming claimed that watching the series made them more likely to try other arts programmes132. This was achieved at a reasonable average cost per viewer hour of 6.7p. Documentary programming makes us all more aware of the world we live in, exposing us to the issues and realities that make us informed citizens. The BBC broadcasts over 3,600 hours of documentary television each year, 1,578 on BBC One and BBC Two133. Many documentaries create awareness of social issues that are similar to those that make up our social action programming described in the previous section – the difference is that these programmes create awareness and debate rather than primarily encouraging the audience to take action and giving them the tools to do so. Social documentary series such as One Life and single documentaries such as My Family and Autism examine important issues and bring them to a wide 129 From TV Strategy data, submitted to Ofcom. BARB analysis. 131 BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 132 BBC Omnibus survey after the series was broadcast. 133 BARB analysis. 130 57 audience. One Life reached an impressive 12.4 million people for more than 15 minutes during its first series134. Case Study: My Family And Autism Need Autism diagnosis has increased considerably over the last decade. Approximately 400,000 people in the UK suffer from autism, 160,000 from the high-functioning Asperger’s form. It is highly debilitating for sufferers and their families. Only a quarter recover within five years and 10% kill themselves. Parents need more information and advice about how to cope with the problems and overcome their sense of isolation.135 Approach My Family and Autism took an upbeat look at the daily life of Mrs. Jackson and her four autistic sons through the eyes of one of those sons, 14-yearLuke. In the programme, Luke introduced medical issues that affect autistic children. There was a helpline and a live online chat following the programme for families affected. Benefits The programme reached 3.7 million people136 and achieved a remarkably high audience appreciation index of 80137, as well as winning several awards. The programme ranked among the most memorable programmes of the year across all channels138. In all, 5,185 viewers called the helpline139 and 6,500 participated in the live web chat with Luke and his mother. This was the third highest volume for a live chat in 2003-2004. It was achieved at a competitive cost per viewer hour of 5.3p. Investigative documentaries are powerful ways of bringing uncomfortable truths to the audience and have an important role in creating an informed and questioning democracy. The Secret Policeman was very influential, uncovering racism in the Manchester police force and bringing these issues to a wide audience including younger viewers. It created wide public and political debate for months afterwards. Consumer education is an important element of the BBC’s public service remit. The BBC is in a unique position, able to give independent consumer advice since it is not reliant upon advertisers for funding. Watchdog, the flagship consumer programme on BBC One, reaches 8.6% of the population for at least 15 minutes weekly140 and educates viewers about their consumer rights in the areas of finance, goods and services, and utilities. 134 BARB analysis. This paragraph: Hansard / Mental Health Foundation / Mind / Institute of Psychiatry / Medical Research Council. 136 BARB analysis. 15 minute non-consecutive reach. 137 BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 138 BBC PBTS. 139 BBC/Capita call centre data. 140 BARB analysis. 135 58 The BBC’s current affairs programmes and services help to create an informed and questioning citizenship. The audience appreciates this - 42% of BBC viewers agreed strongly that “the BBC helps me understand what’s happening in the UK and the world today”141. Current affairs output is one of the main contributors to this. Programmes such as BBC One’s Panorama (averaging audiences of 2.7 million142), inform and educate by investigating the important political and social issues of the day ranging from asylum to Seroxat, the latter contributing to the debate which led to changes in the way drugs are given approval. But this traditional approach tends to attract an older, more traditional audience and so new approaches have been tried such as those in This World and If… on BBC Two. Our programming aims to reflect the world outside the UK to the whole audience. This can be difficult, particularly for younger audiences, but programmes such as World Weddings on BBC Two, exploring cultural and social issues faced by couples from around the globe who are about to marry, and Holidays in the Danger Zone, using a travelogue format, have helped to bring international affairs to younger viewers, and also achieved high audience approval ratings143. BBC One has created themed days of programming to address important issues that affect the whole nation. First there was NHS Day, revealing through a televised poll - viewers’ major concerns about the health service and then putting those concerns live to Tony Blair. This was followed by Crime Day and, last January, Debt Day. 141 BBC audience research BARB analysis. 143 BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 142 59 Case Study: Debt Day Need Seventy-four per cent of the population are in debt (excluding mortgage debt). One in five households say they are finding it difficult to meet debt repayments and one in three households have no savings at all. The average British citizen has £3,500 outstanding in unsecured loans144. As interest rates begin to rise, the BBC wanted to make the audience aware of the issues faced. Approach A day of programming and events about personal debt and spending culminated in BBC One’s Hey Big Spender! programme which brought into the studio a wide range of people facing debt issues. Popular presenters such as Alvin Hall helped to draw larger audiences to this difficult subject. Benefits The combined reach of the programmes was 11.4 million, 24% of the available audience145. The key programmes, Scambuster and Hey Big Spender!, received relatively lower appreciation indices of 70 and 65146. Hey Big Spender! ranked the 80th most memorable programme that week147. It received 15% share, well below the slot average on BBC One148. But there was considerable impact beyond the broadcast. The Hey Big Spender! website attracted 470,310 visits in the week before and after transmission, 43,653 used a “cashometer” to assess their own financial position and 3,000 people signed up by email for further information and help. Because drawing large audiences to such difficult areas is so difficult, Hey Big Spender!’s cost per viewer hour was 12.4p and Scambusters averaged a more normal 6p149. Viewers feel that they learn from many factual programmes. For example, 73% of the people who watched The Genius of Mozart agreed that they had learnt from the programme and 53% felt it had made classical music easier to understand150. Factual is the genre with the clearest learning impact but there has been increasing collaboration between drama and factual to find ways of attracting new audiences. Charles II: The Power and the Passion told the story of the monarch and his court, his squabbling family, and his glamorous mistresses - offering viewers 144 Bank of England (Quarterly Bulletin Winter 2003), Citizens’ Advice Bureau, Financial Services Authority, IPPR. Applies to entire paragraph. 145 BARB analysis. 146 BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 147 BBC PBTS. 148 BARB analysis. 149 BBC Finance / Human Capital analysis. 150 BBC Omnibus survey after broadcast. 60 an insight into political and contemporary life in 17th century England. The programme reached 11 million people151, and ranked the 5th most memorable programme in the first few weeks of transmission152. Similarly, Hawking, a collaboration between Science and Drama, explored the struggles Steven Hawking faced with his illness but also introduced viewers to the theories of the ‘Big Bang’ and atomic physics. Hawking reached 7.8 million viewers153, had an extremely high audience appreciation index score of 82154, and ranked as the fourth most memorable programme in the week that it was transmitted155. 4.3 Radio BBC Radio’s national networks reach 62.8%156 of the population through their analogue services each week and broadcast over 250 hours of factual, news, current affairs or arts programming157. Radio 2 and Radio 4 are the major providers of factual and current affairs programming; Radios 2, 3 and 4 provide most of the arts programmes; and news programming is spread across all the networks (Figure 33). Total Hours Broadcast (000s) Figure 33: Hours of Factual Programming on BBC Radio 7 6 5 Arts Current Affairs News & Weather Factual 4 3 2 1 0 Radio Radio Radio Radio Radio 1 2 3 4 5 Live Source: BBC Annual Report 03/04 BBC Radio is also encouraging the growth of digital radio through the launch of five digital only networks. 1Xtra is designed to satisfy the needs of young black audiences, and the Asian Network the needs of the broader Asian community. Both carry targeted social action programming for these underserved audiences. BBC radio audiences feel that they learn a lot from BBC network radio158. Radio 3 and 4 are seen as the most successful in delivering learning to their 151 BARB analysis. BBC PBTS. 153 BARB analysis. 154 BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 155 BBC PBTS. 156 RAJAR data from BBC Annual Report 2003/04; 15 minute weekly reach. 157 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 158 BBC Radio Listener Survey. 152 61 audience, but the rest of the networks are not that far behind, as is shown in Figure 34159. Figure 34: Learning from BBC Radio Learned new skills/developed existing ones Learned many things from BBC 58% 55% 37% 22% 45% 43% 24% 21% 25% 25% Radio 1 Radio 2 Radio 3 Radio 4 Radio 5 Live Apr to Jun 2004 Source: BBC Radio Listener Survey 4.3.1 Radio 1 Radio 1 reaches just under half of all 15-24 year olds and one in five of the population over the age of 15160. At its heart is a commitment to showcasing new talent and new work. In a typical week 65% of all music played on Radio 1 is new and 45% is by UK artists161. Radio 1 keeps young people up to date with news and analysis through regular Newsbeat bulletins, which achieve average audiences of 2.3 million162. There are also two 15-minute editions of Newsbeat each day. As part of Lamacq Live, Radio 1 broadcasts factual programming about serious subjects in ways that interest its young audience. The documentaries range from investigative journalism uncovering how the BNP are trying to influence young voters to presenter Bobby Friction’s travels in Eastern Europe exploring young people’s attitudes to the EU. Radio 1 also creates regular social action campaigns across a wide range of issues relevant to young people – such as drugs, sexual education and health – as described on page 42. OneMusic, Radio 1’s online service offering advice on entering the music business, is described in more detail on page 44. 159 Ibid. RAJAR. 161 BBC Radio programme schedules. 162 RAJAR. 160 62 4.3.2 Radio 2 Radio 2 is the most popular radio station in the UK, reaching 12.9 million people each week163. As well as playing the widest range of popular music in the UK, Radio 2 is committed to encouraging participation in and appreciation of music. Its songwriting initiative, Sold on Song, offers aspiring songwriters advice and masterclasses with established writers. The network broadcasts over three hours a week of documentaries and features, from UK Black, the story of the UK’s black music scene, to No Easy Walk to Freedom, Jeremy Vine’s documentary series on the emergence of democracy in South Africa. Radio 2 broadcasts specially commissioned factual programmes for special events - to commemorate Remembrance Day, David Jason told the story of a group of young territorial soldiers who met on a Sussex playing field in the spring of 1939 in The Boys From The 113. Radio 2 has always had a substantial commitment to social action programming, broadcasting an average of eight campaigns a year. The station has covered a variety of topics responding to the needs of its audience; these have included fertility, being newly single, diet, and trust between parents and teenagers. This is described in more detail in the social action section on page 38. In future the network plans to give social action an even greater priority by creating a rolling schedule of activity that builds on enduring themes rather than the current emphasis on single campaigns. 4.3.3 Radio 3 BBC Radio 3 is unique. It is not only a music and arts radio network but also plays a vital role in the UK’s creative economy through its cultural patronage. Radio 3 contributes to learning in a number of ways. Composer of the Week, Discovering Music and CD Review all encourage lifelong learning and consistently earn high reaction indices164. While 85% of Radio 3’s output is classical music, 3.5% is world music and jazz and 4.3% arts, documentary and debate165. The network also seeks to engage younger listeners with targeted programmes such as Making Tracks, broadcast each afternoon, and designed to introduce children between 7 and 11 to different genres of music beyond pop. The programme has an audience of 310,000166 and has been extended online and through a series of live concerts. All the BBC’s performing groups have learning managers. In 2003/04 these performing groups and the Proms ran 350 educational events, attended by 27,000 children, teenagers and adults167. 163 RAJAR. Appreciation indices are a measure of enjoyment. BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 165 BBC Annual Report 2003/04. 166 BBC Radio analysis / RAJAR. 167 ibid. 164 63 4.3.4 Radio 4 The backbone of Radio 4 is in-depth news and current affairs but the network also broadcasts regular documentaries, features, magazine programmes and debates. Series such as Woman’s Hour, Money Box and Gardeners’ Question Time, all contribute to the learning experience of listeners, drawing regular audiences of 2.7, 1.1, and 1.32 million respectively168. Radio 4 is committed to factual programming across arts, science, history, medicine, the environment, literature and many other topics. It commissions over 150 hours of science programming a year, including Nature, Case Notes (about medicine), All in the Mind (about health and the human brain), Leading Edge (about cutting edge scientific advances) and Costing the Earth. Maths is also covered in series such as 5Numbers and its sequel, Another 5Numbers, which aim to present complex ideas in an engaging and accessible way. All these programmes receive high reaction indices from audiences169. Radio 4 also broadcasts the Reith Lectures each year, and last year these were downloaded from the internet by 50,000 people. 4.3.5 Radio Five Live Live news and sport dominate but the network also broadcasts investigative reporting and discussion shows on topical political and social issues. Innovative formats such as Five Live Goes to Parliament aim to engage an audience that is dissatisfied with traditional coverage of news and politics – the programme created its own studio within the Palace of Westminster, giving listeners an unprecedented insight into the workings of the House of Commons. The Julian Worricker Show includes a weekly investigative documentary, drawing 1.8 million listeners. Five Live Report and discussion programmes cover social and news issues. The Sony award-nominated Inside the Mind of a Paedophile and Home Strike - Battered Me, raised awareness of these issues among Radio Five Live’s predominantly male audience. The network has also worked with 1Xtra to simulcast Kick Racism Out, a programme looking at racism in football across Europe. 4.3.6 The digital networks The BBC’s new digital radio networks are also committed to learning. The music networks, 1Xtra and BBC 6 Music, both feature specially commissioned documentaries with information and advice relevant to their audiences. BBC 7 aims to be the home of children’s speech radio with two programmes each day broadcast especially for children: Little Toe carries daily stories and 168 169 ibid. Appreciation indices are a measure of enjoyment. BBC / QUEST (through Research International). 64 readings for younger children, whilst Big Toe is a two-hour, live, daily programme for older children, including news, stories, documentaries and discussions, much of it created by children themselves. The BBC Asian Network offers music, news, sport, debate and drama for UK Asians. It aims to be the main forum for debating issues of concern to this community. As part of its remit, it addresses social action issues in ways that are specifically relevant to the Asian community it serves. 4.4 The future The BBC’s commitment to quality factual radio and television will remain as strong as ever in the future. But our approach will evolve. The mix of programming will progressively change to focus more on the genres and approaches that create the greatest public value – not just learning value, but also democratic, social and cultural value. This does not mean that the BBC’s factual programming will become serious or highbrow. We will continue to make a rich mix of programmes in our endeavour to reach every audience group and to provide them with a wide range of distinctive content. This will be part of our drive for excellence in our programming across television and radio as we seek to increase the public value the BBC creates. 65 Chapter 5 Future strategy So how do we in the BBC hope that our learning contribution might develop beyond the end of the current Charter period? Educational Value: By offering audiences of every age a world of formal and informal education opportunity in every medium, the BBC will help to build a society strong in knowledge and skills. From Building Public Value Learning is one of the five main ways in which the BBC believes it can build public value during the next Charter period. It is central to our thinking. We will continue to explore the best ways to deliver learning content to all audiences and will seek to create more interactive, personal and long-lasting learning experiences. In this way we hope to increase substantially the public value we create, building steadily on the lessons we have learnt. 5.1 The world of education and learning is changing Each succeeding generation is placing more importance on education, hoping that their children will achieve more in education than they did themselves.170 More young people want to go to university than ever before and the majority are achieving their ambition. And there is a broad desire for self-fulfilment across all generations in which learning has an important part to play. In the future, the media will have a more direct role in supporting and harnessing this demand as we move from the first stage of the digital revolution into the second. Where issues of distribution and access dominated the first stage, the second will be about quality and choice of content. This will create significant opportunities to create further public value through learning by tapping directly into growing consumer needs. Learning will be delivered with a new degree of interactivity allowed by broadband; the reserves of accessible content will be far greater than ever before; new ways of learning will be created through connected communities; and the time-pressed or unsure will be able to learn about the exact subject they want, at their own pace and at their chosen time. 5.2 Our vision and strategy for learning Our vision is simple – to capitalise on opportunities created by the spread of broadband and the convergence of different media to develop the BBC into a world-leading, interactive learning resource. We would like this resource to be a personalised one that reacts to individual needs and wants, and fuses different media to achieve maximum effectiveness. This will maximise our learning impact and create the greatest public value. 170 Henley Centre / EU Reports into Perceptions of Education / DfES. 66 Six years ago, our learning content was delivered almost entirely through broadcast media, supported by outreach activities. Since then we have fundamentally changed the nature of our services by creating closely linked online and interactive television learning experiences and by developing a range of partnerships. Over the next six years, we aim to achieve similar progress by investing more in bigger learning projects that create greater immediate learning impact and also leave enduring legacies. To deliver this vision, our strategy focuses on six areas: • Using our reach to engage and enthuse every part of our audience even more effectively • Continuing to produce the most innovative developments in the way interactive learning is created and experienced • Building closer learning relationships with individuals in the audience • Opening up the BBC archive for all and through this lead, encouraging other organisations to take similar steps • Creating far more ambitious partnership networks than we have in the past - partnerships that will have the range and depth to deliver long-term learning experiences for all communities across the country • Exploring ways of building on our community learning experiments as new opportunities are created by a broadband future Our immediate aim is to maximise our own learning impact and effectiveness in the creation of public value. There may, however, be ways that not-for-profit public service broadcasters can work together more closely that will create even greater public value. We are keen to explore these ideas further. 5.3 Future plans in formal learning 5.3.1 Developmental learning for pre-school children and their parents Building on the success of the existing CBeebies web service, we will create structured, developmental learning resources to help parents and their preschool children enjoy learning together; this will be developed with clear objectives that prepare both children and parents for the school years ahead. We believe this service will help boost the already significant learning impact being achieved by the current CBeebies website, which attracts more than one million unique users each month. 5.3.2 A Digital Curriculum for every UK schoolchild In 2006, we will launch the BBC Digital Curriculum. Developed in collaboration with other providers, it will bring the interactive learning revolution to every UK child of school-age, offering a core of high quality interactive resources across 67 key parts of the curriculum, in line with conditions set by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport. The Digital Curriculum will help to increase the use of broadband content in schools and to convert those teachers who remain resistant to the use of ICT. Above all, it will help to bring school and home learning closer together since it will be accessible through any internet connection, even though broadband will be needed for some of the richest multimedia content. 5.3.3 New and improved basic skills services The BBC needs to make sure that its education services reach all parts of society and particularly those who may have been left behind by formal education. Weakness in basic skills is an enduring issue facing millions of adult Britons and more than half a million 16-20 year olds. We will drive two initiatives: the first will be a new service targeting young people who have left school but have not achieved an adequate level in basic skills; the second will be to create long-term broadcast campaigns linked to an enhanced Skillswise service that will encourage the wider audience to take action. 5.4 Future plans in informal targeted learning 5.4.1 The big campaigns We will focus more resources on bigger campaigns that inspire and empower hundreds of thousands of people to participate. They will have the potential to change lives and leave lasting, measurable legacies. Learning will be at the heart of two blockbuster campaigns each year for the next decade; these will sit at the heart of peak-time programming. One blockbuster will be a social action campaign. Every BBC platform (national and regional television, national and local radio, online and interactive television) will combine with public sector and commercial partners to create mass action in an area of need and concern such as literacy or obesity. The other campaign will focus on a factual subject such as history, science, literature or music. It will draw hundreds of thousands of people into active learning through compelling broadcasts, sophisticated, deep interactive learning services and hundreds, if not thousands, of participatory events across the country. Music will probably be central to the first campaign, and an environmental campaign, Greening Britain, will follow. Our campaigns will increasingly tackle major issues with continuing activity over a few years rather than a few months. This longer-term planning will make it possible to create far more effective, sustained partnerships with other 68 organisations who do not operate on the shorter timescales that broadcasting often works to. This way we will not only create mass action, but also maintain it for longer than before, far beyond the initial broadcast. 5.4.2 Opening the archive The BBC Creative Archive will, if justified through the public value test, open up both the BBC archive and those of partner organisations for noncommercial use by the whole population. Collectors, enthusiasts, artists, musicians, students, teachers and many others will be able to search and use the content for any creative use, limited only by technology and their own imaginations. 5.5 The future for wider programming with learning impact It is impossible to describe exactly what the BBC’s wider programming with learning impact will be like in the future. The BBC’s factual, current affairs and drama programme commissioners are continuously seeking new ideas and trying new approaches. We will continue to innovate and experiment. Such experimentation is essential to keep the content fresh and effective. However we can guarantee that the creation of public value will be more central to our commissioning decisions and programme-making. There will be greater emphasis on the distinctive and the original across all our output and the mix of programming broadcast will shift towards genres that demonstrably create public value. What is certain is that the BBC’s commitment to high quality content across television, radio and online will not change and the learning value of this content will be sustained and grown. 5.6 Future plans for partnership activity Learning is already at the heart of a web of partnerships in many of our formal and informal learning projects ranging from The Big Read to the community projects in Hull and Merseyside. But this is just the beginning. We are planning to: • Integrate more partners, more closely, into the early planning stages of our projects, just as we have worked with the Open University for many years • Build longer term campaigns that last for years, which means that the planning horizons will be more compatible with those of our partners 69 • Build longer term relationships with partners through longer campaigns and by sustaining partnerships more effectively from one campaign to the next. We believe that public value will be greatly enhanced through this approach. 70 Appendix A. The BBC’s commercial role in learning “ We will enrich the learning experiences of children and adults by adding creative and commercial value to our unique access to the world’s best media content. ” BBC Worldwide’s Learning division Vision Statement The BBC has been providing educational material to support its programmes on a commercial basis for more than 75 years. In 1938, the commercial and public service activities were split and a new commercial arm, now called BBC Worldwide, was created. BBC Worldwide’s commercial learning activities now include a range of materials, products and services linked to the BBC’s television, radio and online output. The business also operates in other areas of learning such as professional development for teachers, corporate training and international sales. The products and services developed by Worldwide’s Learning business are aimed at schools, universities and colleges, companies and public sector bodies, teachers, parents, pupils and ‘learners’ - not just in the UK, but around the world. In the context of a global education market which can be measured at over £1 trillion, BBC Worldwide’s Learning business is relatively small (but profitable): it has less than a 1% share of the world educational publishing business. The division’s USP is its ability to use rich media content from the world’s most successful public broadcaster to create products and services which provide a solution to customers’ learning needs. In addition to the activities of its specialist Learning division, BBC Worldwide has a number of activities which deliver informal learning to licence fee payers and around the world. These include being: • The UK’s largest exporter of TV programmes, driven to a large extent by programmes described in Chapters 3 and 4 of this submission • Publishers of magazines, books, videos, DVDs and audiobooks based on those programmes • One of the UK’s leading global marketers of children’s intellectual property, with CBeebies programmes such as Teletubbies, Tweenies and Fimbles being at the heart of this activity. 71 1. BBC Worldwide’s role There has been continuing debate about the role of BBC Worldwide and the relationship between the public service and commercial activities of the BBC. As part of its Building Public Value initiative, the BBC is carrying out a comprehensive review of its commercial activities that will consult with external stakeholders and alternative partners as well as with BBC Worldwide. It will set out a new commercial strategy for the BBC, addressing the issues of scope, ownership and fair trading171. The review will report at the end of 2004. 2. BBC Worldwide’s rationale The rationale for the BBC engaging in commercial activity, as presently agreed, is two-fold. First, although the BBC provides some support materials for its educational output free or on a ‘cost-recovery’ basis, there is often a demand for resources that are too expensive or too specialised to be justifiable through the licence fee but for which people are willing to pay a commercially viable price. Second, the intellectual property created as a by-product of the BBC’s public service activity has a commercial value which, properly exploited, provides additional revenues that can be ploughed back into the BBC’s public service activities for the benefit of the licence fee payer. 3. Relationship to the BBC BBC Worldwide’s Learning business invests in the non-theatric, publishing and non-UK rights for output that the BBC wishes to produce. BBC Worldwide does not have exclusive access to BBC output, but it is the Corporation’s preferred commercial partner. As such it has a ‘first look’ at BBC output, and acquires rights on the basis of the BBC’s Fair Trading Guidelines. All rights acquisitions from the BBC, whether as an upfront investment or from the BBC’s archives, are negotiated through the Commercial Agency, the BBC department which is responsible for all sales of IP created through licence fee activities. Product that is not taken up by BBC Worldwide is offered to the external market through the Commercial Agency. 171 See Building Public Value (pp103-106). 72 4. Learning businesses related to public service content The specialist Learning division’s activities comprise the following: • BBC Worldwide publishes teacher and pupil resources on video, DVD, CD-ROM and in print, and sells them to schools. This part of the business has a 7.2% share of the UK market for primary school published materials (source: EPC), is the largest supplier of video resources to schools in the UK and is market leader in the supply of resources to primary schools in geography, history, religious education and music. Successful products are based on long running BBC Schools programmes such as Magic Grandad and Barnaby Bear. • A range of revision guides based on the successful Bitesize and Revisewise brands is produced and sold through retail and direct to schools. • BBC Worldwide sells videos of, and non-broadcast rights to, BBC programmes to academic institutions in the UK and around the world. • BBC Worldwide is the market-leading publisher of book, video/DVD, audio and interactive media products for self-study courses in the UK languages market and has a significant share in the leisure/travel based language learning market. These resources are closely linked to BBC programming. In 2002, BBC Worldwide signed a major partnership with Cambridge University which has resulted in the recent launch of the Get Into brand, a new generation of traditional and interactive media courses. • BBC Worldwide licenses BBC educational programmes to international broadcasters. A BBC Learning branded block is now broadcast on several international channels, including in India, West Africa, Malaysia, Brunei and on the BBC Prime channel in Europe. These programme blocks are supported by a website with links to high quality educational content from the UK. • Worldwide Interactive Learning creates interactive online learning resources, often using BBC content, for clients including the Open University for whom it produces all the materials for its portal open2.net, the Department for International Development, BECTA and the National College for School Leadership. This unit’s strength with UK academic and public sector clients is important to the division and is a platform for international growth in the fast-growing global e-learning market. • In corporate training and development, BBC content is packaged to create a range of video and interactive training materials on subjects such as leadership, management essentials, appraisals and health and safety. 5. • Other commercial BBC learning businesses BBC Worldwide has a significant business developing English Language Teaching courses for international markets, including long running courses such as Follow Me, Muzzy and Ozmo. This unit maintains good links with 73 the ELT operations of BBC World Service, within which the original Follow Me and Muzzy courses were developed. • BBC Worldwide has formed a partnership with the Open University to create the first comprehensive online professional development service for teachers in the UK. This is another example of the important and growing level of successful collaboration and partnership between BBC Worldwide and the Open University. • The Learning business also publishes a number of consumer books and products for improving individual skills, most notably the globally successful range of books by Tony Buzan, whose original series was produced and broadcast by the BBC in the 1970s. 74 Appendix B. Section A A1: Financial summary for 2003/04 - Formal Learning TV £’000 Radio £’000 Online £’000 iTV £’000 Outreach £’000 Total £’000 Total Formal Learning Comprising: 14,238 1,381 8,042 178 5,569 29,408 CBeebies 7,444 - 435 - - 7,879 BBC Services for Schools 6,794 1,381 3,303 178 - 11,656 BBC Essential Skills Services - - 774 - 4,463 5,237 Webwise/Skillswise Learning centres & buses Projects Hull, Merseyside and Dalmellington - - 774 - - 3,541 922 774 3,541 922 Other Formal Learning - - 3,530 - 1,106 4,636 Digital Curriculum Other - - 3,530 - - 1,106 3,530 1,106 Explanatory Notes: CBeebies includes the cost of most of the output from the CBeebies Channel plus related websites. BBC Services for schools includes curriculum-related output, such as Bitesize and The Way Things Work. Much of it is transmitted in the early hours of the day (both TV and Radio), and recorded for use by schools. Webwise and Skillwise are two key educational strands aimed at adult learners, teaching basic literacy, numeracy and how to use the internet. There are seven BBC Learning Centres and 12 BBC buses which assist in delivering learning outcomes to local areas. Community projects in Hull, Merseyside and Dalmellington (in Ayrshire) aim to reach those sections of the community which are currently underserved by the BBC, to promote a collaborative model of learning, and to equip communities with media production skills as well as key employment skills. The Digital Curriculum has not yet been launched; however development and content costs started to be incurred in 2003-4. Other formal learning includes various items such as 21CC, schools officers in the regions and Children’s Gaelic outreach. 75 A2: Financial summary for 2003/04 - Informal Targeted Learning TV £’000 Radio £’000 Online £’000 iTV £’000 Outreach £’000 Total £’000 Total Informal Targeted Learning Comprising: 91,931 1,250 10,232 5,026 4,794 112,558 Factual Landmarks 40,664 - 2,267 4,452 1,186 48,570 Social Action/Lifeskills 3,927 1,093 4,085 574 1,376 11,055 Continuing Learning Services 1,266 157 741 - - 2,164 CBBC 44,485 - 2,222 - - 46,707 Other Informal Learning 1,588 - 255 - 2,231 4,074 Explanatory Notes: Factual Landmarks include cross-platform campaigns such as The Big Read, Walking with Cavemen and Restoration. It also includes Enduring Online Factual Services. Social Action and Lifeskills includes campaigns across all network radio stations, the lifeskills and lifestyle websites and Interactive TV, and outreach programmes such as Neighbourhood Gardener. Continuing Learning Services includes the Learning Zone on TV, One Music and Sport Academy and the BBC Language Services. CBBC includes all CBBC output with a learning remit, across analogue and digital TV and related websites. CBBC output which cannot be included as informal targeted learning has been included within the Informal Learning from General Programming analysis. Other informal learning includes activities such as Blast, Wild in your Garden and Sold on Song which involve informal targeted learning but do not readily fit in to one of the categories above. 76 Section B Please note that the list of output that follows for 2003 to 2004 includes repeated items, as well as new programmes, and therefore does not tie into the spend figures shown in Section A of the Appendix. Also the listings in the informal targeted learning section cannot be considered to be fully comprehensive, given the extensive and complex variety of output that comes from across the BBC. Where possible, audience share has been indicated alongside informal targeted learning programmes. However, with the exception of CBeebies, no audience share has been included with the BBC’s formal learning output, given that it is targeted at very niche audiences. Any data included in this appendix may not match that in the BBC Annual Report for 2003/04, as the categories to which they relate are different. B1: Formal Learning Output The following list pertains to output related to the academic year, Easter 2003 to summer 2004. Formal Learning – Early Learning CBeebies CBeebies Share/Performance 2003/04 Performance of CBeebies Online: Reach to all homes (55.2m*) 5% Total unique users 13,134,658 Reach to multichannel homes (32.6m*) 8.9% Average Monthly Page Impressions 1,094,554 Reach to digital homes (30.3m*) 9.9% (* People age 4+ as at March, source: BARB) 77 % increase on the previous year 171.9 Age 1- 6 Theme Literacy, numeracy, movement, story, music, alphabet Television (986 progs) Fimbles X 200 X 20 mins (of which 70 NEW) Teletubbies X 365 X 25 mins Tweenies X 390 X 20 mins Come Outside X 12 X 15 mins Storytime X 19 X 15 mins Bobinogi X 15 X 10 mins - NEW Songs and problem-solving situations featuring animation and live action – (Welsh) Radio (45 progs) Playtime X 10 X 15 mins. Counting Time X 5 X 10 mins Alphabet Time X 20 X 10 mins Alphabet Time First Phonics X 10 X 10 mins Bobinogs X 15 X 15 mins – NEW Websites Cbeebies Tellytubbies Tweenies Little Animals Activity Centre Bobinogs Formal Learning - Primary Primary: Alba, Art, Worship, Dance Theme Alba - Specially made Scottish Gaelic resources Television (17 progs) Baile Mhuilinn (2) X 17 X 10 mins Radio (30 progs) Fiream-Faram X 20 X 10 mins. / 15 mins – NEW Freadaidh am Feadan X 10 X 10 mins - NEW Theme Alba - Specially made Scottish Gaelic resources Television (5 progs) Samhradh X 5 X 20 mins Specially made Scottish Gaelic resources. Radio (10 progs) Eadar Eisteachd X 10 X 15 mins - NEW Specially made Scottish Gaelic resources. Websites Cruth na Tire 78 Age 5-7 Age 7-9 Age 10-12 Theme Alba - Specially made Scottish Gaelic resources Television (3 progs) Snas X 10 X 15 mins – NEW Radio (11 progs) Sgeul an Orain X 10 X 15 mins Snas Earrannta X 10 X 15 mins - NEW Websites Foghlam Saoranachd Theme Art - Part of Sainsbury campaign Television (1 prog) Watch: Pictures for Schools X 1 X 15 mins - NEW. Theme Collective Worship - Spiritual themes Radio (36 progs) Something to Think About X 36 X 15 mins - of which 18 NEW The series covers a broad range of themes from a variety of cultures and encourages reflection. Theme Collective Worship - Attitudes and religious awareness Radio (36 progs) Together X 36 X 15 mins of which 8 NEW Assembly resources exploring moral and spiritual dimensions of everyday life. Theme Dance - Movement and spatial awareness, Folk dance Radio (43 progs) Hop, Skip and Jump X 15 X 15 mins of which 5 NEW Let’s Move X 28 X 20 mins of which 1 NEW Theme Dance - Rhythm, Imagination Radio (36 progs) Time to Move X 36 X 20 mins – of which 10 NEW Theme Dance - Cultural diversity, Sequences Radio (51 progs) Music for Dance X 7 X 15 mins Dance Workshop X 44 X 20 mins. Age 5-7 Age 5-7 Age 7-11 Age 5-7 Age 6-8 79 Age 7-11 Primary: English and Drama Theme English and drama - Literacy, story, listening/talking, drama, writing Television (105 progs) Magic Key X 30 X 15 mins Based on familiar characters from the Oxford Reading Tree. Words and Pictures X 68 X 15 mins KS1 Starship X 4 X 20 mins Multimedia resources specifically linked to National Tests in English. Let’s Write a Story X 3 X 15 mins Radio (100 progs) Reading Tree Stories X 10 X 15 mins Stories and Rhymes X 32 X 10 mins / 15 mins Hopscotch X 10 X 15 mins - NEW Specifically related to Scottish curriculum : Listening and talking. Let’s Make a Story X 8 X 15 mins - NEW Infant drama based on popular story titles. KS1 Starship X 4 X 15 mins Interactive quizzes for National Tests. One Potato, Two Potato (NI) X 26 X 15 mins Cross-curricular listening resources with local content. Hurley Burley (NI) X 10 X 10 mins - NEW Stories, rhymes, poems and songs from Northern Ireland. Websites Words and Pictures Magic Key KS1 Starship Theme English and drama - Literacy, story, listening/talking, drama, writing, spelling, poetry Television (22 progs) Let’s Write a Story X 3 X 20 mins Let’s Write Non-Fiction X 3 X 20 mins Writing Across the Curriculum Look and Read X 21 X 20 mins of which 8 NEW Spell It Out X 3 X 15 mins Spelling with the Spell-its X 4 X 20 mins Radio (83 progs) Words Alive X 23 X 15 mins Word Games X 10 X 15 mins Just Prose X 6 X 15 mins - NEW Just Poetry X 12 X 10 mins First Steps in Drama X 36 X 15 mins Time for Drama X 5 X 15 mins Mental and physical involvement through drama (made in Scotland). Tales from Europe X 10 X 15 mins Websites Spell-its Look and read 80 Age 5-7 Age 7-9 Theme English and drama - Main contents, literacy, story, drama, writing, spelling, poetry Television (51 progs) Let’s Write a Story X 4 X 15 mins Let’s Write Non-Fiction X 3 X 20 mins Spell-Its X 4 X 20 mins English Express X 22 X 20 mins (BAFTA award winning series) Primary Focus: Literacy and Language: Media X 13 X 20 mins. (NI) Victorian Mystery X 5 X 20 mins - NEW Radio (153 progs) Just Poetry X 6 X 10 mins Word Games X 10 X 15 mins Listen and Write X 36 X 20 mins Word Fun X 5 X 15 mins Machine Gunners x 10 X 15 mins Radio abridgement of popular novel. Drama Workshop X 20 X 20 mins / 15 mins of which 10 NEW Today and Yesterday X 20 X 20 mins. NI curriculum for upper primary. School Plays X 10 X 20 mins - NEW Just Prose X 6 X 15 mins - NEW Children of Winter X 10 X 15 mins – NEW Radio abridgement of award-winning novel. NLS Adaptations X 10 1X 20 mins – NEW Adaptations of Literacy Strategy texts. World Writing X 10 X 15 mins – NEW Work from writers of a wide range of cultural backgrounds Websites Spell-its Theme Environmental Studies - Local studies in Scotland Television (20 progs) What? When? Where? Why? In the Dark X 3 X 15 mins What? When? Where? Why? Toys X 2 X 15 mins What? When? Where? Why? Trees X 2 X 15 mins What? When? Where? Why? Pets and Animals X 3 X 15 mins What? When? Where? Why? Technology X 3 X 15 mins What? When? Where? Why? Science X 2 X 15 mins What? When? Where? Why? Woodlands in Scotland X 3 X 15 mins - NEW What? When? Where? Why? Scotland’s schools X 2 X 15 mins - NEW This series responds to curricular need in Scotland, looking at environmental and social issues, rural and urban balance, living things and technology. Websites Woodlands in Scotland Living things bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/teachersnotes 81 Age 9-11 Age 5-7 Theme Environmental Studies - Faiths, Europe, Scottish history and geography, Scottish culture Television (15 progs) See You See Me: Buildings of Faith X 4 X 20 mins See You See Me: Cycle into Europe X 3 X 20 mins See You See Me: Picts and Scots X 3 X 20 mins See You See Me: Citizenship: Making Decisions X 2 X 20 mins - NEW See You See Me: Scottish Physical Features X 3 X 20 mins - NEW This series develops understanding of environmental, social, national and spiritual matters. Radio (10 progs) Scottish resources 7-9: Scottish Songs X 3 X 15 mins Scottish resources 7-9: Scottish Poems X 2 X 15 mins Scottish resources 7-9: Picts and Scots X 3 X 15 mins Scottish resources 7-9: Safe Listening X 2 X 15 mins Listening resources: Traditional and more-up-to-date songs and poems to underline diversity and issues of health and safety. Websites bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/teachersnotes Scots and Picts Scottish physical features Theme Environmental Studies - Scottish environment, history, citizenship, links with France Television (15 progs) Around Scotland: Bruce’s Scotland X 5 X 20 mins Around Scotland: Scotland During the Time of Mary Queen of Scots X 3 X 20 mins Around Scotland: France X 2 X 20 mins Around Scotland: Transport in Scotland X 3 X 20 mins - NEW Around Scotland: Citizenship : Election Day X 2 X 20 mins - NEW Looking at contemporary and historical issues from the Scottish perspective. Radio (11 progs) Scottish resources 10-12: Wallace’s Scotland X 5 X 10 mins Scottish resources 10-12: Scotland During the Time of Mary Queen of Scots X 2 X 10 mins Scottish resources 10-12: People in the Past X 2 X 10 mins Scottish resources 10-12: Relationships X 2 X 10 mins - NEW Looking at contemporary and historical issues from the Scottish perspective. Websites bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/teachersnotes Election Day Around Scotland ID Theme Geography - Islands, Local study, Remote places Television (8 progs) Watch: Barnaby Bear X 8 X 15 mins – of which 4 NEW Websites Barnaby Bear 82 Age 7-9 Age 10-12 Age 5-7 Theme Geography - Environments, Weather, Europe, Remote countries Television (51 progs) Mountains and Coasts X 4 X 20 mins Writing About the Landscape X 1 X 20 mins Water – Bangladesh, USA, Britain X 3 X 20 mins Weather, Place and People X 4 X 20 mins Writing About Weather, Place and People X 1 X 20 mins Portrait of Europe X 4 X 20 mins Using the Land X 4 X 10 mins Shorts: France X 5 X 10 mins. Shorts: Environmental Change X 5 X 20 mins Postcards: Kenya X 5 X 10 mins - NEW Life and landscape. Postcards: Bangladesh X 3 X 10 mins - NEW Mexico X 3 X 20 mins - NEW. Environment: Water, Air and Land X 5 X 20 mins. Village, Town and City X 4 X 20 mins. Radio (10 progs) Come to Kochi X 10 X 15 mins - NEW Study of a locality in a less economically developed country. Websites Rivers and coasts What is weather Two cities Theme Northern Ireland - Cross-curricular resources arising from the local environment Television (16 progs) Primary Focus X 16 X 20 mins. Age 7-11 Age 9-11 Primary: History Theme History - Chronology, past and present Television (16 progs) Watch: Magic Grandad X 16 X 15 mins – of which 4 NEW Develops a sense of chronology and links between past and present. Websites Famous people 83 Age 5-7 Age 7-11 Theme History - Ancient Egypt, Modern Britain, Invaders Television (47 progs) Britain Since 1948 X 6 X 20 mins Writing About Britain Since 1948 X 1 X 20 mins Children in the Second World War X 2 X 20 mins Children in Victorian Britain X 3 X 20 mins. Saxons and Vikings X 4 X 20 mins Writing about Saxons and Vikings X 1 X 20 mins Ancient Egypt X 5 X 20 mins Timelines X 5 X 20 mins Develops understanding of historical continuity. Pyramid X 2 X 15 mins - NEW The Romans in Britain X 4 X 20 mins - NEW. The Aztecs X 4 X 20 mins - NEW A Walk Through Time X 5 X 20 mins Ancient Greece X 5 X 20 mins. Websites Ancient Greece Romans Vikings Anglo-Saxons Victorians WW2 children Walk through time Around Scotland See you see me bbc.co.uk/wales/didyouknow: Interactive quiz on Welsh history, and resources on Welsh geography and culture. Primary : Languages (includes both formal and informal targeted output) Theme French - Foreign Language and culture for younger learners Television (10 progs) Salut Serge! – 10 programmes X 30 mins. Websites bbc.co.uk/schools/primaryfrench Theme Spanish - Foreign Language and culture for younger learners Television (10 progs) Globo – 10 programmes X c5 mins. (repeated). Websites bbc.co.uk/schools/primaryspanish 84 Age 9-11 Age 9-11 Theme Arabic - Foreign Language and culture for younger learners Television (1 prog) Primary Arabic: Life and Language – 1 programmes X 20 mins. - NEW Age 9-11 Primary: Mathematics Theme Mathematics - Shapes, time, numbers to 100, counting on, money, addition and subtraction, mental maths, preparation for national tests Television (62 progs) Numbertime X 58 X 15 mins of which 5 NEW KS1 Starship Maths X 4 X 10 mins Radio (37 progs) Numbertime X 33 X 15 mins KS1 Starship Maths X 4 X 15 mins Websites Numbertime Starship Theme Mathematics - Money, measure, division, fractions, problem solving, shape and space Television (40 progs) Megamaths X 40 X 20 mins Radio (20 progs) Megamaths: Mental Maths X 20 X 15 mins Websites Megashapes Megamaths Theme Mathematics - Mental maths, problem solving Television (43 progs) Maths Challenge X 43 X 10 mins/15 mins Humorous animation involving missions to solve problems, and Mental Maths. Radio (53 progs) Maths Challenge X 35 X 15 mins Maths Adventure X 24 X 15 mins - NEW. Age 4-7 Age 7-9 Age 9-11 Primary: Music Theme Music - Musical themes, Narrative songs, Elements of music Television (1 prog) Watch: The Land of all Weathers X 1 X 15 mins Radio (34 progs) The Song Tree X 16 X 20 mins. Let’s sing X 18 X 20 mins – NEW. 85 Age 5-7 Age 7-9 Theme Music - Musicians, Singing Television (5 progs) Music Makers: Professor Allegro X 5 X 20 mins Radio (30 progs) Time and tune X 38 X 20 mins – of which 10 NEW. Theme Music - Dramatised musical story Television (5 progs) Music Makers: Infinity Diner X 5 X 20 mins Radio (38 progs) Music Workshop X 28 X 20 mins. of which 10 NEW Singing Together X 10 X 20 mins Theme Northern Ireland - Themes and music arising from ten Northern Ireland locations Radio (10 progs) Musical Mystery Tour X 10 X 20 mins. Age 9-11 Age 7-9 Primary: Citizenship Age 5-7 Theme PSHE/ PSD and Citizenship - Other people Television (8 progs) Watch: Coming to England X 3 X 20 mins Drama looking at issues around prejudice, based on Floella Benjamin’s childhood. Watch: Our Friends X 2 X 20 mins Watch: Bullying X 3 X 20 mins Theme PSHE/ PSD and Citizenship - Attitudes Television (6 progs) New Kid in Class X 2 X 20 mins The Chat Room X 3 X 20 mins Issues relating to people with learning difficulties, and others’ attitudes to them Personal and Persuasive Writing X 1 X 20 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/schools/id 86 Age 7-11 Age 9-11 Theme PSHE/ PSD and Citizenship - Responsibilities Television (21 progs) Focus: Citizenship: Band Aid X 3 X 20 mins Focus: Citizenship: Minorities X 3 X 20 mins Focus: Growing Up X 3 X 20 mins Focus: Substance Misuse X 3 X 20 mins Focus: Social Inclusion Dramas X 3 X 20 mins Focus: Citizenship: Thinking Skills X 6 X 10 mins - NEW Focus enables junior children to question their treatment of other people through debate. Primary: Religious Education Age 5-7 Theme Religious Education - Festivals, Christianity Television (8 progs) Watch: Christianity X 3 X 15 mins Examines the themes of gifts, friends and helpers. Watch: Celebrations X 5 X 20 mins - NEW Festivals from 5 faiths are explored. Theme Religious Education - Holy texts, Major religions, Beliefs and values Television (21 progs) Pathways of Belief: The Bible and the Qur’an X 4 X 20 mins - NEW Pathways of Belief: Islam and Sikhism X 4 X 15 mins Pathways of Belief X 5 X 15 mins Pathways of Belief: Christianity X 5 X 15 mins Pathways of Belief: Judaism X 3 X 15 mins This series examines sacred texts and basic beliefs of religions. Radio (10 progs) Stop, think and wonder X 10 X 15 mins - NEW Linked specifically to Scottish requirements for Religious and Moral Education. Websites bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/teachersnotes Theme Religious Education - Morals Radio (20 progs) Talking Points X 20 X 20 mins These programmes focus on personal search and complete a sixty-part series. Age 7-9 Age 10-12 87 Primary: Science Age 5-7 Theme Science - Scientific processes Television (52 progs) Science clips X 12 X 10 mins - NEW Cats eyes X 40 X 15 mins. Exploring the natural world. Theme Science - Scientific processes, Physics Television (54 progs) Pod’s Mission X 16 X 15 mins NEW Scientific animation and real world examples. Science clips X 12 X 10 mins - NEW The Way Things Work X 26 X 15 mins - NEW Websites Pod’s mission Theme Science - Communicating scientific ideas Television (14 progs) Science clips X 12 Science Zone X 2 X 20 mins Brings real-life scientific enquiries into the classroom. Age 7-9 Age 9-11 Primary: Special Needs Age 4-7 Theme Special Needs - Language and curriculum Television (22 progs) Bini Special Needs X 1 X 25 mins - NEW Highly structured stories with simple language. Something Special X 4 X 15 mins – NEW Early Years language is developed through a rich combination of video, graphics, sign language and symbols leading into text. Hands Up! X 17 X 15 mins Supporting profoundly Deaf children in accessing the curriculum through BSL. Primary: Wales Theme Wales - Early Years: language and topics Television (15 progs) Bobinogi X 15 X 10 mins - NEW Songs and problem-solving situations featuring animation and live action. Radio (15 progs) Bobinogs X 15 X 15 mins - NEW Websites Bobinogs 88 Age 3-6 Theme Wales - Welsh language resources Television (3 progs) Cristnogaeth X 3 X 15 mins - NEW Radio (4 progs) Twinkle the Christmas Star : Christmas Musical X 4 X 30 mins - NEW Theme Wales - Welsh language resources Radio (4 progs) Sioe Nadolig – Hen ddyn Doeth y Lleuad X 4 X 30 mins - NEW Age 5-9 Age 7-11 Primary: National Tests Age 9-11 Theme National Tests - Preparation for tests Television (20 progs) Revisewise X 14 X 10 mins Revisewise at home X 6 X 120 mins. Multiple media approach to test preparation. Radio (6 progs) Revisewise X 6 X 30 mins Websites Revisewise - Revision for KS2 in English, Maths, Science bbc.co.uk/schools/digger - Digger and the Gang Activities to support years 3 and 4 of the National Strategies for Literacy and Numeracy . bbc.co.uk/schools/dynamo - Literacy, numeracy and science games, designed for home use. 89 Primary: General Theme General Websites bbc.co.uk/schools/preschool - BBCi Schools: Preschool home page bbc.co.uk/schools/4-11 - Schools home page bbc.co.uk/scotland/education - BBCi Education Scotland home page bbc.co.uk/wales/education - BBCi Wales Education and Learning home page bbc.co.uk/northernireland/education - BBCi Northern Ireland Learning home page bbc.co.uk/schools/parents bbc.co.uk/schools/parenting bbc.co.uk/schools/teachers bbc.co.uk/cbbcnews/hi/static/teachers - Newsround teacher’s section bbc.co.uk/schools/revisewise/teachers - ReviseWise teacher’s section bbc.co.uk/communicate - BBC chatroom and message boards. bbc.co.uk/webguide/schools - Pick of the best non-BBC sites for learning bbc.co.uk/schools/whatson bbc.co.uk/schools/guide - Listings and search engine for schools programmes bbc.co.uk/sosteacher - A service for pupils and students to ask a teacher a question on homework, coursework or revision (with replies in 24 hours) and to search the database of over 15,000 previously asked questions bbc.co.uk/schools/id - Learning to be You : interactive activities on themes included in PSHE and Citizenship Studies throughout the schools age-range. Onion St - Advice and revision tips Theme Project Hull / Project Merseyside Broadband Library resources Primary curriculum areas (interactive websites with integrated video/archive clips) PC platform Primary Genie: Numeracy Primary Genie: Literacy Words and Pictures year 1 Victorian children World War II children Bridges Places in Merseyside Vikings Primary French - c 100 clips searchable under 13 common topics 90 Age primary, various levels Formal Learning – Secondary Secondary: English Theme English - Writing skills, Shakespeare plays and context, literature Television (30 progs) Curriculum Bites : English X 1 X 120 mins Writers’ Block: X1 x 120 mins Shakespeare X 6 x 20 mins, 4 x 30 mins The Machine Gunners X 10 x 15 mins Language Skills: Big Issues X 5 x 20 mins Turning points X 3 X 20 mins. Scene X 1 X 30 mins. KS3 Bitesize English X 3 X 120 mins. Radio (5 progs) Language Skills: Big Issues X 5 x 20 mins Websites Boost Reading scheme for secondary pupils with delayed skills KS3 Bitesize English Theme English - Shakespeare, set texts, Drama Television (21 progs) Macbeth Shorts X 5 x 20 mins English File: Get the Meaning X1 x 20 mins The Animated Canterbury Tales X 6 x 30 mins The Animated Epics: Beowulf and Moby Dick X 2 x 30 mins Poems from Other Cultures and Traditions X 4 x 30 mins Stopping Distance X 1 x 60 mins Scene and dramas X 4 X 30 mins.. 91 Age 11-14 Age 11-16 Age 14-16 Theme English - Dramatised texts Television (42 progs) Scene and dramas X 9 x 30 mins of which 1 NEW L8r X 6 x 10 mins NEW English File: The Signalman, The Withered Arm, The Rime of the Ancient Mariner X 1 x 120 mins English File: The Birth of Horror, Shock Horror! X 4 x 30 mins Miller Shorts X 4 x 30 mins In Context X 6 x 20 mins Dead Drunk 1 x 30 mins Poetry for GCSE: X 2 X 30 mins, 2 x 20 mins Reading media texts X 3 X 30 mins Priestly Shorts: An Inspector Calls X 3 x 20 mins GCSE Bitesize English X 3 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize English X 1 X 120 mins. Websites GCSE Bitesize English GCSE Bitesize English Literature Standard Grade Bitesize English Theme English - Literary study Television (12 progs) The contenders X 6 X 30 mins.- NEW Literary Study: The Cone Gatherers X 2 x 20 mins - Scotland Literary Study: Sunset Song X 2 x 20 mins - Scotland AS Guru English X 2 X 120 mins. (repeated) Websites bbc.co.uk/scotland/education AS Guru English Bitesize Highers English Age 16+ Secondary: Expressive Arts Theme Expressive Arts – A diverse range of musical examples and styles for the students to explore involving famous musicians Television (13 progs) Music File X 5 x 20 mins Mad about Music X 1 x20 mins, 6 x 20 mins Marsalis on Music X 1 x 60 mins 92 Age 11-14 Theme Expressive Arts - PE, Art and Music: Dance, world music and composition; art, craft and design practice; contemporary artists working in different ways. Television (14 progs) Diverse Music X 1 x 120 mins- NEW The Art X 6 x 20 mins Contemporary Visions X 1 x 120 mins NEW Sportsbank Special: Dance TV X 4 x 30 mins GCSE Bitesize PE X 1 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize PE X 1 X 120 mins. Websites GCSE Bitesize Music GCSE Bitesize PE Standard Grade Bitesize PE Theme Expressive Arts - Basics of jazz Television (1 prog) Cool Keys 60 mins Introduced by Jools Holland Websites Blast Theme Expressive Arts - Key areas of GCSE Physical Education syllabus Television (10 progs) Sportsbank Clips X 5 x 20 mins Sports Science X 1 x 20 mins Musical Traditions X 4 x 30 mins (Northern Ireland) Theme Expressive Arts - Key areas of GCSE Physical Education syllabus Television (10 progs) Sportsbank Clips X 5 x 20 mins Sports Science X 1 x 20 mins Musical Traditions X 4 x 30 mins (Northern Ireland) Age 11-16 Age 11-18 Age 14-16 Age 14-16 Secondary: Geography Theme Geography - World geography; social geography Television (25 progs) Mapping crime X 1 x 60 mins - NEW Investigating Asia X 5 x 20 mins Shape of the world X 1 X 25 mins. Australia 2000 X 6 x 20 mins France 2000 X 6 x 20 mins Japan 2000 X 3 x 20 mins Brazil 2000 X 3 x 20 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/northernireland/education/ks3geography Sustainable development (NI) 93 Age 11-14 Theme Geography - Global geographical issues; examination preparation Television (30 progs) World 2000 X 10 x 30 mins World Physical X 1 x 120 mins Geography in Animation X 10 x 10 mins Flightpaths X 2 X 10 mins. Living with Globalisation X 3 x 20 mins GCSE Bitesize Geography X 3 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize Geography X 1 X 120 mins. Websites GCSE Bitesize Geography Standard Grade Geography Theme Geography - Environment, health Television (4 progs) Intermediate Geography: Environmental Issues in Europe X 2 x 20 mins Intermediate Geography: Development and Health X 2 x 20 mins Radio (2 progs) Intermediate Geography: Development and Health X 2 x 20 mins Websites Bitesize Highers Geography Age 14-16 Age 16+ Secondary: History Theme History - Early 20 Century British Society as recorded by of the pioneers of photo-journalism. Interpretation. Television (19 progs) Britain 1500 - 1750 X 4 x 15 mins Britain 1750 - 1900 X 5 x 20 mins Britain 1906 – 1918 X 1 x 60 mins 20th century wrap X 1 X 20 mins. First World War X 6 X 20 mins. Curriculum Bites: History 11 – 14 X 2 x 60 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/history 94 Age 11-14 Age 14-16 Theme History - Eyewitness accounts Television (53 progs) The American West X 1 x 60 mins - NEW Curriculum Bites: History 14 – 16 X 2 x 60 mins The Arab-Israeli Conflict X 1 x 60 mins - NEW The Soviets X 5 x 25 mins The Cold War X 5 x 25 mins 20th Century World X 5 x 20 mins 20th century wrap X 1 X 20 mins. Nazi Germany X 5 x 25 mins Medicine through Time X 5 x 24 mins American Voices X 5 X 25 mins. A History of America 1917-1941 X 5 x 20 mins Black Peoples of the Americas X 5 x 20 mins World since 1945 X 1 X 20 mins. Intermediate Modern Studies: Equality in Society X 2 x 20 mins GCSE Bitesize History X 3 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize History X 2 X 120 mins. Radio (2 progs) Equality in Society X 2 x 20 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/education/modern bbc.co.uk/ni/education/stateapart World War One GCSE Bitesize History Standard Grade Bitesize History Theme History - Scottish curriculum themes Television (8 progs) Intermediate History: Mary Queen of Scots and the Scottish Reformation X 2 x 20 mins - NEW Intermediate History: Immigrants and Exiles X 4 x 20 mins Intermediate Modern Studies: Power and influence .. X 2 x 20 mins - NEW Radio (2 progs) Intermediate History: Immigrants and Exiles X 2 x 20 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/scotland/education Bitesize Highers History Age 16+ Secondary : Languages Theme French - Language and culture magazine programmes featuring interviews, voxpops, animation, songs, drama Television (17 progs) Quinze Minutes Plus X 11 x 15 mins Vingt Minutes X 6 x 20 mins 95 Age 11-14 Theme German - Language and culture magazine programmes featuring interviews, voxpops, animation, songs, drama Television (11 progs) Hallo aus Berlin X 11 x 15 mins Theme Spanish - Language and culture magazine programmes featuring interviews, voxpops, animation, songs, drama Television (10 progs) Revista X 10 x 15 mins Theme French - Magazine programmes, revision resources and dramas linked to GCSE/ Standard Grade topics / themes Television (28 progs) Clémentine X 10 x 15 mins Le Café des Rêves X 5 x 20 mins Jeunes Francophones X 10 x 20 mins GCSE Bitesize French X 2 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize French X 1 X 120 mins Websites GCSE Bitesize French Standard Grade Bitesize French Theme German - Magazine programmes, revision resources and dramas linked to GCSE/ Standard Grade topics / themes Television (11 progs) D-Mag X 5 x 20 mins Susanne X 5 x 20 mins GCSE Bitesize German X 1 X 120 mins. (repeated) Websites GCSE Bitesize German Theme Spanish - Magazine programmes, revision resources and dramas linked to GCSE/ Standard Grade topics / themes Television (11 progs) Isabel X 5 x 20 mins Voces Españolas X 5 x 15 mins GCSE Bitesize Spanish X 1 X 120 mins. (repeated) Websites GCSE Bitesize Spanish Theme French- Language and culture Television (3 progs) France 2000 (French version) X 3 x 20 mins Age 11-14 Age 11-14 Age 14-16 Age 14-16 Age 14-16 Age 16+ 96 Secondary : Maths Theme Maths - Applications of Maths, exam preparation Television (4 progs) The Maths Channel X 1 x 120 mins KS3 Bitesize Maths X 3 X 120 mins Websites Mathsfile KS3 Bitesize Maths Theme Maths - Applied Maths; exam revision Television (16 progs) Maths File: Art and Design X 5 x 20 mins Maths File : Travel and tourism X 1 X 20 mins. Mathsphere X 1 X 120 mins. GCSE Bitesize Maths X 3 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize Maths X 2 X 120 mins TGAU Bitesize Mathemateg X 4 X 30 mins Websites GCSE Bitesize Maths Standard Grade Bitesize Maths TGAU Bitesize Mathemateg Theme Maths - Problem-solving Television (6 progs) The Contenders X 6X 30 mins. NEW Websites AS Guru Maths Bitesize Highers Maths Age 11-14 Age 11-16 Age 16+ Secondary: Modern Studies Theme Modern Studies - Current affairs and issues Websites Standard Grade Bitesize Modern Studies Theme Alba - Specially made Scottish Gaelic resources Websites Bitesize Highers Modern Studies 97 Age 14-16 Age 16+ Secondary: Citizenship Age 11-14 Theme PSHE, Citizenship and Careers Advice - Active Citizenship Television (16 progs) Mapping Crime X 1 x 60 mins - NEW Turning Points: X 6 x 20 mins A-Z of Politics: Government and Parliament X 1 x 60 mins Active Citizenship (1 x 20 mins, 1 X 25 mins., 1 X 10 mins.) ID Citizenship X 4 x 15 mins Citizenship 2000 X 1 X 120 mins. (NI) Websites bbc.co.uk/schools/getinvolved Theme PSHE, Citizenship and Careers Advice - Careers Television (47 progs) Scene and dramas X 15 X 30 mins. Fast Tracks Science and Engineering X 10 x 10 mins Job Bank X 2 x 10 mins Lifeschool: Preparation for Adult Life (8 x 30 mins, 5 X 20 mins., 3 X 25 mins.) Aim Higher X 2 x 15 mins GCSE Bitesize Business Studies X 1 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize Modern Studies X 1 X 120 mins. (repeated) Websites Citizen X - 11-16 Eyewitness - 11-16 ID learning to be you - 11-16 Aim Higher - 13-15 Theme PSHE, Citizenship and Careers Advice - Drama for issues-related stimulus Television (25 progs) L8r X 6 x 10 mins Stopping Distance X 1 x 30 mins Job Bank and tutorial topics X 14 x 10 mins Dead Drunk X 1 x 30 mins Globalisation X 3 X 20 mins Websites Go Get It! (Employability) bbc.co.uk/ni/learning Theme PSHE, Citizenship and Careers Advice - Key Skills Television (14 progs) Key Skills X 6 x 30 mins NEW The Contenders X 6 X 30 mins. - NEW AS Guru General Studies X 2 X 120 mins. (repeated) Websites bbc.co.uk/keyskills Working Lunch AS Guru General Studies AS Guru Study skills 98 Age 11-16 Age 14-16 Age 16-19 Secondary: Religious Education Theme Religious Education - Christianity and critical thinking Television (2 progs) Curriculum Bites: Key Stage 3 Religious Education X 2 x 120 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/religion/re Theme Religious Education - Big religious questions, beliefs and concepts Television (45 progs) Taking Issue X 9 x 20 mins The RE Collection: Forgiveness X 1 x 20 mins Belief File: Islam X 5 x 20 mins Resources for Teaching Christianity X 1 x 20 mins Belief File: Sikhism X 2 x 20 mins Belief File: Buddhism X 1 x 20 mins Belief File: Hinduism X 3 x 20 mins Belief File: Judaism X 3 x 20mins Belief File: Issues X 5 x 20mins Bible in animation X 4 X 15 mins. Christianity (X 1 X 60 mins., 1 X 120 mins.) Miracle maker X 1 X 120 mins. Testament X 8 X 30 mins. Theme Religious Education - Philosophy and ethics, ultimate questions and critical thinking; realities of practising faith Television (19 progs) Curriculum Bites: Key Stage 4 Religious Education X 1 x 120 mins The Test of Time X 4 x 30 mins Belief File: Issues X 5 x 20 mins The RE Collection X 2 x 20 mins Taking issue X 5 X 20 mins. GCSE Bitesize RE X 2 X 120 mins (repeated) Websites bbc.co.uk/religion GCSE Bitesize Religious Studies Theme Religious Education - Old and New Testament Television (17 progs) Testament X 8 x 30 mins Resources for Teaching Christianity (1 x 15 mins, 1 X 10 mins) The Miracle Maker X 1 x 90 mins The RE Collection: X 2 x 30 mins Belief File X 4 X 30 mins 99 Age 11-14 Age 11-18 Age 14-16 Age 16-18 Secondary: Science Theme Science - Science in action in everyday life Television (27 progs) Science in Action X 6 x 20 mins Curriculum Bites: Science 11 – 14 X 1 x 120 mins Short Circuit X 15 x 20 mins The Human Body X 1 x 120 mins Wan2talk Science 1 X 120 mins. KS 3 Bitesize X 3 X 120 mins Websites KS3 Bitesize Science Theme Science - Careers in Science and teaching approaches Television (11 progs) Fast Tracks Science and Engineering X 10 x 10 mins Contemporary Science Teaching X1 x 30 mins Websites Sci Files (Wales) Theme Science - Double Science curriculum topics Television (47 progs) Curriculum Bites: Science 14 – 16 X 1 x 120 mins Key Skills X 3 x 60 mins - NEW Short circuit X 24 X 20 mins. GCSE Bitesize Science X 4 X 120 mins (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize Science X 3 X 120 mins (repeated) TGAU Bitesize Ffiseg X 4 X 30 mins. TGAU Bitesize Bioleg X 4 X 30 mins. TGAU Bitesize Cemeg X 4 X 30 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/keyskills GCSE Bitesize Chemistry GCSE Bitesize Biology GCSE Bitesize Physics TGAU Bitesize Chemistry TGAU Bitesize Biology TGAU Bitesize Physics Standard Grade Bitesize Physics Standard Grade Bitesize Biology Standard Grade Bitesize Chemistry 100 Age 11-14 Age 11-16 Age 14-16 Age 16+ Theme Science - Exam preparation Television (2 progs) AS Guru Biology X 2 X 120 mins. Websites Bitesize Highers :Biology Bitesize Highers :Chemistry Bitesize Highers :Physics AS Guru Biology Secondary: Special Needs Theme Special Needs - New reading scheme aimed at improving literacy skills Websites Boost Theme Special Needs - For teenagers with severe learning difficulties or disabilities: coping with everyday life, developing skills and independence, learning how to behave in public, learning about relationships Television (8 progs) Go for it! Relationships X 1 x 120 mins Go for it! Choices X 5 x 15 mins Documentary Scrapbook (1 X 20 mins, 1 X 25 mins.) Theme Special Needs - The programmes are designed to build confidence in young adults with learning difficulties or disabilities by providing practical help and demonstrating how situations can be handled successfully Television (5 progs) Go for it! Lifeskills X 5 x 20 mins Age 11-14 Age 14-16 Age 16+ Secondary: Technology Age 11-14 Theme Technology – Invention Television (20 progs) Techno: inc Young Foresight (20x 20 mins) of which 3 NEW. 101 Theme Technology - Real world; exam preparation Television (18 progs) Techno: ICT in the Real World X 4 x 15 mins Fast Tracks Science and Engineering X 10 x 10 mins Contemporary Science Teaching X 1 x 30 mins GCSE Bitesize Technology X 2 X 120 mins. (repeated) Standard Grade Bitesize Technology X 1 X 120 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/science/robots Theme Technology - Problem-solving, key skills Television (15 progs) L8r X 6 x 10 mins NEW Key Skills X 3 x 60 mins The Contenders x 6 X‘ 30 mins - NEW Websites bbc.co.uk/keyskills GCSE Bitesize Design Technology GCSE Bitesize ICT Standard Grade Bitesize Computer Studies Theme Welsh - Language Television (8 progs) Bitesize Cymraeg X 4 X 30 mins Bitesize Cymraeg Ail Iaith X 4 X 30 mins (second language) Websites TGAU Bitesize Welsh TGAU Bitesize Welsh as second language Age 11-16 Age 14-16 Age 14-16 102 Theme Project Hull / Project Merseyside Broadband Library resources Several curriculum areas and revision KiT platform (Kingston Communi -cations) Bitesize GCSE : English interactive website with integrated video clips Bitesize GCSE : Maths interactive website with integrated video clips Bitesize GCSE : Science interactive website with integrated video clips PC platform Bitesize GCSE :English interactive website with integrated video clips Bitesize GCSE : Maths interactive website with integrated video clips Bitesize GCSE : Science interactive website with integrated video clips Bitesize GCSE: SOS Teacher Live feature for students to ask questions of teachers Key Stage 3 Geography Interactive Citizenship (CITZ-H) Locally generated films Wild Hull Locally made film of animal life in the city Holiday Spain goes to Hull Local interviews Biology – video clips searchable under 20 common key stage 3 topics Chemistry – video clips searchable under 8 common key stage 3 topics Physics – c 200 video clips searchable under 16 common key stage 3 topics Geography – c 400 video clips searchable under 27 common key stage 3 topics Theme Buses and Open Learning Centres Outreach 12 BBC buses located in Cumbria, Derby, Devon, Greater Manchester, Humberside, Lancashire, Lincolnshire, Liverpool, Northern Ireland, South Yorkshire, Tees, Tyne and Wear and Wales. Plus 7 BBC Open Centres located in Hull, Stoke, Blackburn, Sheffield, Merseyside, Wrexham and Newport. Over 180,000 people have been reached so far through the scheme. 103 Age 11-16+ Formal Learning – Adult Adults: Work-related Learning Theme Work-related learning: - Webwise offers IT solutions for business problems; other resources provide information as well as training case studies. - Skillswise develops good practice and basic skills. Television (276 progs) Webwise for Business (10 X 60 mins., 2 X 30 mins.) Working in the Community (23 X 60 mins. (repeated), 7 X 30 mins., 2 X 15 mins.) Working in construction X 10 X 60 mins. Working in engineering (10 X 60 mins., 1 X 45 mins. 6 x 30 mins. 1 X 15 mins.) Working in retail X 10 X 60 mins. Working in hospitality X 10 X 60 mins. Working in travel and tourism (11 X 60 mins., 4 X 30 mins.) Customer care X 2 X 30 mins. Anger at work X 10 X 60 mins. Issues of difference X 10 X 60 mins. Literacy X 5 X 60 mins. Skills for life (inc Skillswise) (10 X 60 mins., 1 X 40 mins., 12 X 30 mins., 9 X 15 mins.) IT X 25 X 60 mins. Make your mark (21 X 60 mins., 6 X 15 mins., 1 X 30 mins., 6 X 10 mins.) Confidence (10 X 60 mins., 14 X 15 mins., 1 X 30 mins. (repeated)) Youth nation X 12 X 120 mins. each repeated 4 times Creativity (11 X 30 mins., 3 X 60 mins.) Theme Business & Management - Open University Business & Management programmes Television (25 progs) 22 X 30 mins. 1 X 50 mins. 2 X 60 mins Adults: Languages Theme Portuguese - Language and culture Television (20 progs) Talk Portuguese - 6 programmes X 15 mins. (repeated) Discovering Portuguese – 6 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Brazil Inside Out – 5 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Brazil 2000 – 3 X 20 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Talk Portuguese : Brazil inside out : BBC Brasil 104 Theme French - Language and culture Television (66 progs) France Inside out – 5 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) France 2000 – 4 programmes X 20 mins Talk French – 6 programmes X 15 mins (repeated) The French Experience know-how - 2 programmes X 60 mins The French Experience – 20 programmes X 15 mins. (repeated) The French Experience 2 – 10 programmes X 15 mins. (repeated) The French Experience: rencontres – 2 programmes X 60 mins. French on a plate – 5 programmes X 60 mins. (repeated) Le français au pluriel - 1 programme X 60 mins. French journey - 2 programmes X 60 mins. Get by in French – 1 programme X 60 mins. Bon mot - 1 programme X 60 mins. French Connection - – 1 programme X 60 mins. Documentaries on France – 1 X 60 mins. Open University French programmes La bonne formule - 1 programme X 30 mins. (repeated) Ciné Cinéphiles – 2 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Informer, éduquer, diverter - – 1 programme X 30 mins. (repeated) The golden thread 1 X 30 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : le mensuel : Vingt Minutes transcripts : French steps : Talk French : French Experience : French Experience II : French connection : Tour de France : Languages across Europe : French : Family French : le français cool : French for work : French journey : Vive la revolution BBC Afrique link 105 Theme Spanish - Language and culture Television (52 progs) Talk Spanish - 6 programmes X 15 mins (repeated) Spain Inside out - 5 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) España Viva – 15 programmes X 25 mins. (repeated) Europuzzle: Spain – 1 programme X 60 mins. Spanish journey – 2 programmes X 60 mins. (repeated) Sueños – 20 programmes X 15 mins. (repeated) Get by in Spanish – 1 programme X 60 mins. Documentaries on Spain – 1 X 60 mins. Open University Spanish programme Mosaico Hispanico - 1 programme X 30 mins. Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Languages across Europe: Spanish : el mensual : Beckham news : Spanish steps : Talk Spanish : Sueños : Spanish for work : Spain inside out : Spanish journey : Tomatina Theme Italian - Language and culture Television (56 progs) Talk Italian - 6 programmes X 15 mins (repeated) Italy Inside out - 5 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Italian journey – 2 programmes X 60 mins. Buongiorno Italia! – 20 programmes X 30 mins. Italianissimo - 20 programmes X 15 mins. (repeated) Europuzzle Italy - 1 programme X 30 mins. Get by in Italian – 1 programme X 60 mins. Documentaries on Italy – 1 X 60 mins. Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Languages across Europe: Italian : Italian steps : Talk Italian : Italy inside out : Italian journey: Italian for work 106 Theme German - Language and culture Television (35 progs) Talk German - 6 programmes X 15 mins (repeated) Germany Inside out - 5 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Deutsch Plus - 20 programmes X 15 mins. (repeated) Deutsch Plus 2- 1 programme X 60 mins. Get by in German – 1 programme X 60 mins. Documentaries on Germany – 1 X 60 mins. Open University German programme Wendepunkte - 1 programme X 30 mins. (repeated) Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Languages across Europe: German : German steps : Talk German : Deutsch Plus : Cool German : Germany inside out : One life : German for work Theme Greek - Language and culture Television (8 progs) Talk Greek - 6 programmes X 20 mins. Greek Chronicles – 2 X 60 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Talk Greek Theme Japanese - Language and culture Television (10 progs) Japanese language and people – 10 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : A fan in Japan : Working with the Japanese Theme Chinese - Language and culture Television (20 progs) Real Chinese – 10 programmes X 15 mins. China close up - 10 programmes X 15 mins Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Real Chinese : BBC Chinese 107 Theme UK national languages - Languages and cultures of the UK Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Gaelic : Welsh : story of Welsh : Irish : English : BSL Theme General - Language and culture Television (26 progs) Europe - 1 programme X 60 mins Learning languages 1 programme X 60 mins. (repeated) 2 programmes X 30 mins. (repeated) Languages for work 11 programmes X 30 mins. (some repeated) 12 programmes X 60 mins. (some repeated) Websites bbc.co.uk/languages : Quick fix (30 languages) : Test your …. (several languages) : Euroguide : Languages across Europe : Staffroom (lesson plans for several languages) : Holiday 2004 links Adults: Art & Design Theme Art and design - Galleries, artists, buildings and how environments and movements affect art; expressive arts Television (26 progs) Open University Art programmes 79 Television programmes 67 X 30 mins. 12 X 50 mins. Open University Design programmes 34 Television programmes 11 X 10 mins. 2 X 15 mins. 19 X 30 mins. 2 X 50 mins Websites Blast 108 Adults: Education and Guidance Theme Television (90 progs) Education and Guidance - Advice to OU students and general issues of child education Open University Guidance and advice programmes 11 Television programmes X 30 mins. 79 Television programmes Learning and exams (31 X 30 mins, 11 X 5 mins.) Learning X 2 X 60 mins. Teaching Today (and other CPD) (20 X 30 mins, 2 X 60 mins.) Key skills X 7 X 60 mins. Literacy and Numeracy (2 X 60 mins., 4 X 120 mins.) Adults: English and Drama Theme Television (32 progs) English and drama - Exploring literary texts Open University English and drama programmes 32 Television programmes 22 X 30 mins. 7 X 50 mins. 3 X 60 mins.. Adults: Geography and Environment Theme Television (78 progs) Geography and environment - Cities, economic imperatives, global changes, energy Open University Geography and environment programmes 10 X 10 mins. 1 X 15 mins. 62 X 30 mins. 5 X 50 mins. 109 Adults: Health Theme Health - Ageing, addiction, aesthetics Television (69 progs) Open University Health programmes 3 X 10 mins. 5 X 15 mins. 1 X 25 mins. 57 X 30 mins. 1 X 35 mins. 2 X 50 mins. Adults: History Theme Television (85 progs) History - Political and philosophical change-points; recent American Presidents. Open University History programmes 9 X 10 mins. 65 X 30 mins. 8 X 50 mins. 3 X 60 mins. Adults: IT Theme Television (18 progs) IT - History, ethics and design issues. Open University IT programmes 18 X 30 mins. Adults: Maths Theme Maths - Historical and applied aspects of Maths. Television (60 progs) Open University Maths and number programmes 60 X 30 mins. Adults: Media Theme Media - Media’s reflection of society Television (11 progs) Open University Media programmes 11 X 30 mins. 110 Adults: Music Theme Television (49 progs) Music - Performances, famous musicians and diverse cultures are reflected. Open University Music programmes 3 X 10 mins. 46 X 30 mins. Adults: Science and Nature Theme Television (317 progs) Science and nature - Space exploration technology and laboratory work a well as moral and historical issues for scientists. Biology, Chemistry, Physics. Biology: 106 Television programmes 6 X 10 mins. 3 X 15 mins. 1 X 20 mins. 1 X 25 mins. 67 X 30 mins. 5 X 35 mins. 22 X 50 mins. 1 X 60 mins. Chemistry: 12 Television programmes 12 X 30 mins. Physics: 15 Television programmes 15 X 30 mins. General: 184 Television programmes 33 X 10 mins. 51 X 15 mins. 6 X 20 mins. 82 X 30 mins. 6 X 35 mins. 4 X 50 mins. 2 X 60 mins. Adults: Social Studies Theme Television (49 progs) Social studies - Worldwide issues and political events affecting societies Open University Social studies programmes 7 X 10 mins. 2 X 15 mins. 126 X 30 mins. 4 X 45 mins. 11 X 50 mins. 111 Adults: Special Needs Theme Television (1 prog) Special Needs issues - Autism and Asperger’s syndrome Autism resources for teachers and parents (1 x 30 mins) NEW Asperger’s Syndrome: A programme on autism made by specialists from the Autism Research Centre at CambridgeUniversity. Adults: Technology Theme Television (38 progs) Technology - Technological applications for current problems Open University Technology programmes 38 X 30 mins. 112 B2: Informal Targeted Learning Output The following list pertains to output related to the BBC year, April 2003 to March 2004. Where share is indicated, it refers to average percentage of the audience share during the series run for TV and radio. In the case of online share, an average month’s page impressions (pi) are shown, and occasionally the number of unique users (uu). There is no share available for outreach. Theme Social Action/Lifeskills Share Outreach Led Get writing - Nationwide press campaign, competition, nationwide events, phoneline advice, competition winners event, supported by Marketing trails (Get Writing with Canterbury Tales) and broadcast: Canterbury Tales BBC1 Hustle 6 x 60mins BBC1 Radio 4 – Afternoon reading Slot Get Writing Film (not for Broadcast) bbc.co.uk/getwriting 26% 27% 3% 21% This Place - Supported by 2.1 hours on radio. bbc.co.uk/northernireland/thisplace 7% Social Work - BBC1 Scotland, 3 hours of broadcast, 7% Tales from the Edge - BBC2 Scotland 2 hours of Broadcasting 21% Chancers - BBC1 Scotland 3 hours of Broadcasting bbc.co.uk/scotland/tv/home/documentary/chancers TV promos 75% Wales (2.2.m). Big Fat Problem - Wales Today led the programme and highlighted issues. Special promotion broadcast on average 7 times between 23 March and 15 April 2004. 8,000 people acquired a Healthy Eating Booklet. Adshell campaign reached 39% (639,000people). NHS Direct Wales Helpline received 3,368 calls. The roadshow gave 573 people consultations. Approx. 6,000 people registered to join campaign..1050 pedometers donated by BHF. bbc.co.uk/bigfatproblem - cumulative pis over 6wks 58,481 bbc.co.uk/clampobroblem Numeracy Campaign – A joint project between BBC Wales and The Basic Skills Agency, to promote the use and enjoyment of Maths to teenage children. Supported by 3 different TV Trails on BBC 1 and 2, based on an animation cartoon character, 200 Adshel poster sites around Wales, leaflets and resources packs for schools, and branding for a VHS of Basic Skills Teaching Guides for teachers. bbc.co.uk/learningzone/workskills Neighbourhood gardener - Linked with over 45 colleges in 113 8% TV 6,700 visitors py the UK, and network and local radio stations, supported by broadcast: Gardeners Word BBC 2, 39 x 30 mins bbc.co.uk/neighbourhoodgardener 14% Mobile Bus: in Northern Ireland – (England, Scotland, Wales to be added) New Arrivals: An ESF Funded project which produced a pilot website designed to meet the needs of refugees, asylum seekers and speakers of English as a second or other language bbc.co.uk/newarrivals Blast: A project for 13-19 year olds who have a passion for creative dance, film, art, writing and digital creativity. 10 hours of TV and events across the UK in partnership with local organisations bbc.co.uk/blast Television Led Artworks - BBC 2 Scotland bbc.co.uk/arts/ 5% MOD 2003 – BBC 2 Scotland 3% SSO Proms 1 x 60 mins bbc.co.uk/scotland/musicscotland/bbcsso/ 7.4% Overnight Success (Tourism Shorts) bbc.co.uk/wales/overnightsuccess/ Money Spinners 10 x 60mins bbc.co.uk/lifestyle/moneyspinners 24 % Body Hits II 2 x 30mins BBC 3 (Health) bbc.co.uk/bbcthree/tv/bodyhits/series2.shtml 17% Little Angels 4 x 30mins BBC3 (Parenting) bbc.co.uk/bbcthree/littleangels 16% Who Rules the Roost (x3, then x5) (Parenting) bbc.co.uk/bbcthree/happy_families/who_rules_the_roost.s html 26% Bailiffs II 7 x 30mins BBC1 bbc.co.uk/parenting 114 Radio Led Radio 1: Sunday Surgery - Social Support for a Young Audience. 1 programme weekly on R1. Share 7.2% bbc.co.uk/radio1/onelife/sundaysurgery/ Radio 2: Babytalk, conception and fertility advice. Two days on R2 from 23rd June (Fertility) bbc.co.uk/radio2/campaigns/babytalk/ Diet Trials – tackling the subject of diet and obesity. Two days on R2, in March /April. 16 part TV series on BBC 1. bbc.co.uk/radio2/campaigns/diet/ Talking Teenagers –unlocks communication between adults and teenagers. Embedded into various R2 broadcasts throughout the year. bbc.co.uk/radio2/campaigns/talkingteens/ Radio 2: Student Essentials – Help with career decisions. Embedded into various R2 broadcasts during August (post-exams). bbc.co.uk/radio2/campaigns/studentessentials/ Taking Care - explores the legacy of care for children and adults. Embedded into various R2 broadcasts throughout the year. bbc.co.uk/radio2/campaigns/takingcare/ Radio 4 Check Up 18 x 27 mins, 7% share Home Planet Making History Mapping the Town 12 x 30 mins, 7.6% share Voices of the Powerless, plus BBC Cassette and book of the series bbc.co.uk/radio4/history/voices The Learning Curve- Tuesdays and Sundays 28 mins. Also supported by broadcasts on The Learning Zone on TV 8% share bbc.co.uk/bbc4/thelearningcurve Radio 5 My Sporting Journey 8 x 30 mins. Connected to Sports Relief and had various reports running on other programmes Euro Special Access all Areas Programme- A theme running across programmes and supported by all day events 5 x 60 mins Breakfast – Speak your mind campaign Sports Relief- a theme running across programmes and supported by some dedicated events. Online bbc.co.uk/radio1/onelife - advice for getting on with life (incl. chat room) Writing Scotland - commissioned for BBC Scotland, output in 04/05. bbc.co.uk/parenting - parenting support Story of Welsh . Plus 6x30mins BBC1. Share 25% bbc.co.uk/wales/storyofwelsh/ 115 Theme Factual Landmarks and Major Series Television Led You Thought You Knew (NI. Some outreach also) Scotland the Wild (some outreach also) Scots at Sea Would you pass the 11 + 1.5 hours on TV iTV output Share 10% Animal Camera 6 x 30mins Bermuda Triangle 1 x 60 Big Digs (Meet the ancestors) 1 x 50mins BBC 2 Child of our Time 3 x 60mins BBC1 Colosseum (iTV) 1 x 60 BBC1 Dragons Alive/Reptiles 3 x 60 12% 28% 12% 25% 28% 13% Elephant: Spy in the Herd 1 x 60 Great Inventions 5 x 60 BBC2 Human Mind 3 x60 Intensive Scares/ Eaten Alive 3 x 60mins BBC 1 25% 13% 25% 18% Jungle 3 x 60mins BBC1 Body Snatchers 3 x 60mins BBC1 Leonardo 3 x 60 BBC1 – also exhibition at British Library Michelangelo 2 x 60 Nile 3 x 50mins BBC 2 19% 19% 19% 5% 13% Pompeii 1 x 60 BBC1 Seven Industrial Wonders 7 x 50 St Paul 1 x 60 The Brontes 2 x 60 Walking with Sea Monsters (Indy) 3 x 30 War at Sea 3 x 60mins BBC2 Wild Down Under/Australasia 6 x 50 BBC2 39% 16% 10% 22% 29% 9% 13% Wildlife special / Shark 1 x 50 Mary Shelley 1 x 60 Ackroyd’s London 3 x 50 Byron 2 x 70mins BBC2 Mozart 3 x 60 BBC2 18% 12% 10% 13% 8% Walking with Cavemen 4 x 30mins BBC1 bbc.co.uk/science/cavemen/ 24% Abyss Live II 5 x 40 bbc.co.uk/science 24% Death in Rome bbc.co.uk/history/a.../launch_gms_deathrome.shtml 16% 16% Dunkirk 4 x 60mins BBC2 bbc.co.uk/dna/ww2/ 28% You thought you Knew 3 x 40mins bbc.co.uk/northernireland/youthoughtyouknew 116 Online Average monthly pi’s: 7,038,497 Average monthly uu’s: 734,336 www.bbc.co.uk/history www.bbc.co.uk/science www.bbc.co.uk/nature In April 2004 the BBC science and nature websites merged to form one. The url is now www.bbc.co.uk/sn Theme Cross-Platform Project - The Big Read Television The Big Read, 2 x 1 hour specials BBC1 Average monthly pi’s: 11,775,287. Average monthly uu’s: 848,646 Average monthly pi’s: 2,762,832. Average monthly uu’s: 267,256 Share 6% 9 x 90 BBC 2 BBC 4 Complimentary debate programmes Radio Radio 4, Local Radio Online bbc.co.uk/bigread Outreach Range of supporting resources for schools, colleges and libraries, database of reading groups, Little guide to Big Reading- how to set up your own reading group, Big Read was part of the BBC Arts website which averaged 1,728,711 pi’s per month every library in the UK supporting campaign, plus schools, voting, events etc. 117 Share 12% Theme Cross-Platform Project - Wild in Your Garden Television Wild in your garden BBC 2 Radio Local Radio Broadcasts Online bbc.co.uk/nature Outreach BBC events in 3 urban parks, local radio broadcasts and partner organisations. Average 2,508,458 pi’s per month 250 linked events and activities across the UK. Nearly 20,000 people attended the park events - the one in Sefton Park in Liverpool, hosted by Radio Merseyside, attracted 12,000 people Share 24% Theme Cross-Platform Project - World War II Television D-Day 120 mins BBC One ‘Destination D-Day’ 5 x 60mins BBC 1. Live Coverage of D Day Tues 1st – Sunday 6th June BBC1. Coverage on News 24 Radio 16 hrs of programming leading to D- Day, Radio 4. Special D- Day Coverage 5th and 6th June Radio 4. Coverage on Local Radio throughout 2004- Phone ins, OBs at People’s War Events. Online bbc.co.uk/dna/ww2/ 14,290 page impressions 1 million unique users in one month Outreach People’s War is an online project to build a lasting archive of WW2 testimonies for future generations. To allow non-IT Literate users to contribute their stories, a network of People’s War Associate Centres (400+ organisations, 2,500 centres so far) has been established across the UK to provide supported internet access. Associate Centres include Museums, Libraries, UKOnline centres and Colleges. Theme Cross-Platform Project - Making Sense of the Mind Television The Human Mind – 3 x 60 mins BBC1 Radio Supported by some science programmes Online bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/ - Outreach A series of community discussion events, some funded by the BBC and others by the Wellcome Trust, designed to engage a new audience in science 118 Share 18% Average 11,134 pi’s a month Share 12% Theme Cross-Platform Project - Restoration Television BBC2 11 x 60mins, 2 x 10mins, 1 x 90mins (outreach also) Radio Local Radio Stations have run 85 TV news items regarding Restoration with many more still to come. 150 radio features on Restoration have been broadcast, again with more to come. Online bbc.co.uk/restoration Listing of events and examples of good practice conservation work. Outreach A key factor in obtaining the Heritage Lottery Fund grant. In association with heritage open days BBC, organised a range of events throughout August and September aimed at encouraging public to see conservation and restoration first hand. A special review magazine was also published. Theme Cross-Platform Project - Hitting Home Television Theme was shown in programmes such as Casualty, Dangerous love and EastEnders. Over all there were 7.8hours of Hitting Home themes in BBC 1 programmes, 2.2 hours in BBC2, 55 minutes on BBC3, 3.9 hrs on BBC 4 and 45 minutes on CBBC Radio Programmes on Radio 1, Radio 2, Radio 4, Radio 5 Live, 1xtra, the Asian Network and local radio Online bbc.co.uk/health/hh/index.shtml 119 217,000 pi’s a week Hitting Home was covered by the health website which received an average of 4,277,842 pi’s a month Theme Other Informal Targeted Learning Output Outreach Led Radio 2, Sold on Song – Various Events including a song writing workshop in Deptford bbc.co.uk/radio2/soldonsong BBC Proms – Outreach Brixton 3 x 140 mins, 8 x 60 mins, 4 x 45 mins (radio) TV transmissions lengths varied: 7 on BBC 2, 4 on BBC1, 21 on BBC4 bbc.co.uk/proms Radio 3, World on your street – A showcase for musical talent from across the globe that can be found in the UK. Supported by a 5 part radio series and internet radio show. bbc.co.uk/radio3/world/onyourstreet MEC Symposium Video ICAN – A tool to help people re-engage with civic life: find info, find people, take action. 64 2-3 minute television pieces across England and Wales. 31% share. 181 radio pieces 2-3 mins. bbc.co.uk/ICAN Website typically has 300,00 pis per month and 100,000 uu’s Beechgrove Garden BBC Scotland, BBC2, 14.5 hours broadcast, 11% share Weather Permitting BBC Scotland, BBC TWO, 30 mins broadcast. 10% share Landward - commissioned in ¾ – output of 15 hours in 04/05 Theme Enduring Learning Strand in the BBC – Sport Academy Television Born to Win 6 x 30 mins BBC1 Radio Coverage on Radio 5 live Online www.bbc.co.uk/sportacademy - information and encouragement for children to take up sport Share 17% www.bbc.co.uk/academyparent - To enable parents and their children get the most out of sport, & maximise their fun and enjoyment. Outreach Sport Academy - Every secondary School in the UK (6000) was given a Born to Win pack and 68 Schools ran Born to Win days Theme Enduring Learning Strand in the BBC- Radio 1 One Music Radio Helps to provide face to face support and advice to young musicians. Mentioned and referred to in a variety of shows Online bbc.co.uk/radio1/onemusic Outreach Activities UK wide including running alongside Radio1 on the Road 120 Theme Other Informal Targeted Learning Output Television Soap Arab - Israel Conflict Movie Music Awards Making Tracks BBC Singer of the World in Cardiff – Education Project: 1 x 140, share 6% Inside the Orchestra National Youth Orchestra of Wales collaboration Composers Day Catchphrase Online Catchphrase Website Theme CBBC Reach to all homes (55.2m*) Reach to multichannel homes (32.6m*) Reach to digital homes (30.3m*) (* Source: BARB) Share 0.2% 0.4% 0.4% Television Bamzooki Aka Evo 4 x 10mins BBC1 Blue Peter 3 x a week, 25mins BBC Against all Odds 6 x 25mins BBC1 The Agency Animal Arc 13 x 15mins BBC1 Best of Friends Byker Grove 20 x 25mins BBC1 Cavegirl 46 x 20mins BBC1 Prom in the Park 1 x 30mins BBC2 Eureka 12 x 15 Fame Academy 16 x 60mins , 16 x 15mins BBC1 Genius 6 x 25 Grange Hill 20 x 25mins BBC1 Great North Run 1 x 240mins BBC1 Intergalactic Kitchen 13 x 25mins BBC1 Kerching 20 x 25mins BBC2 Meeting Beckham Nelly nut Show Power’s project The Queen’s Nose 6 x 25mins BBC2 The Raven 21 x 25 Reggie meets Beckham 1 x 24 Rule the school 8 x 25mins BBC2 S Club 7 – Behind the Scenes Serious Desert 6 x 25mins BBC1 Short Change 25 x 25mins BBC1 Smart 15 x 25 BBC1 The Stables 24 x 26 Tales from the Edge Ugetme 46 x 8mins BBC2 Wild UK Xperi- mental 7 x 15mins BBC1 Newsround, 5 times a week , 10 minutes BBC1 Tracey beaker Xchange 10 x 30mins BBC2 9.49% 12.23% 12.51% 121 10.49% 1.02% 13.4% 10.79% 12.74% 11.67% 23% 12% 12.44% 31% 8.5% 10.99% 0.78% 12% 13% 12.57% 11.45% 15% 12.69% 13.28% 1.3% 0.4% 9.66% 16.5% 2.03% 0.3% Page Impressions Online Tracey Beaker on-line: bbc.co.uk/cbbc/tracybeaker 8,476,264 pi X-change: bbc.co.uk/cbbc/xchange 1,872,004 pi CBBC Art on-line: bbc.co.uk/cbbc/art 1,570,265 pi CBBC Sport on-line : bbc.co.uk/cbbc/sport 898,916 Notes: Creative Archive is not being listed as output though online development spend has been shown in section A of the appendix. Please see formal section of appendix for languages output. 122