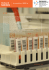Hannover Unified Biobank
Transcription
Hannover Unified Biobank
Zentrales Biobanking am Beispiel der Medizinischen Hochschule Hannover (MHH) Hannover Unified Biobank Prof. Dr. Thomas Illig CEO and Scientific Head of Hannover Unified Biobank (HUB) 23. 06. 2015, University of Innsbruck What is a biobank? • Term "biobank" first appeared in the scientific literature in 1996 • Biological collections of human, animal, plant or microbial samples • Sample collections with associated sample data • Collections that are managed according to professional standards Potential of biobanks • Huge potential (markers, drugs, • individualized medicine, pathoetiology) • New technologies mapping themolecules of life (genes, transcripts, proteins, metabolites) • Controversial • Money (cost) • Real value already coming Biobanking is one of them Growing impact on medical research Huge public health opportunity Importance of biobanks Cancer Genome Atlas (CGA) • Aim: systematic exploration of the entire spectrum of genomic changes involved in human cancer • “You might have thought that doing the science would be the biggest challenge of a massive undertaking like the Cancer Genome Atlas,” • “But acquiring the biospecimens turned out to be the hardest part, bar none. It’s the Wild West out there.” Carolyn Compton NCI bio-repository chief Head of Biomaterials Group for the CGA What may be problems of small biobanks • No second temperature control and no alarm system available • No personnel to take care for freezer problems on bank holidays, weekends or during the night (samples are damaged) • No emergency power available • No empty back-up freezer available • Icing • No data banks that safe storage or quality data of samples • No data security (Pseudonymization) • … Quality of analyzed data strongly dependent on quality of biomaterial Centralized biomaterial banks = cBMBs (BMBF funded: 25 million € / 5 years) • Aachen, Berlin, Heidelberg, Kiel, Würzburg, Munich (M4) • Centralized biobanks without BMBF funding eg Jena, Leipzig, Dresden, Hannover, Mannheim, Gießen, Essen, … • Many other German universities plan centralized biobanks Central professional biobank at Hannover Medical School (MHH) Hannover Unified Biobank = HUB • Establishment of a professional, modern, unified and harmonized biobank at MHH Important quality features for professional biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-Data quality and security (Biobank information system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance, access and owner rights 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks Medical School (MHH) Hannover • More than 9000 employees • Pure medical university (only one in Germany) • Close collaboration with other 2 universities in Hannover • Fraunhofer ITEM, Helmholtz Braunschweig • Participation in 2 German Health Centers (DZL, DZIF) • 2 Excellence clusters (Rebirth, Hearing4all) • 3 SFBs • 8 Forschergruppen • 5 „Kompetenznetzwerke“ • 1 „IFB“ for transplantation • 70 different clinics and institutes Move to new building: Clinical Research Center Hannover (CRC), June 2014 Important quality features for modern biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-data quality and security (Biobank information management system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance of biobank, access and owner rights of samples and data 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks 1. Sample quality (pre-analytics, storage, retrieval) • HUB infrastructure in Clinical Research Center (CRC). • 400 m2 of storage space − for millions of samples − automated -80°C repository (in construction) − liquid nitrogen tanks and -80°C freezers (partly ordered) − Connection to MHH via pneumatic underground line • 200 m2 of lab space − automated sample preparation for body liquids − automated DNA and RNA extraction 1. Processes and workflow lab; body liquids • All steps documented (Time stamps, temperature logging) • Samples latest after 2 hours in freezer or N2 tank 1. Gapless documentation of biobank processes • Pre-analytics and transport (time stamps) • Storage and retrieval (constant temperature monitoring) 1. Pre-Analytics 1. Storage overview of HUB Storage capacity: 6 million 1 ml tubes 1. Automated Storage Important quality features for modern biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-data quality and security (Biobank information management system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance of biobank, access and owner rights of samples and data 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks 2. IT-Data quality and security Biobank Information Management System (BIMS) • • Currently MHH Enterprise MySamples Licence (MyData) 200 users • Customizing and development of MySamples (Scanner, search function improved, protocols, reports, quality attributes, delivery of samples to other institutes, …) • New BIMS: Kairos CentraXX (used already in 15 other big biobanks in Germany) • Customizing of CentraXX to MHH needs until Dec. 2016 2. Biobank Information System (BIMS) of HUB identifying data (IDAT) Lab system MHH (opus::L) Clinical systems MHH (SAP, SubSystems) Study- / research systems Pseudonymization (ZIMt) Master Patient Index (MPI) / (Mainzelliste) study data, consent-status, external pseudonym (PIDe) sample- / analysis data jobs, positions, IDs cinical data Scanner LiquidHandlingRobot DNA/RNA extraction robot diagnoses, basic data Datawarehouse (MHH/ZIMt) clinical data, molecular data rack-ID, sample-ID, sample-position, working step BiobankInformation System (BIMS) sample quality data Analysis / Research analysis-pseudonym (PID2) position, IDs pick lists / jobs Hamilton ---80°C robot BiobankPseudonym (PID1) temperature, liquid Level, sample content Liquid nitrogentanks Important quality features for modern biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-data quality and security (Biobank information management system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance of biobank, access and owner rights of samples and data 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks 3. Governance, access and owner rights Important quality features for modern biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-data quality and security (Biobank information management system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance of biobank, access and owner rights of samples and data 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks 4. Project management • Biomaterials and volumes (serum, plasma, DNA, tissue, urine, …) • SOPs (pre-analytics, transport, storage) • Informed consent (Broad, project specific) • IT management (sample registration tool, MySamples, CentraXX) • Publication of sample collections (BBMRI catalogue, Deutsches Biobankregister, MHH HUB website) • Import of „old“ sample data to MySamples or CentraXX, transport of „old“ samples to HUB 4. Projects • 500 000 samples in database • 280 000 samples physically stored from altogether 130 projects 4. Third party funded projects • German Centre for Lung Research (DZL) • German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Transplant cohort • Integrated research and treatment center transplantation (IFBTx), BMBF • Combatting bacterial resistance in Europe (EU IMI) • Probase (Prostate cancer, Krebshilfe) • DIGIT HF (Herzstiftung) • German national cohort (local samples, Hannover / Braunschweig) • Re-birth (Excellence initiative) • NeoCyst (Polycystic kidneys, BMBF) Important quality features for modern biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-data quality and security (Biobank information management system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance of biobank, access and owner rights of samples and data 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks 5. Certification of HUB • DIN ISO 9001 certification in 2015 • GAMP 5 validation of the IT system 2016 • GxP conformity in 2018 Important quality features for modern biobanking 1. Sample quality (processes, infrastructure, capacity) 2. IT-data quality and security (Biobank information management system, pseudonymisation) 3. Governance of biobank, access and owner rights of samples and data 4. Project management 5. Certification of biobank processes 6. Education and training Often only possible in large central biobanks 6. Education and training • Biobanking day (4 x per year) • User training IT/BIMS: my samples/Centraxx (up to 6 times per year) • Different biobank lectures at MHH • Guided tours in biobank Thank you very much for your attention HUB Team Norman Klopp, Markus Kersting Inga Bernemann, Jana Prokein Dirk Drobek, Karin Heine Sisko Bauer, Mercedes Clavero Bettina Wilhelm, Manfred Mertin Thomas Illig Not presented: Christina Hartmann, Urbana Perez-Martin, Kordula Brückmann DZL samples and projects in HUB • Asthma: KIRA , PASTURE, SOLAR, GABRIEL, ISAAK, PARSIFAL, PARSIFAL TUSCON, VERMEE, MAGICS, DNA, serum (Hansen) • COPD: ABACOPD, different biomaterials (Welte, Barten) • Cystic fibrosis: human and bacterial collections (Tümmler) • ELD: body liquids from lung transplanted persons (Gottlieb) • ELD: cells (Martin) • PH: serum, plasma (Hoeper) • Pneumonia and ALI: CAPNETZ, different biomaterials (Welte, Barten) • Total of 120 000 DZL samples stored in HUB • Extraction of 2 700 genomic DNA samples from CapNetz Sample quality in HUB • Excellent storage conditions for millions of samples • High grade of automation in storage and preanalytics (Hamilton Systems) • Emergency power supply and alarm system • Continuous temperature monitoring • Barcodes for sample identification • Sample tracking during all steps of pre analytics, storage and retrieval [Coriell Institute, New Jersey]