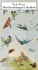PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE
Transcription
PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE
PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 The following photographs in Section 1 identify symptoms in roses which have common causes and can sometimes be caused by Rose Rosette Disease (a/k/a Rose Rosette Virus). Just because you see a symptom or two in Section 1 – does not mean that you have RRD in your garden. The following symptoms can be caused by many things: SECTION 1 Symptom Leaf & stem reddening Normal New Growth Symptom Leaf distortion Drawstring puckering caused by a plant growth inhibitor (photo courtesy J. W. Pscheidt, OSU) Common Causes Normal plant development; new growth starts off red and turns green; environmental conditions impact the length of time it takes for color change; in roses where chilli thrips are feeding, the red color may become marbled with green Rose Rosette Disease Sometimes present; in roses infected with Rose Rosette Disease the stems and leaves may not turn green Rose Rosette Disease - Excessive reddening that does not turn green Common Causes Pest feeding (i.e. spider mites, chilli thrips); fungus (powdery mildew) herbicide damage, mechanical injury Examples of leaf distortion on St. Patrick Hybrid Tea Rose caused by chilli thrips 1 Rose Rosette Disease Usually present Rose Rosette Disease – leaves stay small (usually 1/4 to 1/8th inch) and can look like feathers PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 Powdery mildew can cause leaf distortion (photo courtesy of Baldo Villegas) Symptom Rapid stem elongation and lateral branching Asparagus-like stems are evidence of chilli thrips feeding Herbicide damage caused by vapor drift from products containing glysophate (like Round-Up). Leaves may look like feathers. Normal new growth in weather with intermittent warm days followed by cold days (photo courtesy of Baldo Villegas). Common Causes Normal plant development; plant response to temperature fluctuation and fertilization (most common in spring & fall); chilli thrips feeding Unusual branching can be a symptom of chilli thrips damage 2 Rose Rosette Disease Often present Unusual branching with reddening can be a symptom of rose rosette disease PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 Symptom Leaf chlorosis (yellowing) with mosaic patterns Common Causes Exposure to saline irrigation water; nutrient deficiencies; other viral diseases; lack of water or too much water; heat stress Rose Rosette Disease Sometimes present Chlorosis Chlorosis caused by lack of water Chlorosis caused by iron deficiency (photo courtesy of Dr. David Zlesak) Rose mosaic virus can weaken a plant’s ability to fight disease Chlorosis on rose rosette infected stem (leaves are lighter green than the rest of plant) Symptom Thickened canes Common Causes Normal plant development; environmental conditions; excessive fertilization; plant response to temperature fluctuations 3 Rose Rosette Disease Sometimes present PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 Thick canes caused by excessive fertilization Symptom Premature development of lateral buds New stems forming at the base of the plant (basal breaks) are usually larger in diameter than new growth that forms in the canopy Common Causes Abnormal development due to weather conditions (cool/warm/cool); pest feeding (i.e. chilli thrips); herbicide damage Excessive bud development on very short stems caused by erratic weather conditions Premature bud development on very short stems caused by chilli thrips feeding 4 New growth on stem infected with rose rosette disease (much larger than normal with more prickles than normal) Rose Rosette Disease Often present Premature bud development on Belinda’s Dream rose with rose rosette disease PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 SECTION 2 Rose Rosette Disease causes some very specific symptoms that taken in context with the symptoms in Section 1 can help identify and confirm the presence of the virus. The following unique symptoms are prevalent in roses infected with Rose Rosette Disease: Symptom Abnormal leaflets that may have a feather-like appearance and/or are drastically smaller than normal healthy leaves on that plant Common Causes Herbicide damage and/or contact with plant growth inhibitors and other products containing glysophate (like Round-Up). Roses can outgrow herbicide damage. Sometimes this symptom can be caused by chilli thrips feeding. Rose Rosette Disease Most RRD-infected roses demonstrate feather-like leaves on infected canes Leaves 1/8th Inch or less Symptoms of chilli thrips feeding Symptom Stems and thorns become rubbery and pliable Herbicide damage on modern Hybrid Tea rose Leaf feathering caused by rose rosette disease Common Causes Rose canes that are 1 to 2 days old are tender and pliable. These canes usually harden up within a week of development. Rose Rosette Disease RRD-infected stems do not harden up and remain pliable and usually can be bent in half without damage. Thorns stay rubbery and pliable. Stems and thorns on plants infected with rose rosette disease stay rubbery and bend easily without breaking. Thorns will be soft and pliable instead of hard and rigid. 5 PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 Symptom Multiple distorted stems are produced at the terminal end of branches or from a dormant bud eye resulting in a ‘witches broom’ effect Common Causes No known alternate cause Rose Rosette Disease The most common and definitive symptom of RRD Symptom Bloom distortion and bloom color change Common Causes Bloom distortion is caused by a host of problems (chilli thrips, downy mildew, powdery mildew, weather) Rose Rosette Disease Bloom distortion with a change in bloom color can be an indication of RRD Muddy tan bloom from St. Patrick Hybrid Tea from bush heavily infected with chilli thrips. Bloom would normally be lime green and have true rose form. Chilli thrips caused the bloom to look like a daisy. Balling can occur in a wet humid spring on heavily petaled roses (lots of petals per flower) where the petals are very thin. Moisture and heat cause the petals to stick together keeping the flower from opening normally. 6 Bloom/color distortion on a Hybrid Tea rose infected with rose rosette disease. Bloom would normally be dark pink (photo courtesy of Virginia Cooperative Extension) PICTORIAL DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE Compiled by Gaye Hammond, Past President, Houston Rose Society [email protected], 281/458-6116 Symptom Increased thorniness Common Causes Can be seen with herbicide damage but this is rare. Normal thorn/prickles (photo courtesy of Ingrid Taylar) Rose Rosette Disease Common for stems infected wtih RRD to have excessive thorns. If a healthy stem has thorns spaced 1 inch apart, canes infected with RRD can have 50 to 100 thorns/prickles within that same distance – making the stem look more like a nettle than a rose Excessive thorniness caused by rose rosette disease (photo courtesy of John Hartman Univ. of Kentucky) For more information about any of the topics in this guide, contact a consulting or Master Rosarian from the Houston Rose Society, www.houstonrose.org. See also: Rose Rosette Disease Slide Show, Greg Church, Ph.D., Texas AgriLife Extension, Collin County, Texas, collin.agrilife.org/filed/2011/09/rose-rosette-disease-handout.pdf Rose Rosette Disease: Demystified, Kevin Ong, Ph.D., Texas A&M University, http://www.agrilifebookstore.org/productpleplp-010.htm 7