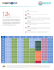
Senior Coordinator: Mouna Abdelhay Level Coordinator: Karam
Transcription
Senior Coordinator: Mouna Abdelhay Level Coordinator: Karam
Vision Darul Ulum College envisions and works towards achieving success in an Islamic environment by drawing its strength and guidance from the Holy Quran and teachings of the Prophet Mohammad (may the peace and blessing of Allah be bestowed upon him). Mission Statements Darul Ulum College of Victoria is an Islamic independent school which is committed to: 1. Providing quality education in an Islamic atmosphere which prioritises the development of religious and ethical consciousness in students. 2. Establishing a faithful learning community which embraces both Islamic and Australian values of freedom of speech and religion; openness and tolerance to difference and diversity and the equality of civil rights, through excellence in teaching and learning. 3. Integrating academic and personal skills with principles inspired by the Quran, Sunnah and Australian values that can empower students to make positive contributions to the wider community. 4. Enabling students to pursue higher education and vocational endeavours as confident and active members of the Australian multicultural society. 5. Promoting intellectual, social, emotional, physical and spiritual development through programs that cater for a broad range of abilities and interests. 6. Supporting participation and the achievement of ‘personal best’ to boost self-esteem and personal wellbeing. 7. Offering students a diversity of enriching activities and stimulating challenges outside the central academic program. 8. Creating and enhancing a culture of continuous improvement. Principal: Abdurrahman Gokler Senior Coordinator: Mouna Abdelhay Level Coordinator: Karam Barakat 1 YEAR 7 TEACHERS 7A Teachers 7C Teachers English Ms RESHIDE SELIMI Ms AYSEGUL VELIDEDEOGLU Mathematics Ms ADIILAH RAHEMAN Ms NERGIS ZEYBEK Science Ms SAFIYE KIRCA Ms SAFIYE KIRCA Tarbiyyah Ms NAJWA IBRAHIM Ms NAJWA IBRAHIM Humanities Ms KARAM BARAKAT Ms AYSEGUL VELIDEDEOGLU Essential Reading Ms RESHIDE SELIMI Ms BANU SEZGIN ART Ms NERGIS ZEYBEK Ms FARZANA KHAN Technologies Ms NERGIS ZEYBEK Ms NERGIS ZEYBEK PE Ms AISHA BAHARIN Ms AISHA BAHARIN Arabic Ms HANAN ELHUSSEIN Ms NAJWA IBRAHIM YCDI Ms KARAM BARAKAT Ms AISHA BAHARIN Qur’an Ms Fouzia Abdullah, Ms Aniza Baharin, Ms Taahira Siddique Curriculum @ DUCV Darul Ulum College of Victoria has undertaken a community declaration that the curriculum provided to its students is guaranteed irrespective of the external factors. Where students are in need of special education, an inclusive curriculum will be made accessible to meet their specific needs. The curriculum at Darul Ulum College of Victoria is organized to cater for the intellectual, physical, social, emotional and spiritual development of all students. The College curriculum is seen as a process rather than as a product. The curriculum provides a broad, balanced and relevant education that ensures continuity, offers a challenge and progression yet takes individual differences into account. The school is committed to the implementation of Australian Curriculum/AusVELS throughout all dimensions/learning areas and across all year levels. 2 QUR’ANIC STUDIES OVERVIEW In the subject of Qur’anic Studies, students begin by learning how to read, pronounce, and join the Arabic alphabet. They also learn how to apply the “Tajweed” rules in their recitation and read with correct rhythm and balance; together with appropriate breathing management. Students start from basics using the “Iqra” series, and with a lot of practice, they work their way towards reading the Holy Qur’an confidently and fluently with minimal assistance. Upon completion of the Holy Quran, students begin memorizing certain “Surahs”. AIM: To gain the pleasure of Allah (SWT) and revive the “Sunnah” (tradition) of Prophet Muhammad (SAW). To ensure correct recitation of Qur’an, so that when it is recited in “Salaat”(Prayers), the recitation will be correct and Salaat will be valid. To encourage and provide opportunity for the students to do khatam (completion) of the Qur’an whilst they are studying at DUCV; as it is the right of the Qur’an that, a minimum of 2 complete recitation should be done within a year. To provide the students with the theory of correct “Qur’an” recitation method through “Tajweed” lessons. To encourage the students to memorize selected “Surahs” and “Masnoon Duas” (prayers) that has been emphasised by our Prophet (SAW) and make it as part of their daily routine. To provide skills for the students to be able to help others in reading the Qur’an in line with the “Hadith” (tradition) which has been quoted; “The best amongst you is he who learns the Qur’an and teaches it.” Through this, they would be able to be of service to the community at large in the medium of spreading the words of Allah (SWT). SCOPE AND SEQUENCE FOR YEAR 7 (N17-N20) SCOPE AND SEQUENCE FOR YEAR 7 CURRICULUM COVERAGE TERM 1 (N17) Naathirah Maryam 1 --- > Al Hajj 46 TERM 2 (N18) Naathirah Al Hajj 47 --- > Ash-Shu’araa 60 TERM 3 (N19) TERM 4 (N20) Naathirah AshShu’araa 61 --->Al Ankabut 45 Naathirah Al Ankabut 46 -- > Sabaa Ayah 48 3 ADVANCE STUDENTS WILL MOVE ONTO THE YEAR 8 CURRICULUM (N21-24) (NAATHIRAH OF SURAH FAATIR TILL END OF TAHRIIM) NEW STUDENTS CURRICULUM Term Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Yr 1 Yr 2 L 1 - L 4 (Iqra 1-6) L 5 - L 8 (Annaba’ till AlMursalaat) L1 - Iq 1 & 2 N1 (An-Naba’ till Al-Fajr Ayah 22) L2 - Iq 3 & 4 N2 (Al-Fajr Ayah 23 till An-Nas) L 3 - Iq 5 N3 (Al-Mulk till Al-Jin Ayah 28) L 4 - Iq 6 N 4( Al-Jin Ayah 29 till end of Mursalaat) Yr 3 Yr 4 L 13 - L 16 L 9 - L 12 (Al(Al-Anfaal Baqarah till Ayah 9 till Al-Anfaal end of AtAyah 8) Tahreem) N 13, 14 & 15 (Al-Anfaal N5&6 Ayah 9 till (Al-Baqarah An-Nahl Ayah 1-165) Ayah 64) N 16, 17 & 18 N7&8 (An-Nahl (Al-Baqarah Ayah 65 till Ayah 166- Ash-Shuara’ 286) Ayah 60) N 19, 20 & 21 N 9 & 10 (Ash-Shuara’ (Al-Imran till Ayah 61 till Al-Maidah Az-Zumar Ayah 36) Ayah 67) N 22, 23 & N 11 & 12 24 (Al-Maidah (Az-Zumar Ayah 37 till Ayah 68 till Al-Anfaal end of AtAyah 8) Tahreem) Yr 5 Hifz 1 (As-Sajdah, AlMulk, Yasin, Juz Amma) Sajdah & Mulk Yaseen An-Naas till AlBuruj Al-Inshiqaq till An-Naba’ LESSON STRUCTURE Students are grouped according to their level of achievement at the start of the year. At the start of each term, students will be given a Parent and Student Course Outline detailing the expected curriculum coverage and assessment schedule and weightage for the term. Classes begin with recitation of “Dua”. One hadith on virtues of “Quran” is recited at the start of class. 4 Lesson will be taught and listened to in a whole group setting with every student in the group listening to the same lesson read by their peers according to the weekly curriculum coverage. Each student will recite the same lesson or portion of the lesson in turn. Students who are not reading are to listen attentively and actively involved in giving constructive feedback on their peers’ recitation at the end of the recitation. Not reading students will be tested on their set homework which comprises of either memorization of translation of selected passage from the Qur’an, “Masnoon Dua”, hadith or worksheet activities Students that are new/ behind curriculum will have a catch up curriculum to work on alongside being exposed to the mainstream curriculum. Students that are behind curriculum will be given a course outline that will aim towards closing the gap to the expected curriculum level. With the group reading structure, it is expected that students get tested daily for their recitation or at least 4 times a week. Audios, graphic presentations, power point presentations, charts, Tajweed Booklets, are used as supporting materials, as well as an English translation of the “Quran”. HOMEWORK AND STUDY Daily lesson are given in class which needs to be read and revised together with previous lessons for 15 minutes daily. For non- reading students, recitation and memorisation of “Masnoon Dua” , translation of ayah for selected passage, hadith and worksheet activities will form part of the daily given lesson for the period that students are not reading. Weak students will have their lessons supplemented with selected pages from the Iqra books, to build up their fluency and confidence. ASSESSMENT Daily lessons will be assessed by the teacher whenever time permits and marks assigned, ranging from Excellent, Very Good, Good or More Practice/Repeat. Students’ behavior in class will also be assessed and this will contribute towards their On Task. The total number of “Excellent” received in daily testing of lessons will contribute towards the Qur’an Incentive program award. Overall term/ semester assessment breakdown will be as below: ASSESSMENT ITEMS TERM 1 SEMESTER 1 TERM 2 SEMESTER 2 CLASSWORK READING 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% (ONGOING Week 1-7) MID TERM ASSESSMENT 5 (WEEK 4 ) PRACTICAL READING TEST 30% 30% 30% 30% CONTENT COVERAGE by end of Term 30% 30% 30% 30% TOTAL 100% 100% 100% 100% (Week 7) Test/exam marks will be marked down if students are behind curriculum for their expected level. Test and exam marks weightage are out of 100% and are divided between Fluency, Makhaarij and Tajweed, for Iqra and Naathirah students. For students doing Hifz, strength of memorisation will also contribute towards the weightage. Students completing Iqra 3, Iqra 6, Naathirah and Hifz Curriculum will be tested by an appointed member from the Qur’an department and will receive a certificate on successful completion of these levels. BENCHMARK Students who fall below 60% in their assessment tasks and/or overall term/ semester achievement will be deemed as, at risk students. These students will be listed under the Student Learning Adjustment Record and a 8 week term intervention program will be organized for the students and parents notified. At the end of the term, their progress will be evaluated to determine whether further intervention or referral is needed. Teachers will work with students to achieve 20% growth by the end of the school’s year for students who achieved 60% and above in their semester 2 mark in the previous year. For students who achieved less than 60% in the semester 2 mark in the previous year, a growth of 510% is expected from these students. New students or students falling behind curriculum will have discussion with their teacher and/or coordinator, to come up with a plan to bring them up to curriculum level. Weak students and students that failed their lessons for 3 consecutive days will be seen by the coordinator in conjunction with their teacher, to discuss strategies to overcome the problem. REQUIREMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Daily monitoring of student’s lessons at home by the parents. A set time on a daily basis for Qur’an recitation at home, preferably with other members of the household. Reading of some “Hadiths” (narrations) on the virtues of reading and memorizing the Holy Qur’an amongst family members, to encourage and create eagerness for the recitation of the holy Quran. 6 Dua by the parents, as quoted in the tradition that: “Prayers by a parent in respect of their child goes up to Allah (SWT) unchecked.” Tarbiyyah Objectives: The purpose of Islamic Studies is to mould a thinking, believing and practicing Muslim. By the time a child graduates from high school, he or she should be a fully-functional Muslim. He or she should be aware of Allah's presence in their life, how to practice Islam, why they are alive, what will happen to them after they die, what Islamic beliefs and teachings are and how to explain them to others, how to interact with others Islamically, the basic history of the Blessed Prophet sallallahu alaihi wasallam, how to understand halal and haram, how to be the best human being, what the general flow of Muslim history has been and finally, how to implement the Shari'ah in their public and private lives. Scope and Sequence: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Islamic History Aqaaid Aqaaid Islamic History Fiqh Fiqh Akhlaaq wal Adaab Akhlaaq wal Adaab Masah on Khuff Istinja Fasting Qadaa of Fasting I’tikaaf Allah, the Majestic Shirk Prophethood Bid’ah Repentance from sin Memorization of duas Qurban Aqeeqah Hunting Umrah Interpretations of religious matters Taqleed Signs of Qiyaamah Destruction of Ka’bah A detailed narrative on the life of The first Khalifa of Islam, Abu Bakar (RA) Pride Humility Anger Guarding the tongue Modesty Dressing Memorization of duas Memorization of duas Ahadeeth A detailed narrative on the life of The second Khalifa of Islam, Omar (RA) Greed Treatment of orphans Muslim brotherhood Importance of Salah in congregation Consistency in performing deeds Memorization of duas Assessment: Quiz 1: 20% Quiz 2: 20% Memorisation: 20% Common Assessment Task/Exam: 40% 7 Recommendations: It is highly recommended that students memorize/revise and practice the masnoon duas on a daily basis. Moreover, they should try to put into practice whatever they learn straight after learning. Languages Arabic YEAR 7 Overview Students begin to understand and use the Arabic language within the world of teenage experience, on topics related to general interest, topics drawn from other domains and the world of learning. They start to exchange personal information, opinions, ideas, feelings and plans orally and through correspondence. They develop their understanding that cultural diversity exists and that customs and traditions vary within countries and over time. They also investigate the important elements that make up a language system and the particular functions of grammatical concepts. Term 1 Dinning at a restaurant Term 2 Shopping The Olympic Games Australian animals Term 3 Islamic Celebrations The Arab World Term 4 Communication modes Assessment Common Assessment Tasks Quizzes Projects Semester Exam Lesson Structure Revision of previous lesson’s concepts 8 Whole class and individual activities/ tasks Group or pair work activities Teacher monitoring and assisting students when assistance is required Reflection of what students have learnt Homework and Study Homework is given once a week. It will mainly consist of: Independent reading Memorizing dialogues to perform role-plays Solving various types of exercises and activities Writing essays, assignments and/or projects Benchmark All students are to show academic growth for all subjects. Those achieving less than 60% to show minimum of 20 % growth Those achieving above 60% to show minimum of 5% to 10% growth Parent involvement Parents/ guardians are urged to contact and liaise with their child’s teacher throughout the year. Appointments with individual teachers can be made by contacting the office. Alternatively, the class teacher may be directly contacted via the following emails: Class Teachers: Ms Nagwa Ibrahim & Ms Hanan Elhussein All parents are expected to observe their child’s progress in this subject and may seek advice from individual teachers as to how they can assist in the learning of their child. Resources Arabic Text books: activities prepared by the teacher, readers, stories and word games. ESL activity books Dictionaries Arabic readers Charts/Posters 9 HUMANITIES Overview Students will study various topics in the areas of History, Geography, Civics & Citizenship and Economics & Business. In history, students will focus on how past events have shaped the world we know today by looking at evidence from ancient times to understand what life was like then. They study the people, events and ideas that changed societies in Ancient Egypt and Ancient China. In geography, students look at sustainable use of water as a resource and will investigate the interaction of human activities with the resource. Students will also examine factors that influence liveability and how it is perceived. In Civics and Citizenship, students explore how the Australia’s system of government aims to protect all Australians; the Australian Constitution and how its features, principles and values shape Australia’s democracy and how the rights of individuals are protected through the justice system. In Economics & Business, students explore what it means to be a consumer, a worker and a producer in the market and the relationships between these groups; the characteristics of successful businesses and how entrepreneurial behaviour contributes to business success. Term 1 Term 2 History: Depth Study 1: Investigating the ancient past Geography: 1. Unit 2.- Place and Liveability History 2. Depth Study 2: The Mediterranean World Ancient Egypt Term 3 Geography: 1. Unit 1- Water in the World Economics 2. Consumer, Market & Business Term 4 Civics and Citizenship1. Australian government & rights History: 2. Depth Study 3: The Asian World Ancient China Assessment: Various assessment tasks will be used throughout the year based on Knowledge and Understanding and Inquiry / Skills. These include: Common Assessment Tasks (Unit test , Skills) Classwork activities ( Quizzes) Projects- based on practical work, oral or written work/investigations / findings, research assignment. End of Semester examinations Lesson Structure 10 Revision of previous lesson’s concepts Whole class and individual activities/ tasks Group or pair work activities Teacher monitoring and assisting students when assistance is required Reflection of what students have learnt Homework and Study To complete a variety of set homework tasks (ranging from completing class work to providing research for projects or assessment tasks) once or twice a week as per teacher’s instructions. By due date. Duration of completing homework tasks: 15- 30 min per task. Duration of study time for Humanities- 30 minutes once per week. Students are required to use their School Diary to record all homework, work requirement and assessment task submission dates Students are required to maintain and complete a glossary of words relating to each topic of study. Benchmark Students are required to receive 60% or above in all set assessment tasks. Requirements and Recommendations To have all textbooks and student workbooks at all times during class. To revise content taught in class the same night to ensure a greater level of understanding is achieved. To supervise and monitor your child’s progress and homework tasks written in diary. Students can be encouraged by parents to read around these subjects, and visits to the local library and reputable internet sites are an invaluable way of gaining in depth knowledge and context to any period. SCIENCE Through the learning of Science, students are provided with the opportunity to develop an understanding of important concepts. Science knowledge can develop through collaboration and connecting ideas across the discipline. Students comprehend the contribution of Science to our culture and society and its application in our lives. Science and technology contribute to finding solutions to a range of contemporary issues. These solutions may impact on other areas of society. 11 The Science Curriculum at Darul Ulum College aims to improve students’ inquiry skills, general knowledge, scientific literacy and their understanding of Science as a human endeavour by highlighting different approaches to a scientific view of the World. Science Curriculum STRANDS SUBSTRANDS SCIENCE UNDERSTANDING Biological Chemical Physical Earth and Space Sciences SCIENCE INQUIRY Questioning and predicting Planning and conducting Processing and analysing data and information Evaluating and communicating SCIENCE AS A HUMAN ENDEVOUR The nature and development of Science Use and influence of Science Lesson Structure Science lessons at Darul Ulum College are taught using an integrated inquiry model. The lessons aim to engage students with hands on experience and activities that encourage them to ask questions and with support, discover ways of finding answers to their enquiries. Incursions that focus on assisting students make sense of the Science in their lives and around them are organised and complement, as well as contribute to the teaching of Science. Scope and Sequence Throughout Science students make observations to reveal patterns and relationships to make predictions about phenomena. Students construct and use a range of representations including graphs, and models to represent and analyse patterns or relationships using digital technologies. YEAR 7 SCOPE AND TERM 1 CH 1: Investigating science CH 5: Habitats and Interactions Homework/Study TERM 2 CH 6: Classifications Ch 8: Machines SEQUENCE TERM 3 CH 2: Physical and Chemical properties of substances CH 4: Mixtures TERM 4 CH 3: Earth Resources CH 9: Earth in Space Homework is an integral part of the student’s education. Through homework activities the student is able to develop appropriate study habits and skills that are essential for growth and academic achievement. For this reason, Science Homework is set for once per week. However, the subject material covered must be reviewed daily. Assessment 12 Levels of achievement will be reported for the following assessment items: Practical work Topic tests/Common Assessment Tasks (CATS) Written work Problem solving/inquiry activities Research /Extended Investigations End of semester examinations Teachers use a range of formal and informal assessments to enable the attainment of the outcomes. Benchmarks and Recommendations Darul Ulum College aims to engage students in Science topics and then establish learning experiences where students are given the opportunity to explore and explain their understandings. It is encouraged that parents support students in seeking answers to their questions and assist them in making sense of the environment and Science in their daily lives through research and discussion. MATHEMATICS By the end of Year 7, students solve problems involving the comparison, addition and subtraction of integers. They make the connections between whole numbers and index notation and the relationship between perfect squares and square roots. They solve problems involving percentages and all four operations with fractions and decimals. They compare the cost of items to make financial decisions. Students represent numbers using variables. They connect the laws and properties for numbers to algebra. They interpret simple linear representations and model authentic information. Students describe different views of three-dimensional objects. They represent transformations in the Cartesian plane. They solve simple numerical problems involving angles formed by a transversal crossing two parallel lines. Students identify issues involving the collection of continuous data. They describe the relationship between the median and mean in data displays. Students use fractions, decimals and percentages, and their equivalences. They express one quantity as a fraction or percentage of another. Students solve simple linear equations and evaluate algebraic expressions after numerical substitution. They assign ordered pairs to given points on the Cartesian plane. Students use formulas for the area and perimeter of rectangles and calculate volumes of rectangular prisms. Students classify triangles and quadrilaterals. They name the types of angles formed by a transversal crossing parallel line. Students determine the sample space for simple experiments with equally likely outcomes and assign probabilities to those outcomes. They calculate mean, mode, median and range for data sets. They construct stem-and-leaf plots and dot-plots. 13 Topics Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 1. Numeracy 1 8. Algebra 11. Numeracy 2 14. Representing and Interpreting data 2. Positive Integers 10. Probability 12. Positive and Negative Integers 15. Coordinates and Cartesian Plane 13. Linear Equations 16. Transformations 3. Indices and 5. Geometry Primes 4. Rational Numbers 9. Measurement 17. Views of 3-D shapes 6. Decimals 18. Money 7. Percentages Homework and study Students will be given 20 minutes Mathematics homework every night. Students are encouraged to selfstudy for 30 minutes and revise the concepts covered in class. Assessments Semester Assessment Weightage Common Assessment Tasks 30% Quizzes 20% Projects 10% Exam 40% TOTAL 100% 14 Health and Physical Education Overview of the Curriculum – Year 7 The Health and physical education (H & PE) curriculum is organised into two strands –Personal, social and community health and Movement and physical activity. Students proficiently perform complex movement and manipulative skills. They maintain regular participation in moderate to vigorous activity and they combine motor skills, strategic thinking and tactical knowledge to improve individual and team performance. In addition, they demonstrate skills to make informed decisions, and propose and implement actions that promote their own and others’ health, safety and wellbeing. Term Movement and physical activity topics Personal, social and community Health topics 1 Handball / Sports day preparations. 1. Introduction to P.E – three activities 2 Hockey 2. Bullying 3 Baseball 3. Personal Hygiene Tips 15 4 Basketball 4. Fitness Tests Scope and Sequence: Year 7 Lesson structure Health and PE at DUCV are conducted in both indoor and outdoor settings. The lessons begin with five minute warm- ups and students are taught a range of skills. They participate in a variety of team and individual games and activities, using and building on skills and strategies from other sports as well as continuing to develop new, sport-specific, skills. The lessons end with cool down activities in order to help the students relax. Assessment Assessments range from the following: Quiz’s Textbook activities Projects Rubrics – Sports skill Checklists Resources A range of sporting equipment are regularly used during H & PE lessons, depending on the nature and focus of each lesson. The school Gymnasium (MPH) is also used in most lessons. Requirements and recommendations Due to occupational Health and Safety (OH & S) requirements, students are required to wear runners and the school’s full sports uniform during all Health & PE lessons. English Year 7 Level 7 Description 16 In Levels 7 and 8, students communicate with peers, teachers, individuals, groups and community members in a range of face-to-face and online/virtual environments. They experience learning in both familiar and unfamiliar contexts that relate to the school curriculum, local community, regional and global contexts. Students engage with a variety of texts for enjoyment. They listen to, read, view, interpret, evaluate and perform a range of spoken, written and multimodal texts in which the primary purpose is aesthetic, as well as texts designed to inform and persuade. These include various types of media texts including newspapers, magazines and digital texts, early adolescent novels, non-fiction, poetry and dramatic performances. Students develop their understanding of how texts, including media texts, are influenced by context, purpose and audience. Literary texts that support and extend students in Levels 7 and 8 as independent readers are drawn from a range of realistic, fantasy, speculative fiction and historical genres and involve some challenging and unpredictable plot sequences and a range of non-stereotypical characters. These texts explore themes of interpersonal relationships and ethical dilemmas within real-world and fictional settings and represent a variety of perspectives. Informative texts present technical and content information from various sources about specialised topics. Text structures are more complex including chapters, headings and subheadings, tables of contents, indexes and glossaries. Language features include successive complex sentences with embedded clauses, unfamiliar technical vocabulary, figurative and rhetorical language, and information supported by various types of graphics presented in visual form. Students create a range of imaginative, informative and persuasive types of texts, for example narratives, procedures, performances, reports and discussions, and are beginning to create literary analyses and transformations of texts. TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4 Language: Text: Go Grammar! 1 Grammar: Unit 15 + Unit 21 Spelling: Spelling can be taught in context. Punctuation: Unit 31 + 32 Language: Text: Go Grammar! 1 Grammar: Unit 29 + Unit 6 + Unit 14 Spelling: Spelling Focus 1 Punctuation: Unit 33 + 34 Language: Text: Go Grammar! 1 Grammar: Unit 1 + Unit 2 + Unit 12 Spelling: Spelling Focus 2 Punctuation: Unit 35 + 36 Language: Text: Go Grammar! 1 Grammar: Unit 17 + 18 Spelling: Spelling Focus 3 Punctuation: Unit 37 + Revision Test 7 * Past NAPLAN papers can be used for teaching this area also. Please note: the above units reflect what MUST be taught according to the updated Australian Curriculum. Teachers have the flexibility to teach units in context of their Literature and Literacy teaching; keeping in mind that students will be assessed on the stipulated skills above. Literature: Girls: ‘Bridge to Terabethia’ (Paterson) NOVEL * Past NAPLAN papers can be used for teaching this area also. Please note: the above units reflect what MUST be taught according to the updated Australian Curriculum. Teachers have the flexibility to teach units in context of Literature and Literacy teaching; keeping in mind that students will be assessed on the stipulated skills above. Literature: Please note: the above units reflect what MUST be taught according to the updated Australian Curriculum. Teachers have the flexibility to teach units in context of Literature and Literacy teaching; keeping in mind that students will be assessed on the stipulated skills above. Please note: the above units reflect what MUST be taught according to the updated Australian Curriculum. Teachers have the flexibility to teach units in context of Literature and Literacy teaching; keeping in mind that students will be assessed on the stipulated skills above. Literature: POETRY resource developed by M. Azim and other teacher Literature: POETRY resource developed by M. Azim and other teacher 17 Boys: ‘Class Acts’ (Clausen) PLAY Literacy: THEME Persuasive Language Text: Insight English Skills 7 Unit 4: Print Advertisement Unit 5: Speech ‘I have a dream…” Please note: teacher discretion is required for the depth in which they choose to cover a unit. Teachers can use resources in addition to the text which has the stipulated theme at its core. Girls: ‘Bridge to Terabethia’ (Paterson) NOVEL Boys: ‘Class Acts’ (Clausen) PLAY Literacy: THEME Exploring Imaginative Texts Text: Insight English Skills 7 Unit 20: Graphic novel – Kampung Boy Unit 3: Mystery Novel: Falling from Grace Please note: teacher discretion is required for the depth in which they choose to cover a unit. Teachers can use resources in addition to the text which has the stipulated theme at its core. prepared/selected poetry resources prepared/selected poetry resources Literacy: THEME Discovering Cultures Through Texts Text: Insight English Skills 7 Literacy: THEME Uncovering Current Issues Text: Insight English Skills 7 Unit 7: Poem – A Poison Tree Unit 8: Poem – Municipal Gum Please note: teacher discretion is required for the depth in which they choose to cover a unit. Teachers can use resources in addition to the text which has the stipulated theme at its core. Unit 14: Internet Text Unit 18: Newspaper Article Please note: teacher discretion is required for the depth in which they choose to cover a unit. Teachers can use resources in addition to the text which has the stipulated theme at its core. Assessments Year 7 TERM 1 LANGUAGE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing 1 Language Test (Go Grammar!1) (Common Assessment Task) 15% LITERATURE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing; Speaking and Listening *1 CLASS PROJECT (Based on Literature) 10% LITERACY: Mode: Reading and Viewing: 1 Reading Comprehension Test (Persuasive Text/Literacy Theme) (Common Assessment Task) 15% Mode: Writing: 1 Persuasive Essay (Common Assessment Task) 40% Mode: Speaking and Listening: 1 Persuasive Oral Presentation 20% TERM 2 LANGUAGE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing 1 Language Test (Go Grammar!1) (Common Assessment Task)10% LITERATURE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing; Speaking and Listening *1 CLASS PROJECT (Based on Literature) 10% LITERACY: Mode: Reading and Viewing: 1 Reading Comprehension Test (Narrative Text/Literacy Theme) (Common Assessment Task) 10% Mode: Writing: 1 Narrative Writing (Common Assessment Task) 20% Mode: Reading and Viewing: 1 Visual Media Analysis (Literacy Theme) 10% Exam 40% TERM 3 LANGUAGE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing 1 Language Test (Go Grammar!1) (Common Assessment Task) 15% LITERATURE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing; Speaking and Listening *1 CLASS PROJECT (Based on Literature) 10% LITERACY: Mode: Reading and Viewing: 1 Poetry Reading Comprehension (Common Assessment Task) 15% Mode: Writing: 1 Poetry Writing (Common Assessment Task) 40% Mode: Speaking and Listening: 1 Oral Presentation (Famous Poet/Poetry) 20% TERM 4 LANGUAGE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing 1 Language Test (Go Grammar!1) (Common Assessment Task) 10% LITERATURE: Mode: Reading and Viewing; Writing; Speaking and Listening *1 CLASS PROJECT (Based on Literature) 10% LITERACY: Mode: Reading and Viewing: 1 Reading Comprehension Test (Literacy Theme) (Common Assessment Task) 10% Mode: Writing: 1 Text Response Essay/Poetry Commentary (Common Assessment Task) 20% Mode: Reading and Viewing: 1 Visual Media Analysis (Literacy Theme) 10% Exam 40% ESSENTIAL READING PROGRAM 18 The College has included in its infrastructure intervention/support and accelerated/preparation programs in the weekly curriculum for literacy and numeracy where possible. The Essential Reading Program is one of them. The aim of the program is: To develop in students, a love or engagement for reading; this will also increase their proficiency in overall literacy. To enable students to be confident in their own reading and to share with others their love of books. To understand and experience the different types of genres or forms of texts and novels. To provide all necessary reading skills to students that will assist them to read for meaning, reading between the lines, predicting, questioning and searching for fact or opinion. To allow students to become independent readers through an appropriate focus on word, sentence and text-level knowledge. To assess weaknesses and strengths and support students in reading. To enhance students reading and understanding ability. To inculcate in students an interest in words and their meaning. Prepare a sound and strong foundation for VCE literacy to maximize student outcomes. Implementation of Essential Reading lessons: 1. Two periods per week have been allocated for Essential Reading at Years 7, 8 and 9 levels. 2. A specific English teacher (mainstream English teacher) will be given the task of implementing this from Years 7 – 9. 3. Teachers conduct silent and aloud reading in the class to model reading behaviour as well as observe students’ reading behaviour 4. Selected novels and different types of texts – as well as current issues and media articles will be read in each class. 6. Comprehension skills to study in Essential Reading are: The Literal Questions: Finding information that is given directly in the text. The Reorganisation Questions: Reconstructing two or more literal pieces of information contained in the text. The Inference Questions: Deducing information not given directly in the text. The Vocabulary Questions: Determining the meaning of unknown words from context. The Evaluation Questions: Gathering information and drawing conclusions. The Reaction Questions: Expressing an opinion based on the information given in the text. Assessment of student reading: Probe assessment results will inform teachers about which comprehension skills to focus on in class. Teachers will monitor the use of the Essential Reading Student Record Booklet. 19 Program expectations from students and parents: We ask students to read 20 - 30 minutes each night and record what they read. We would like our parents to contribute to this program by monitoring their child's reading every night. Reading is an ongoing homework for each night. Parents are to sign readers on a nightly basis. If parents observe that their child is not reading, we urge them to contact their child's teacher or coordinator immediately. Additionally, we can ask Essential Reading teachers to provide parents an activity that they did with students as an example; perhaps photographs of the projects, vocabulary posters created in class etc. Further ways in which parents can help: We would appreciate it if parents could make available for their child, the community newspapers that are delivered to homes free of charge. We kindly request that the households which do not benefit from this service, to purchase a newspaper for their child on a weekly basis. This will enable students to learn about the issues affecting the community at large and thus help them to become more informed individuals. Access to newspapers will also benefit students’ reading skills. We appreciate parent support regarding this matter. ESSENTIAL READING OVERVIEW 2016 YEAR SEVEN TERM 1 READING THEME FOR THE TERM: TERM 2 READING THEME FOR THE TERM: TERM 3 READING THEME FOR THE TERM: TERM 4 READING THEME FOR THE TERM: PERSUASIVE LANGUAGE EXPLORING IMAGINATIVE TEXTS DISCOVERING CULTURES THROUGH TEXTS UNCOVERING CURRENT ISSUES Core Text: Excel Essential Skills (Years 7 to 8) Core Text: Excel Essential Skills (Years 7 to 8) Core Text: Excel Essential Skills (Years 7 to 8) Core Text: Excel Essential Skills (Years 7 to 8) Unit 3: Website Advertisement Unit 12: Advice Article Unit 9: Cartoon Teacher Selected Resources: Unit 1: Novel Extract Unit 7: Picture Book Extract Teacher Selected Resources: Up to teacher discretion as long as texts selected match with the theme for the term. Please incorporate visual text comprehension in your teaching. Up to teacher discretion as long as texts selected match with the theme for the term. Please incorporate visual text comprehension in your teaching. Nightly Reading and Silent Class Reading: DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge Nightly Reading and Silent Class Reading: DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge Teacher Selected Resources: Up to teacher discretion as long as texts selected match with the theme for the term. Please incorporate visual text comprehension in your teaching. Nightly Reading and Silent Class Reading: DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge Teacher Selected Resources: Up to teacher discretion as long as texts selected match with the theme for the term. Please incorporate visual text comprehension in your teaching. Nightly Reading and Silent Class Reading: DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge 20 Text List (TBA at the beginning of the term) Assessment: Text List (TBA at the beginning of the term) Assessment: Text List (TBA at the beginning of the term) Assessment: Text List (TBA at the beginning of the term) Assessment: Assessment 1: Assessment 1: Assessment 1: Assessment 1: Reading Comprehension Quiz (End of Term) = 40% CAT Reading Comprehension Quiz (End of Term) = 40% CAT Reading Comprehension Quiz (End of Term) = 40% CAT Reading Comprehension Quiz (End of Term) = 40% CAT Teacher prepared quiz or a quiz directly from a comprehension textbook (15 multiple choice questions). Focus: Reading strategies based NOT content based. Teacher prepared quiz or a quiz directly from a comprehension textbook (15 multiple choice questions). Focus: Reading strategies based NOT content based. Teacher prepared quiz or a quiz directly from a comprehension textbook (15 multiple choice questions). Focus: Reading strategies based NOT content based. Teacher prepared quiz or a quiz directly from a comprehension textbook (15 multiple choice questions). Focus: Reading strategies based NOT content based. Assessment 2: Assessment 2: Assessment 2: Assessment 2: Major Classwork Activity = 30% Major Classwork Activity = 30% Major Classwork Activity = 30% Major Classwork Activity = 30% Teacher determined activity – may be an in class project that takes a lengthy period of time for students to complete, or a shorter in class activity which deeply assesses student understanding/skills. Teacher determined activity – may be an in class project that takes a lengthy period of time for students to complete, or a shorter in class activity which deeply assesses student understanding/skills. Teacher determined activity – may be an in class project that takes a lengthy period of time for students to complete, or a shorter in class activity which deeply assesses student understanding/skills. Teacher determined activity – may be an in class project that takes a lengthy period of time for students to complete, or a shorter in class activity which deeply assesses student understanding/skills. Assessment 3: Reading Participation = 30% Teachers to give students 10 minutes of each Essential Reading class to do silent reading (DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge text). Teacher to determine ways to assess this task effectively. Teachers can base their scoring judgment on student attitude/participation and by asking students to verbally share their thoughts regarding their reading. Assessment 3: Reading Participation = 30% Teachers to give students 10 minutes of each Essential Reading class to do silent reading (DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge text). Teacher to determine ways to assess this task effectively. Teachers can base their scoring judgment on student attitude/participation and by asking students to verbally share their thoughts regarding their reading. Assessment 3: Reading Participation = 30% Teachers to give students 10 minutes of each Essential Reading class to do silent reading (DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge text). Teacher to determine ways to assess this task effectively. Teachers can base their scoring judgment on student attitude/participation and by asking students to verbally share their thoughts regarding their reading. Assessment 3: Reading Participation = 30% Teachers to give students 10 minutes of each Essential Reading class to do silent reading (DUCV Principal’s Reading Challenge text). Teacher to determine ways to assess this task effectively. Teachers can base their scoring judgment on student attitude/participation and by asking students to verbally share their thoughts regarding their reading. TECHNOLOGIES Technology education integrates both procedural and conceptual knowledge based on a holistic view of design. Students identify needs that have personal relevance, apply design theory and use design processes that encourage flexibility, resourcefulness and imagination in the development, communication and production of quality solutions. The Australian Curriculum: Technologies aims to develop the knowledge, understanding and skills to ensure that, individually and collaboratively, students: • are creative, innovative and enterprising when using traditional, contemporary and emerging technologies, and understand how technologies have developed over time. • critique and evaluate technologies processes to identify and create solutions to a range of problems or opportunities. 21 • • investigate, design, plan, manage, create, produce and evaluate technologies solutions. engage confidently with technologies and make informed, ethical and sustainable decisions about technologies for preferred futures including personal health and wellbeing, recreation, everyday life, the world of work and enterprise, and the environment. Scope and Sequence TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4 STRANDS Digital Technologies knowledge and understanding Digital Technologies processes and production skills Topics / Concepts Desktop Environment Basic Operations Core application tasks Research skills Word Processing skills Digital Digital Technologies Technologies knowledge and processes and understanding production skills Internet Spreadsheet skills Flow charting and Programming Database Skills Assessment Assessment Break down Project Work 50% CATs 40% Classwork & Homework 10% Homework Schedule Once a week Benchmark Darul Ulum College has a standard benchmark for all subject i.e. 60% Study requirements and recommendations It is imperative that students complete all the set work (Classwork, Homework, Projects, and Assignments etc.) to the best of their ability. Students must continuously revise their topics covered so far. ART Art is a special way of expressing one’s feelings and observations/ ideas. It’s a way to express about the things you see, remember or imagine. In the art class students should be able to experience visual art both as artists and as audience. They should be able to discover their ideas, thoughts, imaginations, feelings, belonging and understanding as an artist and at the same time can also see how others have convey the same. Art also address the needs of the students with artistic intelligence and provide opportunity to develop valuable skills among the The Australian Curriculum. The Arts aims to develop students’; creativity, critical thinking, aesthetic knowledge and understanding about arts practices, through making and responding to artworks with increasing self-confidence 22 arts knowledge and skills to communicate ideas; they value and share their arts and life experiences by representing, expressing and communicating ideas, imagination and observations about their individual and collective worlds to others in meaningful ways use of innovative arts practices with available and emerging technologies, to express and represent ideas, while displaying empathy for multiple viewpoints. understanding of Australia’s histories and traditions through the Arts, engaging with the artworks and practices, both traditional and contemporary, of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples understanding of local, regional and global cultures, and their Arts histories and traditions, through engaging with the worlds of artists, artworks, audiences and arts professions. Program Components Keeping the program objective in mind the Art program will have the following components. Components are not to be isolated but are intended to be interlinked throughout the program. Creating and making Exploration of Ideas Creative expression and reflection Development of skills and abilities Exploring and responding Thoughtful, guided responses to arts expressions Critical and creative thinking about art works Development of language and vocabulary Cultural/Historical understanding Role and history of the arts in cultures and societies Factors that influence the arts and artists Knowledge of popular artists Above three components will be taught over 4 Terms/Year under the following subjects: Visual Art, Media Art, Performing Art. Scope and Sequence- see above 23 TERM 1 Visual Art TERM 2 Visual Art TERM 3 Performing Art TERM 4 Media Art Creating and making Inspiration and Ideas Role play ADVERTISEMENTs STRANDs Topics / Concepts Assessment Breakdown Class Project 60% CATs 20% Folio Presentation 20% Homework Schedule Once a week Benchmark Darul Ulum College has a standard benchmark for all subject i.e. 60% Study requirements and recommendations It is imperative that students complete all the set work (Classwork, Homework, Projects, and Assignments etc.) to the best of their ability. Students must continuously revise their topics covered so far. 24 Homework Homework is an essential part of our education at the school. Students have their homework schedule to follow. Consequence for not completing homework: 1. 2. 3. 4. Verbal warning. Warning recorded in the students’ diary for parents to sign. Issuing a form for neglecting homework without a valid reason. Call parent for a meeting to discuss the matter further. Each night 1. Students MUST read for 20 minutes and record activity in their logbooks. 2. Practice Qur’an 30 minutes. 3. Practice their Tarbiyya duas 5 - 10 minutes. Please contact the relevant form teacher if your child is having difficulty completing homework or claiming she has NO homework. 25 Year 7A Homework schedule TOTAL Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Maths (20 mins) English (30 mins) Maths (20 mins) English (30 mins) Maths (20 mins) Tarbiyah (20 mins) Humanities (30 mins) Arabic (30 mins) Science (30 mins) Tarbiyah (20 mins) 1 hour and 20 mins 1 hour and 40 mins 1 hour and 30 mins 1 hour and 40 mins 1 hour and 20 mins Year 7C Homework schedule TOTAL Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Quran (15 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Reading (25 mins) Tarbiyah (20 mins) English (30 mins) Arabic (30 mins) English (30 mins) Tarbiyah (20 mins) Maths (20 mins) Science (30 mins) Maths (20 mins) Humanities (30 mins) Maths (20 mins) 1 hour and 20 mins 1 hour and 40 mins 1 hour and 30 mins 1 hour and 40 mins 1 hour and 20 mins 26