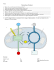
Overview of Photosynthesis
Transcription
Overview of Photosynthesis
An Introduction to Photosynthesis BENCHMARKS: SC.912.L.14.7* SC.912.L.18.7-Identify the reactants, products, and basic functions of photosynthesis. SC.912.L.18.9*- Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. OBJECTIVES: I will state the overall equation of photosynthesis. I will explain how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are part of an interrelated cycle. I will describe the factors that affect photosynthesis. REVIEW What are autotrophs and heterotrophs? Plants, algae, and some bacteria are able to use light energy from the sun to produce food. They are called photosynthetic autotrophs. Animals, fungi, protozoa, and some bacteria obtain their energy from the food they consume. They are called heterotrophs. Take Notes What is photosynthesis? Comes from the Greek words: photo - light synthesis - putting together Therefore, it means “using light to put something together” During photosynthesis, plants use the energy from sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The energy is now STORED in the carbohydrate molecule. 6CO2 + 6H2O+ light C6H12O6 + 6O2 Take Notes How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related? The key process for energy capture (from the sun) and storing it as chemical energy in glucose is photosynthesis. 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Takes place in photosynthetic autotrophs only The energy in glucose is released during cellular respiration by breaking down glucose and using it to recharge ATP. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Takes place in ALL organisms! Do you notice that photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite reactions??!! They form a cycle! Photosynthesis captures and saves energy. Cellular respiration releases and uses the energy. Take Notes Why are light and pigments needed for photosynthesis? Plants gather the sun’s energy with light absorbing molecules called pigments. Chlorophyll Carotene When chlorophyll absorbs light , much of the energy is transferred directly to electrons in the chlorophyll molecule. These high-energy electrons make photosynthesis work. Complete the Gizmo DO NOW in your Gizmo Packet. Guided Gizmo Warm-Up Independent Activity A and B Exit Slip What do we know? 1. The overall process of photosynthesis can be represented using a chemical equation. Like all chemical equations, the equation for photosynthesis must obey the law of conservation of mass. Which of the following is the correct and balanced equation for photosynthesis? A. CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 B. 6CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 C. CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 D. 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Exit Slip What do we know? 2. Which of these statements correctly describes the process of photosynthesis? A. Photosynthesis is an exothermic process because it releases energy. B. Photosynthesis is an endothermic process because it releases energy. C. Photosynthesis is an endothermic process because it requires the absorption of energy. D. Photosynthesis is an exothermic process because it requires the absorption of energy. Exit Slip What do we know? 3. Which of these best describes the conversion of sunlight into the energy in glucose? A. Chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy. B. Kinetic energy is converted to potential energy. C. Electromagnetic energy is converted to chemical energy. D. Potential energy is converted to electromagnetic energy. What do we know? Exit Slip Scientists are measuring the rate at which carbon dioxide (CO2) and water are converted to glucose and oxygen (O2) per hour in various types of houseplants with the same biomass. The houseplants are all exposed to the same amount of sunlight and to the same conditions. The data they collect is given in the table. ALOE VERA COLEUS POTHOS SPIDER PLANT AMOUNT OF CO2 ABSORBED 180 mL 168 mL 164 mL 175 mL AMOUNT OF O2 RELEASED 150 mL 150 mL 150 mL 150 mL Exit Slip What do we know? 4. What is the most likely reason that the plants absorb different amounts of CO2? A. The plants are different heights. B. The plants have different masses. C. The plants have different size leaves. D. The plants are different shades of green. ALOE VERA COLEUS POTHOS SPIDER PLANT AMOUNT OF CO2 ABSORBED 180 mL 168 mL 164 mL 175 mL AMOUNT OF O2 RELEASED 150 mL 150 mL 150 mL 150 mL Exit Slip What do we know? 5. In which process do these plants absorb CO2, water, and sunlight to produce glucose and O2? A. mitosis B. photosynthesis C. replication D. respiration ALOE VERA COLEUS POTHOS SPIDER PLANT AMOUNT OF CO2 ABSORBED 180 mL 168 mL 164 mL 175 mL AMOUNT OF O2 RELEASED 150 mL 150 mL 150 mL 150 mL New Path Learning - http://www.newpathlearning.com/store/bycategory/white-board/multimedia-lessons/photosynthesisrespiration-multimedia-lesson-6468.html Elodea Oxygen Bubble Lab http://www.saddleworth.oldham.sch.uk/science/simulations/wat erweed.htm Biology Corner http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/waterweed_sim.html Photosynthesis Virtual Lab http://www.syngenta.com/country/uk/en/learning-zone/sciencelab/experiments/Pages/Photosynthesis_in_Action.aspx