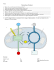
1. Where does the energy that the organisms in
Transcription
1. Where does the energy that the organisms in
Warm up (3 minutes) 1. Where does the energy that the organisms in this ecosystem use to live originally come from? 2. Which organisms in this ecosystem can make their own energy? This stopwatch is timing how long it takes you to get ready. It will stop after everyone - has completed a warm up - has their binder in front of them - has today’s work - is sitting in their assigned seat - has given 3 seconds of silence. Your class will gain points based on how quickly this happens. “Your Future is in Your hands” www.BDCAle.wordpress.com Living Environment: Nature’s Sustainable Design FOCUS QUESTION: How do organisms in an ecosystem get energy? Topic 6.3.1 Energy in Ecosystems, p. Today’s Objective: 9 Today’s Plan: 1. Warm Up (3 min) 2. Photosynthesis Review (10 min) 3. Energy Pyramids and Food Webs (30 min) 4. Regents Practice (10 min) 5. Exit Slip (5 min) Understand the transfer of energy from the sun through different trophic levels in an ecosystem 2 Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 1. All of the energy in an ecosystem originally comes from the sun. Producers, like plants, convert this energy into a form that other organisms can use through the process of photosynthesis. Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 2. Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 3. Formula for Photosynthesis: Solar Energy Carbon dioxide Water Glucose Oxygen Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 4. Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review Secondary Consumers/ Carnivores Decomposers Primary Consumers/ Herbivores Producers/Autotrophs Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 5. In each level of a food pyramid, the amount of available energy decreases because organisms use it for their own metabolism Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 6. Producers: Organisms that make their own energy, also called autotrophs Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 7. Consumers: Organisms that get their energy from other organisms, also called heterotrophs. Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 7. Decomposers: Get energy by breaking down dead organisms and recycling those nutrients back into the ecosystem. Note-‐Taking: Photosynthesis Review 8. Energy transfer in an ecosystem can also be shown in a food web. In a food web, the arrows point in the direcQon that energy is transferred. Design your own food web Direc&ons: Choose one of the ecosystems listed in your student work and create a food web that shows how energy is transferred in that ecosystem! Food Webs Regents Prac>ce Direc&ons: PracQce Ecology Regents quesQons. This stopwatch is timing how long it takes you to get ready. It will stop after everyone - has completed a warm up - has their binder in front of them - has today’s work - is sitting in their assigned seat - has given 3 seconds of silence. Your class will gain points based on how quickly this happens. “Your Future is in Your hands” www.BDCAle.wordpress.com Living Environment: YOU CAN BE A Announcements HERO TOO!!! Nature’s Sustainable Design • NEW MP = FRESH START FOR EVERYONE!!! • Parent Teacher Conferences TODAY a[er school! Come for food, games, and fun! • MP1 ReflecQon Sheets are DUE TODAY! • 6.3 HW is DUE TOMORROW! • DON’T GET A ZERO…BE A HERO! TURN IN YOUR HOMEWORK! 19 Exit Slip (5 minutes) 1. Return to your assigned seat 2. Complete the exit slip 3. Clean up your workstation 4. Secure all handouts in your binder 5. Put your binder away. 1. Which organism in this food web is an autotroph? 2. List two things that would likely happen if grasshoppers were removed from this ecosystem.