PATHOLOGY OF SKIN TUMORS
Transcription
PATHOLOGY OF SKIN TUMORS
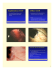
PATHOLOGY OF SKIN TUMORS TYPES OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL TUMORS OF SKIN Seborrheic keratosis. Acanthosis Nigricans. Fibroepithelial polyp. Epithelial cyst (wen). Adnexal (Appendage) tumors. Keratoacanthoma. MORPHOLOGY OF SEBORRHEIC KERATOSIS Variable melanin pigmentation Hyperkeratosis. Small keratin filled cysts (horn cysts & pseudohorn cysts) as invaginations of keratin in to the tumor mass are present. FIBROEPITHELIAL POLYP Fibro epithelial polyp / squamous papilloma / skin tag. A soft, flash colored, bag like, tumor attach to the skin surface. Morphologically, the fibro vascular cores covered by the benign squamous epithelium. Ischemic necrosis may occur. FIBROEPITHELIAL POLYP KERATOACANTHOMA It is, keratin filled crater, surrounded by proliferating epithelial cells, that extend upward in a liplike fashion, over the sides of the crater and downward in to the dermis as irregular tongues. PREMALIGNANT AND MALIGNANT EPIDERMAL TUMORS The types are- I- Actinic keratosis. II- Squamous Cell Carcinoma. III- Basal Cell Carcinoma. PREMALIGNANT AND MALIGNANT EPIDERMAL TUMORS Actinic Keratosis: Occurs in- Lightly pigmented individuals (fair colored). - Chronic sun exposed areas. Mostly occurs on- Face. - Arms. - Dorsum of hands. - Occurs on lips known as actinic cheilitis SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA Predisposing factors in skin are- - Exposure to sun light. - Industrial carcinogens - (tar, oil). - Chronic ulcers. - Draining osteomyelitis. - Old burn scar. - Ingestion of arsenicals. - Ionizing radiation. - Immunosuppression. - Xeroderma Pigmentosa Predisposing factors in oral cavity - Tobacco chewing. - Betel nut chewing. SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA Invasive well differentiated carcinomaIn this, dermal /subcutaneous lobules & groups of atypical squamous cells with pleomorphic & hyperchromatic to vesicular nuclei are found. Keratin pearls are also formed. 1-gross 2- invasive ca. 3- keratin pearls SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA POORLY OR UNDIFFERENTIATED CARCINOMAIt shows highly anaplastic round cells with foci of necrosis & dyskeratosis. Lymphatic metastasis occurs in 5% cases. Undifferentiated SCC-(dyskeratosis) BASAL CELL CARCINOMA Occurs in- Sun exposed areas. - Lightly pigmented peoples (fair colored). Slow-growing. Locally invasive, (after several years of neglect). Rarely metastasize. Early lesion appears as pearly papules. Advance lesion found with ulceration. MICROSCOPY The tumor cells appear rounded with hyperchromatic nuclei. The peripheral tumor cells formed palisading. There is cleft formation occurred between tumor nest & surrounding tissue. 1- nodule with blood vessels, 2- nest & groups of basaloid cells in dermis, 3- palisading & cleft between tumor nodule & stroma DISORDERS OF PIGMENTATION & MELANOCYTES These consist of: 1- Vitiligo. 2- Albinism. 3- Freckle (ephullis). 4- Melasma. 5- Lentigo. 6- Nevi. These consist ofa- Pigmented Nevus (mole). b- Dysplastic nevus. c- Malignant melanoma. MELANOCYTIC NEVUS (PIGMENTED NEVUS, MOLE) Known as benign tumor or hamartoma. Nevus cells are derived from melanocytes and present in clusters or nests. DYSPLASTIC NEVI Appears as flat macule or papule with pebbly surface. Occur on sun exposed or non exposed areas. Typical irregularly pigmented lesion with disorderly proliferation of melanocytes and dermal fibroses. May transform in malignant melanoma. DYSPLASTIC NEVI MALIGNANT MELANOMA Common neoplasm Occurs on skin, oral mucosa, face, esophagus, meninges and eyes. Common in fair persons & arise from melanocytes or nevus cells. Can also form by dysplastic nevus Mostly associated with excessive exposure to sunlight. MORPHOLOGY OF MALIGNANT MELANOMA Morphologically there are two growth phases: I- Radial (Initial phase) II- Vertical growth (Later Phase) MALIGNANT MELANOMA 1-melanocytic hyperplasia, 2-junct.nevus, 3-comp.nev with dysplasia, 4-radial- melanoma 5-vertical-malig.melonoma MALIGNANT MELANOMA (GROSS-RADIAL & VERTICAL GROWTH OF MALIG. MELANOMA & HIGH POWER VIEW) THE END THANK YOU
















![[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and [ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and](http://s1.doczz.net/store/data/006639539_1-9f0ce19e403c365eee4957b8927ed597-70x70.png)

