PROYECTO ESPECIAL BINACIONAL LAGO TITICACA (PELT)
Transcription
PROYECTO ESPECIAL BINACIONAL LAGO TITICACA (PELT)
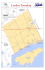
INSTITUTO NACIONAL DE DESARROLLO Proyecto Especial Binacional Lago Titicaca PROYECTO ESPECIAL BINACIONAL LAGO TITICACA (PELT) LOCAL ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS Location and surface The basin of Lake Titicaca is located in Southamerica, to the South of Peru and Northwest of Bolivia. La basin is part of the System Lake Titicaca, River Desaguadero, Lake Poopo and Lake Salar de Coipasa, denominated TDPS. The surface of the basin is 56,270 km2. PERU BOLIVIA Puno The area of the Department is 71,999 km2 and in 2004 the population was 119,462, equivalent to 4.9% of Peru´s population and the 5th populated department of the country. Much of p is situated in the Peruvian the department altiplano, a high plateau in the Andes Mountains ranging in altitude from 3,809 m.a.s.l. to over to 5,000 m.a.s.l. Puno town in mainly built around the western shores of inner Puno Bay, which itself a part of Puno Bay (550 km2), a large bay at the north western of Lake Titicaca (8,167 km2) . Lake Titicaca is at an altitude of 3809 m.a.s.l. and the town extends up surrounding mountains slopes to about 3,950 3 950 m.a.s.l. m a s l The area therefore forms a self-contained unit or basin within the general watershed area of Lake Titicaca. The area is located within the southern tropics around latitude 15 50´and longitude 70W. Topography, Geology, Geomorphology TOPOGRAPHY The study area basin consists mainly of steep hill with slopes from 20º – 45º. They are highest (4,500 m.a.s.l.) and steepest at the western part behind Puno town where they consist mainly of extinct volcanic cones. GEOLOGY The geological setting of the study area is the altiplano depression of the Peruvian Andes Mountains. The itself is a vast intermontane basin in the central Andes of Peru, Bolivia and Argentina Lying between the Western and the Eastern Cordilleras. GEOMORPHOLOGHY The Puno basin is geomorphology very active, due to lake dynamic, rainfall and human activity. Wind erosion is of minor importance. URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEM Evaluation of present conditions At the present, the major rain events flood the street in the several locations in the low lying area of Puno City. The street flooding takes place where the street drainage system is insufficient or does not exist. But the natural gradient towards the drains rain water within a relative short period . The small rivers (microcuencas) located on the steep hill over the city center, disposal of solid wastes, and used construction material are frequently observed due to the insufficient solid waste collection and the lack of sanitation facilities. Those wastes are washes away by the rain events. Through urban drainage ways, reach the bay of Puno. Puno The erosion control measures initiated by PELT for the higher part of the area over 3,850 m.a.s.l. manage to control the serious of the area, although the facilities require periodical maintenance works. PELT intends to extend existing facilities to the whole catchment area of the interior bay. Existing system The City of Puno, originally developed in the low lying area along the shoreline on the interior bay of Puno, later expanded toward west going up the steep slope and recently towards north over the hill. The drainage system utilize the natural drainage ways (small rivers/ravines called microcuencas), but in the city, those drainage y turned into drainage g channels,, which ways now consist the urban drainage systems. The drainage channels presently receive a large volume of silt from the hill slope and unpaved roads of the city. Identifications of problems (1) Street flooding Street flooding is observed mostly in low lying area of the city. Although the flood level does not seriously obstruct the traffic so far, street drainage facilities shall be installed. Only few street in the city have proper drainage facilities. (2) Sedimentation in the drainage ways Sedimentation of silt and debris is observed most of the drainage ways, which reduce the hydraulic capacity of the system. Major sources of incoming silt are earth banks of p road in the steep p hill small rivers,, unpaved and construction site scattered in the city. (3) Rainwater inflow to the sanitary sewer systems The lack of proper street and building drainage facilities leads to the intentional and unintentional rain water discharge into the sanitary sewer system. Existing facilities The natural drainage system consists of small rivers (microcuencas). The major microcuencas are show in the next figure. PELT has been taking the following f measures to control erosion of steep hill the city center. a) Small dams b) Masonry walls to hold soil c)) Infiltration ditches The erosion control facilities for microcuencas are inspected by personnel of PELT at the end of rain season. The repair works for the damaged small dams are required after the major storm events. an drainage systems. Small dams constructed Channel existing Without drainage system Our local engineering solutions PROYECTO ESPECIAL BINACIONAL LAGO TITICACA (PELT) THANKS