Full page
Transcription
Full page
Eudicot stem Xylem epidermis cortex vascular bundle Residual procambium (meristema5c cells) pith pith cortex ring of vascular bundles divides ground 5ssue into cortex and pith Ring arrangement of vascular sieve-‐tube bundles with xylem on the inner half members and and phloem on the outer half companion cells in phloem Phloem Monocot stem Secondary Growth Herbacious stem Woody stem What plants have secondary growth? § None of the modern ferns. § All of the gymnosperms § Many Eudicots but not herbacious plants § No monocots have “normal” secondary growth but a few have anomalous secondary growth Secondary growth: secondary meristems (two types) The vascular cambium is a meristem that produces secondary xylem and secondary phloem The cork cambium is a meristem that produces the phellem (to the outside) and phelloderm (to the inside) Wood is mostly secondary xylem Bark is all tissues outside of the vascular cambium, including secondary phloem, phelloderm, cork cambium and phellem Reminder: What were the primary meristems? protoderm, ground meristem, procambium. What is phellem and phelloderm? Phellem: also called cork cells. These are dead at maturity, cells are impregnated with wax. They function to protect the stem. Phelloderm: cells are living at maturity, this is the inner layer of the periderm. Mainly functions to protect the stem. Periderm is phellem + phelloderm (bark minus secondary phloem) residual procambium residual procambium parenchyma primary xylem primary phloem vascular bundle primary phloem parenchyma Cells begin dividing secondary xylem vascular cambium secondary phloem secondary xylem secondary phloem Vascular cambium forms vascular bundle primary xylem interfascicular cambium fascicular cambium vascular cambium secondary phloem secondary xylem Secondary xylem and phloem form vascular cambium secondary phloem secondary xylem primary growth, some secondary growth year 1 secondary growth 2 Ray system Axial system bark vascular cambium 3 dilated phloem ray secondary phloem annual ring latewood secondary xylem earlywood Cross section of elm wood vessel member latewood annual ring earlywood periderm secondary phloem bark vascular cambium secondary xylem heartwood sapwood Secondary xylem can function for many years. Functional secondary xylem is called sapwood and is located towards the periphery. Heartwood is non-functional secondary xylem that is filled with resin. Cross section of a mullberry branch sapwood heartwood branch (knot) Redwood fiber tracheid transverse ray tracheids bordered pits pare ray radial ray tangen5al ray Gymnosperm wood has rays and tracheids These are sections from redwood. ray ray tracheid phellem cork cambium phelloderm cortex terminal bud lateral bud Secondary growth of branches Last year this year terminal-‐bud-‐ scale scars leaf scar len5cel internode flower bud last year two years ago node leaf scar bundle scar Joshua tree cambium secondary vascular bundle Dragon’s Blood Tree (Dracaena draco) (monocot). The cambium layer produces secondary vascular bundles and parenchyma cells.
Similar documents
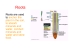 prepared slide of a scross
section (CS) of the
herbaceous monocot Zea
(corn). The monocot stem
does not have a true pith.
prepared slide of a scross
section (CS) of the
herbaceous monocot Zea
(corn). The monocot stem
does not have a true pith.