Statistics in MS Excel
Transcription
Statistics in MS Excel
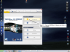
Statistics in MS Excel Industrial Quality Management Week 2 11/1/2011 Udon Thani Rajabhat University Prof. Jeff Nash Table of Contents Objectives: ........................................................................................................................... 3 Statistics Using Excel .......................................................................................................... 4 Statistics Using Excel and MegaStat .................................................................................. 6 Step 1 – Get MegaStat .................................................................................................... 6 Step 2 - Adding MegaStat to Excel ............................................................................... 10 Descriptive Statistics ......................................................................................................... 13 Measures of Data Distribution........................................................................................... 16 The Normal Frequency Distribution .............................................................................. 16 Standard Deviation ........................................................................................................ 16 Mean ............................................................................................................................... 17 Median ............................................................................................................................ 17 Mode............................................................................................................................... 17 Visualizing Data ............................................................................................................. 20 Pie Charts ................................................................................................................... 20 Histograms (Bar Charts) ............................................................................................. 20 Dot Plot ....................................................................................................................... 21 Stem and Leaf Diagrams............................................................................................ 22 Box Plots ..................................................................................................................... 23 Page 2 Objectives: The objective of this document is to provide information to allow the user to: 1. Download the MegaStat add-in from the Internet and install it in Excel. 2. Provide an overview of using Excel for descriptive statistics. 3. Provide an overview of using Excel for inferential statistics. Page 3 คำสำคัญ Statistics Using Excel MS Excel has many built in statistical functions. You can see this by clicking on the Insert Function button in your Excel worksheet. That yields an Insert Function menu as seen next: Page 4 From the Insert Function Menu, select statistical and click on the OK button. This gives a list of about 50 statistical functions from which to choose. A small fraction is shown below: คำสำคัญ Page 5 คำสำคัญ Statistics Using Excel and MegaStat MegaStat is an Excel plug-in that can be downloaded for free from McGraw Hill. MegaStat is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) through which a user can select data and analyses to run. It makes statistical analysis in Excel very easy. เป๊ นฟรี และง่าบมาก MegaStat ต้องการไฟล์ MegaStat.xla Step 1 – Get MegaStat อ.เจฟ ให้สามารถ I have a flash drive with MegaStat. You may copy the file from me. All you need is a file called, MegaStat.xla. Place it in your file directory and remember where. MegaStat.xla Page 6 Alternately you could download MegaStat from McGraw Hill. The URL is: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0010126585/student_view0/megastat.html คำสำคัญ The information and download instructions are at the bottom of this page. It looks like this: Note that there is a tutorial as well. Page 7 Click on one of the download options under “Installing the MegaStat Add-In”. The following menu appears. Click Open. คำสำคัญ Then, Click Allow on the Menu below. Page 8 Then Extract to the desktop, finally clicking on OK คำสำคัญ The following three (3) files are then on your desktop. MegaStat is now on your computer (bottom file). Page 9 Step 2 - Adding MegaStat to Excel คำสำคัญ In your Excel spreadsheet, click on the Microsoft Logo. The menu below will appear. Click on Excel Options at the bottom of this menu. Page 10 This results in the Excel Options menu. Click on Add-Ins and then the Go Button. คำสำคัญ The Add Ins menu appears. Make sure that Analysis ToolPak, Solver Add-In and MegaStat are checked. Click OK. Page 11 MegaStat now appears in your program under the Add-Ins menu. คำสำคัญ Excel and MegaStat are now correctly configured. You are ready to use it. Page 12 คำสำคัญ Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics involves numerically or graphically summarizing data so that it is easier to understand. I‟ll show you a few examples. You can use any data set. I have one that involves grades for quizzes. Click on MegaStat under the Add-Ins menu. The following menu appears. Choose Descriptive Statistics. The Descriptive statistics menu is produced as shown below. 1. 2. 3. 4. Choose the tests that you want to run. Click on any data point Click on the Input range label to expand your selection. Click on the OK button. Page 13 Clicking OK creates a new sheet called, Output with the results of your analysis. Notice that there are many options. A few descriptive statistics are show and 1 dot plot. This is shown in the next figure. คำสำคัญ Click on Input range before clicking on OK An Output sheet is created containing the following results: DotPlot 0 20 40 60 Quiz Grades 80 100 120 Descriptive statistics count mean sample variance sample standard deviation minimum maximum range Quiz Grades 21 84.19 467.56 21.62 11 100 89 Page 14 We can see that there are a lot of statistical procedures that we can u se. Have a look at an earlier menu: คำสำคัญ Descriptive statistics are all under the first two (2) menu items, Descriptive Statistics and Frequency Distributions. Page 15 Measures of Data Distribution The Normal Frequency Distribution A very common way in which data are distributed is called the normal distribution. It looks like this: If we sample data on a specific characteristic which is normally distributed, several important features are seen: คำสำคัญ 1. Data are centered around the middle of the curve, Z=0 above. 2. The curve continues to +/- ∞. It never touches the horizontal axis. 3. The areas under the curve correspond to probabilities. 4. Total area under the curve is equal to 1.0000. Standard Deviation The curve you see above is a standard normal curve. None of your data will be standard. The Z values in the curve above represent the Number of Standard Deviations from the mean. Also note that the mean value is 0. You need a way to convert your data to standard normal form. That is done with the following formula: Page 16 Where: x is your value of interest; is the mean value observe, is standard deviation. Population standard deviation is given by the following formula: where n is the number of data points. In the end, we consider standard deviation a measure of the width the probability distribution for a given data set. Sample standard deviation, s, is given as: Mean The mean is nothing more than the average, and it is expressed as: Median Median is the point at which the 50% of the data has a greater value and 50% has a smaller value. The median of a data set is found through inspection or by using software. Mode The mode of a data set is its most commonly occurring value. If no value occurs at least twice, there is no move. If several values occur with the same frequency, the data set has multiple modes. The mode of a data set is found through inspection or by using software. Let‟s follow this with an example. Page 17 Example 2.1 Given that a course is taught for two classes, the following data was generated: Grades Quiz # Class 1 Class 2 1 78 2 73 3 88 4 91 5 99 6 56 7 42 8 65 9 83 10 69 Calculate the standard deviation for Class 1 as follows: Class 1 x 78 73 88 91 99 56 42 65 83 69 Sum: Divide by n divide by n-1 Calc Calc s (x - 3.60 -1.40 13.60 16.60 24.60 18.40 32.40 -9.40 8.60 -5.40 (x - 12.96 1.96 184.96 275.56 605.16 338.56 1049.8 88.36 73.96 29.16 2660.4 266.04 295.6 16.311 17.193 Page 18 Results for class 2 are as follows: Class 2 x 77 81 69 83 59 63 78 75 81 76 Sum: Divide by n divide by n-1 Calc Calc s (x - (x - 2.80 7.84 6.80 46.24 -5.20 27.04 8.80 77.44 -15.20 231.04 -11.20 125.44 3.80 14.44 0.80 0.64 6.80 46.24 1.80 3.24 579.6 57.96 64.4 7.6131 8.025 The median for Class 1 is 75.5 while that for Class 2 is 76. Class 1 has no mode value; the mode of Class 2 is 81 (it occurs twice). Now, please compare the mean (average) values of Class 1 and Class 2. Then compare the standard deviation of Class 1 and Class 2. What do these numbers tell us? Which class did better? Page 19 Visualizing Data Often it is helpful if we can „see a picture of the data‟. There are many ways to do this. I would advise using software for this. Hand drawing is just so time consuming! It‟s also quite difficult to make changes. Pie Charts These charts are a segmented circle representing relative proportions. This is the only one of the graphics that cannot be drawn by MegaStat. Use the chart wizard. Data for Class1 and Class 2 are as shown. 90-100 90-100 80- <90 80- <90 70 - <80 70 - <80 60 - <70 60 - <70 Histograms (Bar Charts) The same data are represented as histograms. 30 20 10 0 Histogram 60 Percent Percent Histogram 40 20 0 Class 1 Class 2 Page 20 Dot Plot Dot plots allow you to see data on an axis as well as multiple instances of the same values. Dot plots for Class 1 and Class 2 data are given asL DotPlot 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 70 75 80 85 Class 1 DotPlot 50 55 60 65 Class 2 Page 21 Stem and Leaf Diagrams Stem and leave diagrams are textual but have a graphical look. Results from Class 1 and Class 2 are shown below: Stem and Leaf plot for stem unit = leaf unit = Class 1 10 1 Frequency 1 1 Stem 4 5 Leaf 2 6 2 3 2 6 7 8 59 348 38 2 9 19 Stem and Leaf plot for stem unit = leaf unit = Class 2 10 1 Frequency 1 2 Stem 5 6 Leaf 9 39 4 7 5678 3 8 113 10 Page 22 Box Plots Box plots give indications of standard deviation. I show these for Class 1 and Class 2 data: BoxPlot 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 70 75 80 85 Class 1 BoxPlot 50 55 60 65 Class 2 Page 23 Homework 1. Given the following 10 numbers: 756, 791, 707, 743, 744, 759, 766, 781, 756, 761, determine the following: Sample Standard Deviation Range Mean Median Mode You may do this with Excel, if you wish. 2. Given a process with an average completion time of 91 seconds with a population standard deviation of 3.5 seconds, calculate the Z-values for the following times: 84 seconds 98 seconds 103 seconds 3. Given a factory line that fills 30,000 boxes per day. Each box is to be filled with 250 grams of product. The population standard deviation is 1 gram. What is the probability of randomly selecting a box that has weight: 250 grams? (also, how many boxes does this represent?) 251.21 grams> (also, how many boxes does this represent?) < 247.36 grams (also, how many boxes does this represent?) 4. Present the data in question 1 as: A dot plot A stem & leaf diagram A box plot You should use Excel for this. Due November 14, 2554 Page 24 Appendix 1 Standard Normal Table Z 0 0.01 0 0 0.004 0.1 0.0398 0.0438 0.2 0.0793 0.0832 0.3 0.1179 0.1217 0.4 0.1554 0.1591 0.5 0.1915 0.195 0.6 0.2257 0.2291 0.7 0.258 0.2611 0.8 0.2881 0.291 0.9 0.3159 0.3186 1 0.3413 0.3438 1.1 0.3643 0.3665 1.2 0.3849 0.3869 1.3 0.4032 0.4049 1.4 0.4192 0.4207 1.5 0.4332 0.4345 1.6 0.4452 0.4463 1.7 0.4554 0.4564 1.8 0.4641 0.4649 1.9 0.4713 0.4719 2 0.4772 0.4778 2.1 0.4821 0.4826 2.2 0.4861 0.4864 2.3 0.4893 0.4896 2.4 0.4918 0.492 2.5 0.4938 0.494 2.6 0.4953 0.4955 2.7 0.4965 0.4966 2.8 0.4974 0.4975 2.9 0.4981 0.4982 3 0.4987 0.4987 0.02 0.008 0.0478 0.0871 0.1255 0.1628 0.1985 0.2324 0.2642 0.2939 0.3212 0.3461 0.3686 0.3888 0.4066 0.4222 0.4357 0.4474 0.4573 0.4656 0.4726 0.4783 0.483 0.4868 0.4898 0.4922 0.4941 0.4956 0.4967 0.4976 0.4982 0.4987 0.03 0.012 0.0517 0.091 0.1293 0.1664 0.2019 0.2357 0.2673 0.2967 0.3238 0.3485 0.3708 0.3907 0.4082 0.4236 0.437 0.4484 0.4582 0.4664 0.4732 0.4788 0.4834 0.4871 0.4901 0.4925 0.4943 0.4957 0.4968 0.4977 0.4983 0.4988 0.04 0.016 0.0557 0.0948 0.1331 0.17 0.2054 0.2389 0.2704 0.2995 0.3264 0.3508 0.3729 0.3925 0.4099 0.4251 0.4382 0.4495 0.4591 0.4671 0.4738 0.4793 0.4838 0.4875 0.4904 0.4927 0.4945 0.4959 0.4969 0.4977 0.4984 0.4988 0.05 0.0199 0.0596 0.0987 0.1368 0.1736 0.2088 0.2422 0.2734 0.3023 0.3289 0.3531 0.3749 0.3944 0.4115 0.4265 0.4394 0.4505 0.4599 0.4678 0.4744 0.4798 0.4842 0.4878 0.4906 0.4929 0.4946 0.496 0.497 0.4978 0.4984 0.4989 0.06 0.0239 0.0636 0.1026 0.1406 0.1772 0.2123 0.2454 0.2764 0.3051 0.3315 0.3554 0.377 0.3962 0.4131 0.4279 0.4406 0.4515 0.4608 0.4686 0.475 0.4803 0.4846 0.4881 0.4909 0.4931 0.4948 0.4961 0.4971 0.4979 0.4985 0.4989 0.07 0.0279 0.0675 0.1064 0.1443 0.1808 0.2157 0.2486 0.2794 0.3078 0.334 0.3577 0.379 0.398 0.4147 0.4292 0.4418 0.4525 0.4616 0.4693 0.4756 0.4808 0.485 0.4884 0.4911 0.4932 0.4949 0.4962 0.4972 0.4979 0.4985 0.4989 0.08 0.0319 0.0714 0.1103 0.148 0.1844 0.219 0.2517 0.2823 0.3106 0.3365 0.3599 0.381 0.3997 0.4162 0.4306 0.4429 0.4535 0.4625 0.4699 0.4761 0.4812 0.4854 0.4887 0.4913 0.4934 0.4951 0.4963 0.4973 0.498 0.4986 0.499 0.09 0.0359 0.0753 0.1141 0.1517 0.1879 0.2224 0.2549 0.2852 0.3133 0.3389 0.3621 0.383 0.4015 0.4177 0.4319 0.4441 0.4545 0.4633 0.4706 0.4767 0.4817 0.4857 0.489 0.4916 0.4936 0.4952 0.4964 0.4974 0.4981 0.4986 0.499 Page 25
Similar documents
Installing Megastat
 Once you have saved MegaStat.xla, you need to add it into your Excel program.
Open MS Excel. You will notice that unless you have added Add-Ins previously,
there won’t be an Add-Ins tab across the ...
Once you have saved MegaStat.xla, you need to add it into your Excel program.
Open MS Excel. You will notice that unless you have added Add-Ins previously,
there won’t be an Add-Ins tab across the ...