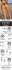Weight Training Addendum
Transcription
Weight Training Addendum
Major Muscle Groups Location Muscle Group Function Iso Techniques Stretches Upper Body Upper Body Shoulders The shoulders help give a wide range of movement and maintain the main shoulder joint. They are responsible for bearing heavy loads whether lifting, pushing, or pulling. Upper Body Deltoids The deltoidsare responsible for overhead lifting and preventing joint dislocation when a person carries heavy objects. Upper Body Biceps The biceps turn the hand and flex the elbow. They aid in lifting and pulling. Upper Body Triceps The triceps primary support the extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm), which makes them responsible for pushing. Upper Body Trapezius (Traps) Upper Body Pectoralis The traps are to stabilize and move the scapulae and support the arm. The pectoralis muscles are most important for the adduction (movement of a body part closer to your center line) and anteversion (the degree of front to back movement of a rotating body part) of the shoulder joint. Shoulder Raises, Circles, Military Presses, Clean and Press Push ups, Bench press, Side & Rear arm raise, Punching Hammer Curls, Barbell Curls, Dumbbell Curls, Preacher Curls Arm Pull-Overs, Towel Stretch, Bear Hug Scratch your Back, Arm Pull Overs, Crucified Arms Arrest, Wall Pushes, Finger Bends Push ups, Bench press, Scratch your back, Morning Yawn, Arm Pull Overs Shrugs, Rows, Reverse Flys Armpit Checks, Ear to Shoulder, Chin to Collar Push Ups, Bench Press, Flys Office Study Break, Arrest, Wall Search Core Core Erector Spinae (Back) Core Latissimus dorsi (Lats) Core Abdominals (Abs) Core Obliques The eretor spinae extend the entire vertebral column which straightens the back and provides support for side-to-side rotation. The lats are primarily responsible for the extension, adduction, abduction, and flexion from an extended position of the shoulder joint. The abs promote the stability of the pelvis and lower back, flexion of the trunk, and compression of the abdominal contents. The obliques act as opponents to the diaphragm, helping reduce the volume of the chest cavity during exhalation and its contraction rotates and sidebends the trunk by pulling the rib cage and midline towards the hip and lower back of the same side. Bent-Over Rows, Pull-Ups, Hyperextension Prostrate Worship, Cat stretch, Sit and Reach Pull-Ups, PullDowns, Rows Side Bend, Prostrate Worship, Back Smacks Crunches, SitUps, Planks Upward Dog, Side Bend, Bridge Side Six-Inches, Side Planks with Knee Pull, Side Track Crunches Star Side Bends, Lie and Twist, Recovery Twists Squats, Lunges, Step Ups Kneet to Chest, Ankle to Forehead, Prostrate Knee Tucks Lower Body Lower Body Gluteus Maximus The gluteus maximus aids external rotation and extension of the hip joint, supports the extended knee through the iliotibial tract,and is the chief antigravity muscle in sitting and abduction of the hip Lower Body Quadriceps The quadriceps extend the knee, stabilizes the patella and knee joint during gait, and support hip flexion. Squats, lunges, leg extension Feet to Backside, Reverse Runner's Stretch, Lunge Lower Body Hamstrings The hamstrings cross and act upon the knee and hip and therefore are responsible for hip and knee extension and rotation. Squats, leg press, leg curls, Touch your Toes, Runner's Stretch, "L" Form Extension Lower Body Gastrocnemius & Soleus (Calves) The calves flex the area between the foot and shin at the ankle joint and flexing the leg at the knee joint. Calf raises, Ankle circles, Balance Board Step Drop, Toe Pulls, Runner's Stretch