Metric Measurement Worksheet kh da BASE dcm gram (g)
Transcription
Metric Measurement Worksheet kh da BASE dcm gram (g)
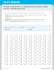
Name___________________________________ Per. ______ Metric Measurement Worksheet kilo, hecto, deka, (base—no prefix), deci, centi, milli k h da BASE d c m gram (g) liter (L) meter (m), etc. Part 1: Metric Units Choose an appropriate metric prefix and/or base unit for the following (h, da, and d prefixes will not be used): ANSWER: mg 1. Mass of ibuprofen in 1 Advil tablet Ex. mass: grams, and small: milli 2. Mass of a person 3. Mass of a slice of cheese 4. Volume of a sample of hydrochloric acid for a chemistry experiment 5. Volume of a bathtub 6. Thickness of a quarter 7. Height of a building 8. Distance from Katy to NYC 9. Length of your arm Part 2: Metric Conversions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 1 km 1g 5.70 g 0.8 kL 783 kg 459 mm 10 m 0.375 L = = = = = = = = _____________ m _____________ cg _____________ mg _____________ L _____________ g _____________ m _____________ cm _____________ mL 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 4.37 cm 75 daL 25 L 5000 m 0.012 g 500 mg 789 mL = = = = = = = _____________ m _____________ L _____________ dL _____________ km _____________ mg _____________ g _____________ L Name_________________________________ Per. ______ Scientific Notation Worksheet When using scientific notation: 1. a. Should numbers greater than or equal to 10 be expressed with positive or negative powers of 10? (circle one) b. Should numbers less than 1 be expressed with positive or negative powers of 10? (circle one) 2. What about a number that falls between 1 and 10? Ex. 7 Express the following in scientific notation: 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 985,000 0.000087 8.845 0.0232 0.75 7,456,921 65,510 200 0.0002 1100 4550.7 4 ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ Express the following in regular notation: 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 8.99 x 10 – 2 2.95 x 10 3 5.443 x 10 4 1.97 x 10 – 6 3.4 x 10 – 1 6.0002 x 10 3 2.55 x 10 – 5 7.9998 x 10 2 4.008 x 10 – 2 9.999 x 10 7 4 x 10 – 3 ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Name___________________________________________ Period____________________ Date___________ Measuring with Precision Below are three meter sticks. As you proceed down the page, each meter stick has a smaller division marked. When you read any scale, you always record the measurement by reading the smallest interval (division) on the scale and then estimate the next smallest division (“record what you know plus one more”). As you proceed down the page, you can see how your measurement becomes more precise and you have more significant digits in your reading. A significant digit is a digit that has physical meaning. Directions: For the metric ruler below, record the correct reading. Hint: what is the smallest interval? a. _______ b. _______ c. _______ d. _______ e. _______ f. _______ Name___________________________________________ Period____________________ Date___________ Measuring Volume What volume is indicated on each of the graduated cylinders below? The unit of volume is mL. What temperature is indicated on each of the thermometers below? The unit for temperature is oC. a) _______ b) _______ c) _______ Name: _________________________________ Period: _____ Significant Figures Worksheet #1 Determine how many significant figures are in each of these numbers. 1) 2.03 11) 1.0030 21) 0.00872 2) 0.0224 12) 967 000 22) 0.000008 3) 10.05 13) 0.00967 23) 0.800008 4) 5000000 14) 900.0 24) 500 000 000 5) 1.0 15) 0.005 25) 708 6) 0.1005 16) 500 26) 0.908 7) 0.002030 17) 0.050 27) 78 000 8) 1.005 18) 0.005670 28) 780.00 9) 0.004300 19) 0.1110 29) 0.00600 10) 1000.1 20) 670 000. 30) 20.040 Determine how many significant figures are in each of these numbers. 31) 7.080 x 107 33) 5 x 1017 35) 1.080 x 1012 32) 4.0 x 104 34) 4.50 x 107 36) 3.40 x 108 Perform the following calculations and express the answer with unit and in proper significant figures. 37) 210.6 mm + 14.57 mm = 42) 500 km x 32 km = 38) 74.000 cm + 8.6 cm = 43) 8560.0 m x 1000 m = 39) 84 cm + 111.7 cm = 44) 0.100 cm x 0.85 cm = 40) 84.34 g – 5.2 g = 45) 9200 g ÷ 873 g = 41) 9.81 cm – 3.151 cm = 46) 985 m2 ÷ 500. m = Name: ___________________________________ Chemistry - Significant Figures Worksheet #2 How many sig figs does each of the following have? 1. 0.02 11. 8040 2. 0.020 12. 0.0300 3. 501 13. 699.5 4. 501.0 14. 2.00 x 102 5. 5000 15. 0.90100 6. 5000. 16. 90100 7. 6051.00 17. 4.7 x 10-8 8. 0.0005 18. 10800000. 9. 0.1020 19. 3.01 x 1021 10. 10001 20. 0.000410 Calculate the following and express your answer with unit and in the proper number of sig figs: 21. 1.35 cm x 2.467 cm = __________________ 22. 1035 g / 82 mL = ___________________ 23. 12.01 mm + 35.2 mm + 6 mm = ______________ 24. 55.46 g - 28.9 g = __________________ 25. 0.21 m x 3.2 m x 100.1 m = _____________________ 26. 0.15 mg + 1.15 mg + 2.051 mg = ____________________ 27. 15 g / 6 mL = ____________________ 28. 505 mL - 450.25 mL = ____________________________ 29. 1.252 cm x 0.115 cm x 0.012 cm = __________________ 30. 1.278 x 103 m2 / 1.4267 x 102 m = ____________________ Introduction to Dimensional Analysis Worksheet 1. Equivalents – Please write the equivalents for each of the items in the provided space: a. 1 week = ____7_____ days f. 1 pint = _________ cups b. 365 days = _________ year g. 1 week = _________ days c. 4 quarts = _________ gallon h. 1 mile = ________ feet d. 2.54 cm = _________ inch i. 60 sec = _________ min e. 12 inches = ________ foot j. 120 min = ________ hours 2. Conversion factors equal to one – Any number over itself is equal to one. For example, 139/139 = 1. Likewise, 3/3 = 1. In the same way, 1 week/7 days = 1. Use the equivalents from part 1 above and write each one as a fraction equal to 1. 1 week a. _____7 days___________ f. ____________________ b. ____________________ g. ____________________ c. ____________________ h. ____________________ d. ____________________ i. ____________________ e. ____________________ j. ____________________ 3. Multiplying by one – Any value multiplied by one is that same value. For example, 139 x 1 = 139. Use the fractions equal to one from part 2 to multiply each value below by “1”. Carefully choose the fraction you write so you can cancel the unit provided and end up with the unit requested. a. 21 days x _______ = ______ weeks f. 5 cups x _______ = ______ pints b. 272 days x _______ = ______years g. 3.2 weeks x _______ = ______ days c. 1.6 gallons x _______ = ______ quarts h. 590 ft x _______ = ______ miles d. 6 inches x _______ = ______ cm i. 400 sec x _______ = ______ min e. 39 inches x _______ = ______ ft j. 325 min x _______ = ______ hours Name___________________Class________Date____ I. Dimensional Analysis Practice with Metric Units 1. 453 cm x _______ = _______ m 2. 13.4 mm x _______ = _______ m 3. 0.12 m x _______ = _______hm 4. 15.0 km x _______ = _______ m 5. 3.2 km x ______ x ______ = ______ mm 1 hr II. 1 hr DA Practice with Imaginary Units 6. 58 whoas x = ___ uhoh’s 7. 0.25 bogs x = ___ cocos 8. 155 popos x = ___ dodos 9. 0.122 shays x = ___ toes 10. 29 hobos x = ___ momos III. DA Practice with Miscellaneous Units 11. 6.00 yr x = ___ day 12. 7.5 x 106 in x = ___ mi 13. 50.0 yd x = ___ in 14. 15 mi x = ___ yd 15. 2.0 gal x = ___ cups Name Date Period Dimensional Analysis/Factor Label Practice Using the conversion factors in your notes and a PENCIL, solve the following. Show work next to each problem and box your answer. Steps for solving: 1. identify unit given 2. identify unit you’d like to convert to 3. identify conversion factor(s) needed 4. set up using the DA technique only and solve 5. round answer to the correct number of sig figs 1. 137 lbs = ? oz 2. 25 yds = ? ft 3. 46 pints = ? gallons 4. 6 days = ? seconds 5. 6 500 943 oz = ? tons 6. 72 inches = ? feet 7. 1 year = ? seconds 8. 64 oz = ? lbs 9. 12 feet = ? inches 10. 89 374 seconds = ? weeks 11. 29 years = ? seconds Name Date Dimensional Analysis Practice Period Single Step Conversions 1. How many quarts are in 3.0 gallons of milk? 2. Cork has a density of 0.35 g/mL. What is the volume of 20. g of cork? 3. One mole of oxygen has a mass of 32 g. What is the mass of 5.5 moles of oxygen? 4. If one mole of gas has a volume of 22.4 L, how many moles are there in 25.0 L of gas? 5. If one mole of nitrogen has a mass of 28 g, how many moles of nitrogen gas are in 7.0 g of nitrogen gas? 6. A large nugget of naturally occurring silver metal has a mass of 3.20 x 10 4 troy ounces. What is the mass in kilograms if 1 troy ounce is equivalent to 0.0311 kg? 7. If 1 mole of octane produces 5450. kJ of heat when burned, how many moles of octane must be burned to produce 15,100. kJ of heat? Multiple Step Conversions 8. An old barometer hanging on the wall of a mountain hut has a reading of 27.0 inches of mercury. 1 inch of mercury equals 0.0334 atm (“atmospheres”) and 1 atm = 101.3 kPa (“kilopascals”), what is the pressure reading of the barometer, in kPa? 9. Sugar costs $0.98/kg. 1 metric ton = 1000 kg. How many metric tons (“t”) of sugar can you buy for $350.? 10. Solve the following using the fact that beakers cost $8.40 per dozen. a. Harry drops 3 dozen beakers. How much will Harry’s chemistry teacher charge him? (sig figs don’t apply) b. Harry breaks another batch of beakers and is charged $13.30, what was the number of beakers that he broke? (give the actual number, not how many dozen) 11. An ancient Celtic chicken farmer wished to purchase a gift for his wife. The gift was worth 2 horses. At the local market, 3 horses were worth 5 cows, 1 cow was worth 4 hogs, 3 hogs were worth 4 goats, and 1 goat cost 9 chickens. How much was the gift going to cost the farmer, who had to pay in chickens? (sig figs don’t apply) 12. In a primitive society, the following exchange rates exist: 1 fot = 5 vum, 2 sop = 3 tuz, 4 bef = 3 tuz, 9 fot = 2 bef (a) A man has 4 sop and wants to convert all of it into vum. How many vum will he get? (sig figs don’t apply) (b) A woman needs to pay for some food costing 12 sop. She has only fot in her purse. How many fot should she pay? (sig figs don’t apply) Metric Conversions (use DA, not decimal hopping) 13. Write the conversion factor between each of the following: a. kg and g b. mL and L 14. Convert the following: a. 25 kg into grams b. 50.0 mL into L 15. If 1 L of granite has a mass of 5.50 kg, a. what is the mass of 7.00 L of granite? b. what is the volume occupied by 22 kg of granite? c. what is the mass, in grams of 5.00 mL of granite?