METRIC WP4 Meta-Analysis and Typology for Regional Innovation
Transcription
METRIC WP4 Meta-Analysis and Typology for Regional Innovation
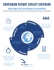
Zurich University of Applied Sciences Meta-analysis of main principles and typology for regional innovation Merja Hoppe Martin Winter Brussels, 19 March, 2015 Objectives and steps Objective Building regional types of innovation potential in transport Steps 1. Defining indicators for innovation in transport on a regional base 2. Measuring regional innovation potential in transport 3. Defining main principles of innovation in transport 4. Identifying types of innovative European regions 1. Indicators for innovation in transport Output Firm activities Enabler RIS Regional Innovation Scoreboard (EC ) => RIST Transport sector Share of government R&D spending Highly educated persons employed Share of employees in science and technology Employment technology and knowledge-sectors Number of patents per 100,000 employees / y Share of innovative enterprises Share of enterprises introducing new products (new to the market) Share of enterprises introducing new products (new to the firm) Growth value added Growth employment • Data for transport available • Enabler, activities, output Facetts of innovation Need to assess 2. Regional innovation potential in transport Innovation potential total Innovation activities • Potential accross Europe • Different levels Consider disparities Potential is also a decision 3. Main principles of innovation in transport Principles Regional characteristics related to innovation Established Prosperity High income & productivity, innovative enterprises => Critical size of eneterprises for innovation Automotive Production Logistics & automotive, production => Specialization, public funds for R&D Science and Employment High purchasing power, productivity growth => High level of education, technical professions R&D in Science and Technology Technical/scientific professions, low unemployment, R&D => Investment in R&D enterprises Infrastructure and Development Employment growth => R&D, dense transport network Successful Product Innovations Product launches, labour productivity & added value => Innovative enterprises Value Added Added value High financial proportion R&D 4. Types of innovative European regions • Strong national schemes • Path dependency Basic role of transport Innovation supporting economy • Metropolitan areas • Economic structural change • Recovery and economic growth Open questions about links Regions ofregions economic structural change Smart and rising regions Emerging Metropolitan regions Conclusions • National factors important => Path dependency to be considered for funding • Transport reflects actual economic situation / crisis => Innovation depends on general economic development Regional economic situation • Different innovation potential transport services => Process innovation, efficiency in energy and emissions = potential!! Transport sector + innovation Regional innovation potential