SOC 111.3 - Centre for Continuing and Distance Education
Transcription
SOC 111.3 - Centre for Continuing and Distance Education
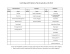
Please Note: This Class Syllabus is an important step in updating the format of our distance courses. If for any reason the Class Syllabus does not match the print Course Guide or online course information, the Class Syllabus shall be taken as correct. CLASS SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE: Foundations in Sociology: Society, Structure, Process COURSE CODE: SOC 111.3 TERM: Spring/Summer 2015 COURSE CREDITS: 3 DELIVERY: Independent Studies COURSE SECTION: X01 START DATE: May 6, 2015 END DATE: August 11, 2015 Course Description One part of a two-part introduction to the discipline of sociology, the study of society. It examines theories and methods for studying changes to the nature and organization of society from pre-modern, to modern and post-modern. Students will be introduced to core sociological concepts used to understand social inequality, social order, social change, and globalization. Formerly: Part of SOC 110.6. Note: Students who have taken SOC 110.6 may not take this course for credit. Course Objectives As students proceed through the course, they should be able to: 1. Understand sociology as a discipline concerned with the systematic study of relationships between individual and society. 2. Develop a “sociological imagination” that enables you to view social phenomena critically by understanding social structure and processes. 3. Recognize the primary ways in which sociologists define, research, and analyze sociological problems. 4. Identify and investigate the nature of major sociological features of Canadian society and other societies, including historical patterns, institutional structures, and structured inequalities. 5. Pose and analyze problems for sociological investigation. March 19, 2015 gm ck pk np SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process Course Overview SOC 111.3 Foundations in Sociology: Society, Structure, Process is an opportunity for you to discover a new discipline and, hopefully, to begin to see the world in a new way. Sociology deals with the familiar, although often in unfamiliar ways. It is concerned with aspects of our everyday lives as well as with hidden structures and historical processes that are both known and unknown to us. As you work through the course, you will encounter much that appears to be common sense. However, you will also be sensitized to new ways of asking questions and gathering information to supplement what you already know about the social world. In the process, you may reach some surprising conclusions. You will be confronted with new concepts, theories, and facts to be learned. Most importantly, however, you should concern yourself with the various tools that sociology offers you to explore and answer questions about our social world. Your Instructor Nancy Poon Contact Information Email: [email protected] Telephone: 306.966.5816 306.384.3584 (leave msg) 306.260.8004 (leave msg or text) Office: 258 Arts and Sciences SKYPE: virtualnancy Preferred method of contact: • Via email or text for inquiries and announcements; please have the identifier “SOC 111” somewhere in your message • Telephone for discussion The best time to telephone me is in the evenings. For in-person visits, please make an appointment. Profile I am currently a sessional lecturer with both the Department of Sociology at the University of Saskatchewan and Saskatchewan Polytechnic. I currently teach Introductory Sociology; Sociology of the Family and Sociology of Health, Culture and Values for Saskatchewan Polytechnic. For the University of Saskatchewan I currently teach Introductory Sociology Courses as well as Penology and Corrections. I have taught Criminology, Women and Law, the Sociology of Law, and Youth, Justice and Social Control. I completed my Ph.D. in 2009. My areas of interest include criminology, penology and corrections, women and law, women, race and the justice system, and finally social theory and knowledge mobilisation as they contribute to democratic processes. Page 2 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process I am also in the process of writing up results of a national survey of the housing situations of women prior and post incarceration in Canada. Required Resources Readings/Textbooks 1. Pearson Custom Sociology: Foundations in Sociology: Society, Structure, Process with MySocLab Student Access Code Card. (2013). Tiemann, K., et. al. (eds.) Toronto: Pearson Learning Solutions. ISBN-13: 978-1-256-82938-6 Textbooks are available from the University of Saskatchewan Bookstore: http://www.usask.ca/consumer_services/bookstore/textbooks Other Required Materials 1. Print Course Materials package sent from CCDE. Recommended Resources (Optional) Use Online Source – MySocLab MySocLab delivers proven results in helping individual students succeed. It provides engaging experiences that personalize, stimulate, and measure learning for each student. MySocLab can be used by itself or linked to any learning management system. You can download the Pearson eText on your iPad. To learn more about how MySocLab combines proven learning applications with powerful assessment, visit www.mysoclab.com. • • • • Register online Go to pearsonmylab.com Follow the instructions to register as a student. After you register you can sign in any time at pearsonmylab.com The access code is printed underneath the flap to the right of your access code card (packaged with the textbook you purchased). For help, go to our 24-hour Customer Technical Support site at 247pearsoned.custhelp.com Page 3 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process Class Schedule Week Module Readings May 6-27, 2015 Module 1 – Sociological Imagination: Classical and Modern Theories Chapters 1, 2, 3 May 28-29 Break May 30June 3 Module 2 – Scientific Study of the Social World: Research Methods June 4-25 June 4-25 Evaluation Due Date No Evaluations Chapter 4 Assignment 1 Due Date: June 3, 2015 Chapter 5 & 6 Module 3 – Social Inequality and Political Economy Assignment 2 Due Date: June 29, 2015 Break No Evalautions June 26July 15 Module 4 – Mass Media, Social Change, and Social Movements Chapters 7 & 8 July 16August 6 Module 5 – Globalization and Environmental Issues Chapters 9 & 10 July 17-20 Break Assignment 3 Due Date: July 29, 2015 No Evlautions August 14, 2015 (9:00 a.m.) FINAL EXAM Note: If for any reason the Class Syllabus Reading List does not match the Module Reading List, the Class Syllabus shall be taken as correct. Grading Scheme Assignment 1 20% Assignment 2 20% Assignment 3 30% Final Exam 30% Total 100% Information on literal descriptors for grading at the University of Saskatchewan can be found at: http://students.usask.ca/current/academics/grades/grading-system.php Please note: There are different literal descriptors for undergraduate and graduate students. Page 4 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process More information on the Academic Courses Policy on course delivery, examinations and assessment of student learning can be found at: http://policies.usask.ca/policies/academicaffairs/academic-courses.php The University of Saskatchewan Learning Charter is intended to define aspirations about the learning experience that the University aims to provide, and the roles to be played in realizing these aspirations by students, instructors and the institution. A copy of the Learning Charter can be found at: http://policies.usask.ca/documents/LearningCharter.pdf Evaluation Components CCDE Writing Centre - Quality writing help for free! Anyone taking a distance class (online, independent studies, televised, or multi–mode delivery) administered by the CCDE can use this free service. The Writing Centre provides tools and support to help you write effective essays, reports, or reviews. Simply submit a project draft, and a qualified tutor will assess your work and offer advice to improve your project. Contact the CCDE Writing Centre at http://www.ccde.usask.ca/writing To fulfill course requirements, you must submit three assignments and write a final examination. Assignment 1: SOC 111.3 (X01) Assignment 1 Value: 20% of final grade Due Date: See Class Schedule Purpose: To understand the relationship between society and the individual and how social theories attempt to explain this relationship. Description: Answer the following questions in essay form. Use 12-point font, Times New Roman, and double-spaced. Write 2-3 pages for each question. 1. What is sociological imagination? Discuss how the sociological perspective can be applied to an understanding of the individual as well as the collective. 2. Compare and contrast the functionalist and conflict theories of society, giving special attention to the assumptions and emphases that distinguish these two approaches. Provide your own comments or arguments. Assignment 2: SOC 111.3 (X01) Assignment 2 Value: 20% of final grade Due Date: See Class Schedule Purpose: To understand the concept of social inequality and to examine the explanations as to why inequality persists in a modern liberal democratic society such as our own. Description: Answer the following questions in essay form. Use 12-point font, Times New Roman, and double-spaced. Write 2-3 pages for each question. 1. Compare and contrast any two of the theoretical explanations for social stratification. Which do you prefer? Why? Page 5 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process 2. Many commentators argue that job selection and working conditions are matters of individual choice and free markets. Using your own experience or empirical evidence, indicate whether or not this is a valid argument. Assignment 3: SOC 111.3 (X01) Assignment 3 Value: 30% of final grade Due Date: See Class Schedule Purpose: To examine a social problem or phenomenon using the knowledge you’ve gained in this course as well as other insights you may have gained through your own personal experience. Description: Write an analytical paper on a specific social issue under one of the following general topics: • Mass media and society • Social movements or collective behaviour • Social change • Globalization If you are uncertain about how to organize your essay, feel free to e-mail me an outline of your proposal and I will give you some feedback. Your paper should be 8-10 pages (12-point font; Times New Roman; and double-spaced) in length. You must provide a bibliography, including references to all sources of information that you draw upon in your paper. The purpose of this assignment is to give you experience in defining a sociological problem and providing a systematic answer or response to that question based upon your own experience and investigation. It is to be an analytical paper in the sense that you will be providing information that not only describes the issue with which you are dealing, but in addition, you will be working towards an explanation of the problem. The process that you should follow in developing your analysis can be outlined as follows: 1. Develop a specific title for your paper. Define your problem or research question: What are you trying to find out, and why? 2. Indicate the possible ways of answering the question: Which theories, approaches or explanations can be used, or have been used by others, to answer the question of a similar nature? Identify, briefly, the strengths and limitations of each approach. 3. Identify your argument: Indicate how you are going to answer the question (i.e., which approach will you take or which set of factors will you conclude are most important to explain your problem), and justify why. 4. Provide your empirical evidence (your own experience/observation or secondary data) and analysis: Organize and present your information. Your findings must be set up in such a way as to show how and why you have answered your question in the way that you have. You may use your textbook as a source of information, but you should also incorporate other books and articles. Page 6 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process 5. Conclude your analysis: Provide a brief concluding section to summarize your analysis and to indicate its importance. Final Examination Value: Date: Length: Purpose: modules. 30% of final grade See Class Schedule 3 hours A comprehensive, invigilated examination on all of the material covered in all Description: The final examination will be composed of a series of essay questions. The essay questions will offer you some choices. Questions will be based on the following topics: 1. Social stratification and social inequality 2. Social change and social movements 3. Collective behaviour 4. Work and political economy in the capitalist society 5. Relationship between individual and society 6. Micro sociology and macro sociology 7. Globalization and environmental issues. You should understand the different sociological theories on these issues. Read and review your textbook and Course Guide. The best preparation for the exam consists of reviewing the content of each module. The location listed in PAWS for your exam is the Saskatoon location. If you want to write your final exam outside Saskatoon, you must complete an Application for Final Examination form, available at: https://ccde.usask.ca/exam-info This will let us know where you would like to write your exam. Students writing in Saskatoon do not need to complete this form. Submitting Assignments Submission forms and pre-addressed envelopes are included in your course materials package. Assignments may be submitted by mail, fax, or in person. Some instructors may also accept assignments submitted electronically. Check with your instructor on the preferred mode. Options for Submitting Assignments: • • • • Electronically to your instructor by e-mail or the Blackboard Learn system (check with your instructor on preferred electronic mode). By fax (with completed submission form) to CCDE at (306) 966-5245. In person (with completed submission form) to the Main Office at the Centre for Continuing and Distance Education (address below) Monday through Friday between 8:30 a.m. and 4:30 p.m. After Hours: Via the drop slot located at the top of the central stairwell, on the Fourth Floor of the Williams Building (address below). By mail (with completed submission form) to: Page 7 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process The Centre for Continuing and Distance Education (CCDE) Room 464, Williams Building University of Saskatchewan 221 Cumberland Avenue North Saskatoon, SK S7N 1M3 Please note that assignments sent by mail should be postmarked no later than the due date, and faxes should be sent prior to 4:30 p.m. Saskatchewan time on the due date. You should keep a personal copy of all assignments submitted. Additional Information Course Requirements To fulfill course requirements, you must submit three assignments and write a final examination. The schedule of assignment due dates and the date of the final examination is listed in your Course Schedule. Please adhere to these dates as they will help you pace your learning. If you think that an assignment will be late, contact your instructor immediately. Students with Disabilities If you have a diagnosed disability (learning, medical, physical, or mental health), you are strongly encouraged to register with Disability Services for Students (DSS). In order to access DSS programs and supports, you must follow DSS policy and procedures. If you suspect you may have a disability, contact DSS for advice and referrals. For more information, see http://www.students.usask.ca/disability/ or contact DSS at 306-966-7273 or [email protected]. Integrity Defined “Integrity is expected of all students in their academic work – class participation, examinations, assignments, research, practica – and in their non-academic interactions and activities as well.” (Office of the University Secretary) It is your responsibility to be familiar with the University of Saskatchewan Guidelines for Academic Conduct. More information is available at http://www.usask.ca/secretariat/student-conduct-appeals/IntegrityDefined.pdf Module Objectives Module 1: Sociological Imagination: Classical and Modern Theories 1. Understand that Sociology is a scientific study of the relationship between individuals and society. 2. Describe what sociological imagination is and how sociologists investigate social phenomena in different ways. 3. Know the linkages and differences between macro and micro approaches to sociology and between classical and modern sociological theories. Page 8 of 9 SOC 111.3 – Foundations in Sociology Society Structure Process Module 2: Scientific Study of Social World: Research Methods 1. 2. 3. 4. Understand the rules and procedures that guide sociological research. Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative approaches to sociology. Know different research methods used in sociological research. Appreciate the importance of ethics in sociological research and explore the influence of feminist theory on sociological methods. Module 3: Social Inequality and Political Economy 1. Understand different sociological theories of social inequality. 2. Describe how social inequality produced within the class structure affects people’s life chances and experiences. 3. Explain the ways in which work, as a fundamental social activity, is related to the labour process in the capitalist society. 4. Understand the nature and significance of the Canadian political and economic institutions. Module 4: Mass Media, Social Change, and Social Movements 1. See how mass media, social change, and social movements are studied sociologically. 2. Know different sociological theories on mass media, social change, and social movements. 3. Examine how the internet reflects long-standing issues in the sociology of mass media. 4. Understand why social movements have historical importance in the process of social change. Module 5: Globalization and Environmental Issues 1. Distinguish between globalization effects in rich and poor countries. 2. Explore the major contributions of sociology to issues of globalization and environment. 3. Outline the major ecological changes and indicators of environmental destruction that have occurred in Canada. Acknowledgements Course Author Li Zong, Ph. D., (Department of Sociology, University of Saskatchewan) Page 9 of 9