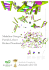Joining of Adjacent Nucleotides 2. Describe the purpose of DNA
Transcription
Joining of Adjacent Nucleotides 2. Describe the purpose of DNA
1. Describe the three steps and molecules involved in the semi-conservative replication of DNA (be sure to include the enzymes involved): “unzipping” Complementary Base Pairing Joining of Adjacent Nucleotides 2. Describe the purpose of DNA replication. Identify the site of DNA replication within the cell. Define recombinant DNA (rDNA). 3. Identify the roles of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, and ribosomes in the process of transcription and translation including: Initiation Elongation Termination 4. Complete the following chart: Template strand of DNA mRNA (codons) tRNA (anticodons) Amino acid sequence TAC GGT CCC CGC ATT 5. An error occurred when DNA was being replicated. The original DNA sequence was TAC ATA GGG and a “T” was placed in the sixth nucleotide position instead of an “A”. a) What kind of genetic mutation is this? HINT: you must convert the DNA sequence to a mRNA sequence in order to read the codon chart._________________________________ b) What is the result of this type of mutation? 6. Sketch the cell membrane – including phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, carbohydrates, and cholesterol Identify the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions of the phospholipid bilayer. Explain why the cell membrane is described as “selectively permeable” 7. What is diffusion? Give an example of diffusion in the body. Provide 3 factors that affect the rate of diffusion across a cell membrane. 8. In an experiment, the bottom of a thistle tube is covered with a membrane permeable only to water. The thistle tube is filled with a 10% sucrose solution and placed in a beaker containing a 5% sucrose solution. What will happen to the solution in the tube after one hour? A. The concentration of sucrose will decrease and become isotonic to the solution in the beaker. B. The concentration of sucrose will increase and become isotonic to the solution in the beaker. C. The concentration of sucrose will decrease and become hypotonic to the solution in the beaker. D. The concentration of sucrose will increase and become hypotonic to the solution in the beaker. On the diagram above – label HYPERTONIC and HYPOTONIC 9. Label the following diagram of the Lock and Key Model of Enzymatic Action. What is activation energy? How do enzymes affect it? Explain how the following affect enzyme activity: High temperatures Low temperatures Exposing the enzyme to lead Changing the pH from the optimal pH