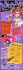Zinc - Kwun Tong Government Secondary School
Transcription
Zinc - Kwun Tong Government Secondary School
Kwun Tong Government Secondary School Chamistry - Periodic Table of elements ( Zinc ) Name: Chan Maxwell Chun Sum Zinc bucket Class: 3A (30) Zinc oxide Zinc chloride Basic Properties Group IIB ; Period 4 Electrons arrangement: 2, 8, 18, 2 Crystal structure: Hexagonal Status at room temperature: Solid (Hard & Btittle) Melting & Boiling points: 419.6°C, 906°C Has 33 isotopes but only 5 are stable (64, 66, 67, 68, 70 Zn) Zinc sulfide Canthbe burn in the air and become Zinc Oxide (2Zn+O2 -> 2ZnO) th The 4 common metal and the 24 most aboundant element in earth Useage Ancient use: Used for brass in weaponry Industrial use: Anti-corrosion (coating of iron and steel because Zn is more reactive than iron or steel) ; Anode material for batteries (in alkaline and zinc– carbon batteries) ; Alloys with copper (e.g. nickel silver, typewriter metal, deep drawing and commercial bronze) ; Zinc chloride (in fire retardant) ; Zinc sulfide (luminescent pigments of X-ray and television screens) ; Salting material (in nuclear weapons) Biological use: 2-4 gram of Zinc in our body (brain, muscle, bones and eye) ; Enzyme (an essential trace element necessary for plants, animals and microorganisms, also make as useful catalytic agent in hydroxylation) ; Proteins (Zn ions coordinated to the amino acid side chains of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, cysteine and histidine) Medical use: Dietary intake (Can protect against sunburn and diaper rash, prevent halitosis, kill prostate cancer cells, heal over the cut, etc.) Discovery of Zinc By a German chemist Andreas Sigismund Marggraf in 1746 By heating a mixture of calamine and C in a vessel without Cu Precautions Zinc toxicity: Excessive Zn suppress Cu and Fe absorption Brass alloy Free zinc ion: Corrosive and highly toxic to plants, invertebrates and vertebrate fish 1 30 Zn Zinc Zinc tablets Zinc-carbon battery 65.39 Alkaline-battery Zinc Andreas Sigismund Marggraf
Similar documents
Opportunities in US Zinc Industry - Market Size, Analysis, Trends, and Forecasts
 Zinc is the third most widely used non-ferrous metal after aluminium and copper. The single largest use of zinc is for industrial purpose; when combined with steel, it offers excellent corrosion resistance, while its resultant alloys when combined with aluminium produce different components. Other uses of lead include lead foil, plumbing, soldering, sound proofing, ammunition etc.
Zinc is the third most widely used non-ferrous metal after aluminium and copper. The single largest use of zinc is for industrial purpose; when combined with steel, it offers excellent corrosion resistance, while its resultant alloys when combined with aluminium produce different components. Other uses of lead include lead foil, plumbing, soldering, sound proofing, ammunition etc.