By Ir. Hor Tek Lip PEDU and MUDA LAKES of KEDAH
Transcription
By Ir. Hor Tek Lip PEDU and MUDA LAKES of KEDAH
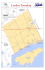
PEDU and MUDA LAKES of KEDAH By Ir. Hor Tek Lip Pedu & Muda Lakes Locations ¾ Pedu Lake • Upstream Sungai Pedu • District of Padang Terap, Kedah Darul Aman • 6014’ 18.71” N (Latitude) and 1000 45’ 59.71” E (Longitude) ¾ Muda • • • Lake Upstream Sungai Muda District of Sik, Kedah Darul Aman 60 06’ 49.07” N (Latitude) and 1000 44’ 38.04” E (Longitude) AHNING LAKE (1988) PEDU LAKE (1969) MUDA LAKE (1969) BERIS LAKE (2004) LOCATION OF PEDU, MUDA, AHNING AND BERIS LAKE Origin of Pedu & Muda Lakes ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ Pedu and Muda Dams construction started 1966 Pedu Dam – Rockfill Muda Dam – Concrete Buttress Impoundment started 1969 Man made reservoirs Manage by Muda Agriculture Development Authority (MADA) Major Rivers Into Pedu Lake ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ Sungai Pedu Sungai Bong Sungai Keleh Bulan Sungai Jek Sungai Peluk Sungai Mong Gajah Major Rivers Into Muda Lake ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ Sungai Sungai Sungai Sungai Muda Che Song Teliang Nipis Kulit WATERSHED ¾ Dipterocarp forest ¾ Hilly ¾ Muda Catchment Trees • 273 taxa (260 species, 4 subspecies & 9 varietes) • 18 taxa endemic to area ¾ Salt Licks • 11 nos in Muda • 2 nos in Pedu Characteristic of Pedu & Muda Lakes and Basin Characteristic Pedu Muda 171 km2 984 km2 Maximum Lake Length 16.50 12.00 Maximum Lake Width 8.20 7.00 1,080 x 106 m3 160 x 106 m3 52 km2 15.5 km2 Catchment area Lake volume (Maximum Storage) Lake area Pedu & Muda Water Level Maximum depth Water level range Pedu Muda 56.70 m 25.90 m 67.07 m MSL to 98.60 m MSL 82.20 m MSL to 103.29 m MSL Daily Water Level and Storage of Pedu Dam 1999-2009 330.00 Spill Level +320 ft MSL W a te r L e v e l ( fe e t) 320.00 310.00 960.00 860.00 300.00 290.00 760.00 280.00 660.00 270.00 260.00 560.00 250.00 460.00 240.00 230.00 360.00 220.00 210.00 260.00 200.00 160.00 Date Water Level Spill Way Daily Water Level and Storage of Muda Dam 1999 - 2009 340.00 200.000 W a te r L e v e l ( fe e t) 330.00 180.000 Spill Level +330 ft MSL 320.00 310.00 160.000 140.000 300.00 120.000 290.00 100.000 280.00 80.000 270.00 260.00 60.000 40.000 250.00 20.000 240.00 0.000 Water Level Date Spill Level Storage Water Balance for Pedu and Muda Lakes Type Of Flow Inflow/ Year (MCM) Outflow/ Year (MCM) Pedu Muda Maximum 1050 1256 Minimum 565 65 Average 812 741 Maximum 1133 876 Minimum 93 133 Average 743 634 Water Retention Time Water Retention Time Pedu (year) Muda (year) Theoretical Filling Time 1.33 0.22 Theoretical Flushing Time 1.45 0.25 Rainfall in Pedu and Muda Catchment Monthly Rainfall (mm) Annual (mm) Lake Minimum Maximum Average Average Minimum Maximum Pedu 0 713 198 2379 1843 3406 Muda 0 650 207 2407 1972 3014 Water Quality of Lakes Pedu Muda Highest 30.10 28.00 Lowest 25.70 25.60 Highest 5.28 3.88 Lowest 2.51 1.60 Highest 59.5 59.4 Lowest 46.6 43.6 HCO-3 (mg/L) Average 3.13 2.84 PH Average 7.19 7.20 Alkalinity (mg/L of CaCO3) Average 2.57 2.33 Parameter Water temperature (oC) DO (mg/L) Conductivity (µmhos/cm) Management of the Lake and Basin Stakeholders ¾ Two types of stakeholders in the lakes ¾ Direct stakeholders • Operates in the lake and basin. ¾ Indirect stakeholders • Downstream of the lakes & its basin. • Benefits from water in the lakes. Direct Stakeholders • • • • • • Muda Agricultural Development Authority (MADA) Kedah Forestry Department Kedah State Government Kedah State Fisheries Department Local Fishermen Operating In The Lakes Kedah State Wildlife Department Indirect Stakeholders Drainage and Irrigation Department (DID) • Syarikat Air Darul Aman (SADA) • MADA Farmers • Uses of Lakes and Its Basin Water Supply Irrigation • water to Muda Area 750 – 800 MCM Domestic • • • and Industrial water supply Northern Kedah and Langkawi Perlis 8.5 m3/s (734 mld) Fishing Small scale fishing Sport fishing (angling) Aquaculture 1% of lake surface area Pedu lake • • 340,000 m2 (3,300 nos. fish cages) 4 approved locations Muda lake • • 89,000 m2 (890 nos. fish cages) 3 approved locations Aquaculture Industrial Zone Permission from MADA and State Fisheries Department Basin Uses Tualang honey (wild honey) LOCATION :1. Charuk Ayer Keroh 2. Pulau Kerbau 3. Charok Jek 4. Depan Desa Utara Resort ( 20 unit sediada ) APPROVED AQUACULTURE LOCATIONS IN MUDA LAKE LOCATIONS 1. Pulau Sintok 2. Kuala Che Song 3. Charok Terau TASIK MUDA APPROVED AQUACULTURE LOCATIONS IN MUDA LAKE Major Impact Stories Resorts Development in Pedu Lake Construction started 1990 Complete & Operational December 1994 235 nos. of buildings & 1 golf course Conflict between MADA and resort operators Locations of some chalets and part of golf course lower than maximum lake level. MADA will lose 163 MCM of water (15% of lake storage capacity) if agree to request MADA rejected the demand Resorts operational only during lower water level Resorts close 2007 Fishing (small scale & sport) 9 Pedu lake • • 9 50 fishermen Koperasi Nelayan Tasik Pedu Muda lake • • 50 fishermen Koperasi Pembangunan Ampangan Muda (KOPAM) Aquaculture in Pedu lake 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 Fish reared is Tilapia Started January 2004 157 cages used to date 93 usable cages now 33 cages filled with fishes Strong wind and wave damage cages Water quality not affected Under Water Logging in Pedu Lake ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ Part of Pedu lake trees were not remove before the impoundment Trees inundated in water Permit for a company to carried out under water logging Approved period May 1996 – March 2003 3 Total timber harvested 35,529 m Area logged : 332.7 hectares No permit given since then Uncoordinated / Illegal Development 9 9 9 No single management Authority cases of uncoordinated / illegal development Examples • • • 9 9 Honey bees gallery and chalets in Muda lake illegal boat construction yards shelters built by fishermen and hunters Presently no threat to the environment Problem in the future Major Lakes Basin Governance Issues Five direct stakeholders Manages the lakes & its basin State forestry department State wildlife department State Fisheries department State District Office MADA Environmentally Sensitive Areas of Rank 1 Basic issues : • Controlling public access to the lake and basin. • Preventing illegal logging. • Controlling collection of forest produce. • Preventing poaching of wildlife. • Enforcing the methods of fishing in the lake. MADA • Section 426A of the National Land Code • Enforcement authority in areas under its Jurisdiction • Action against illegal settlement • Shoreline long • Time consuming & costly Key challenges To Lake Governance Formation of State Park • Linkages between existing departments & new authority Formation of High Conservation Value Forest (HCVF) • Determination process on going • Management of HCVF Minimizing the Impact of Development • greater coordination among the government agencies / departments • A permit system should be set up Preservation Of The Eco-System And Biodiversity • • No single department responsible A mechanism must be set up