Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Transcription
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
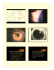
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD Failures of Neural Development: Environmental ((external)) factors Fetal alcohol syndrome y ((FAS)) Cause Consumption of alcohol during pregnancy Ch Characteristics t i ti Physical—diminished height, distinctive facial features, altered nose and eyelids Behavioral and cognitive—mental retardation, hyperactivity, and irritability Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: Dr. Ken Jones New York Times, 2007 The physical landmarks of the human face are very similar from one face to another. A simian crease is a single palmar crease as compared to two creases in a normal palm. Simian crease occurs in about 1 out of 30 normal people, but is also frequently associated with other conditions such as Down syndrome, Aarskog syndrome or fetal alcohol syndrome. Brain of baby with no exposure to alcohol Brain of baby with heavy prenatal exposure to alcohol Photo courtesy of Sterling Clarren, MD A child with FAS (a) shares the typical craniofacial features, including microcephaly, short palpebral fissures, fissures a small nose, and long (from nose to mouth) upper lip with t a deficient de c e t philtrum, with a mouse fetus whose mother was treated with alcohol on her seventh day of pregnancy (b). Illustrated for comparison is a normal mouse fetus of the same developmental stage (c). The face and forebrain of a normal gestational Day 11 mouse embryo (a and b) compared with those of three embryos compared with those of three embryos (c and d; e and f; g and h) affected to differing degrees by maternal ethanol treatment on Day 7 of pregnancy illustrate concurrent loss of the ‘‘midline’’ of the midline tissues. tissues In particular, note the abnormally close proximity of the nostrils, with absence of portions of the medial nasal prominences portions of the medial nasal prominences (m), as well as similar abnormal proximity of the ganglionic eminences (g) and absence of the septal region (s) region (s). Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2001, 43: 148–154 Brain abnormalities Acallosal – agenesis of the corpus callosum Thin corpus callosum - disgenesis Normal child FAS children with focally thin Corpus callosum or acallosal. (Mattson, Jernigan, & Riley, 1994).