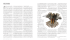Outbreak of Brooder Pneumonia in Broiler Chicks
Transcription
Outbreak of Brooder Pneumonia in Broiler Chicks
80 Indian Vet. J., July 2014, 91 (07) : 80 - 81 Outbreak of Brooder Pneumonia in Broiler Chicks Avijit Dey1 and P.S. De Regional Research Sub-station and Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Ratua, Malda- 732 205, India (Received : 27-07-2013; Accepted : 07-10-2013) Abstract Materials and Methods An outbreak of brooder pneumonia was investigated in broiler chicks (n= 728) in five poultry firms maintained by unemployed rural youths of Manikchak block of Malda district of West Bengal. The chicks of 7-10 days old were affected. The morbidity (65 per cent) and mortality (46 per cent) were very high due to acute nature of the disease. Since there is no specific treatment, some managemental strategies were followed to control the disease. An outbreak of Brooder pneumonia was investigated in broiler chicks (n= 728) in five poultry firms maintained by unemployed rural youths of Manikchak block of Malda district of West Bengal during June- July, 2010. The chicks of 7-10 days old were affected with the disease. The affected chicks were observed to exhibit severe difficulty in breathing by gasping, inappetance and increased thirst. Around 65 per cent morbidity was observed in the affected firms. Key words: Brooder pneumonia, Broiler chicks, Outbreak, West Bengal Results and Discussion Brooder pneumonia or Aspergillosis is a disease, usually of respiratory system affecting all kinds of birds viz. chickens, turkeys, ducklings, pigeons. It is observed in two forms; acute outbreaks with high morbidity and mortality in young birds, and a chronic condition affecting adult birds. In broilers the disease some times occurs in endemic form and results a considerable loss in production. This study reports an outbreak of brooder pneumonia in broiler chicks in Malda district of West Bengal. Fig.1 Yellowish cheesy plaques in the lung and air sacs of the birds affected with Brooder pneumonia 1 The disease was characterized by the history of feeding moldy feeds to the chicks. The affected chicks were found to become thirsty with inappetance. The birds were often observed unthrifty with drooping wings. There was severe difficulty in breathing with sudden death of previously healthy birds. Post mortem examination of birds revealed yellowish cheesy plaques on the surface of lungs and air sacs (Fig.1). In some cases, dark red, firm lung peppered with pinhead sized (1-2 mm diameter) Fig. 2 Dark red colour of lungs of a bird covered with ‘bread mold’ fungal mat Corresponding author : Email : [email protected] The Indian Veterinary Journal (July, 2014) Avijit Dey and P.S. De yellow nodules or bread mold fungal mat (Fig.2) were also found. The characteristic gross lesions, symptoms and history of feeding moldy feeds to the chicks diagnosed the disease as brooder pneumonia. Similar type of observations was reported by several workers (Powel et al., 1994; Wobeser, 1997) and described the disease as aspergillosis. Wet feeds and litters facilitate the growth of the fungus Aspergillus sp. Inhalation of large numbers of spores of the fungus as well as reduced resistance of chicks result in infection. As the disease was very acute, the morbidity (65 per cent) and mortality (46 per cent) was very high. Since there is no specific treatment, some managemental strategies were followed to control the disease. The contaminated feeds were discarded and the dirty litters were replaced with fresh litters. All the utensils 81 were cleaned with disinfectants. Fresh clean drinking water was provided to the birds. The control measures reduced the mortality within five days. The premises were fumigated with formaldehyde before housing the new flock. Acknowledgement The first author is thankful to Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya (UBKV) for providing necessary facilities for this study. References Powell, K.A., Renwick, A. and Peberdy, J.F. (1994). The genus Aspergillus from taxonomy and genetics to industrial application. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y., p. 380. Wobeser, G.A. (1997). Aspergillosis. In: Diseases of wild waterfowl (2nd ed). Plenum Press, New York, N.Y., p. 95–101. Indian Vet. J., July 2014, 91 (07) : 81 - 82 Effective Eradication of Syphacia Muris Infection in Rat (Ratus Norvegicus) Breeding Colony by Oral Ivermectin Therapy M. Thangapandiyan1 and S.P. Preetha Department of Veterinary Pathology, Madras Veterinary College, Chennai-600007. (Received : 18-05-2013; Abstract The present study was designed to eradicate the Syphacia muris infection in a rat breeding colony using oral Ivermectin therapy. Syphacia muris infection was confirmed by anal cellophane tape test. Rats were given 25mg of Ivermectin diluted in 1 liter of drinking water to meet the dose of 2.5gm/kg body weight per day. All the rats received four courses of Ivermectin which alternated with drinking water every five days. During treatment and for 3 months afterwards, perianal tape impressions were collected and evaluated. All examinations subsequent to 1 Corresponding author : Email : [email protected] Accepted : 16-11-2013) completion of treatment have proved negative for further parasite. Key words: Syphacia muris, ivermectin, perianal tape Syphacia muris (commonly referred to as a pinworm) is a nematode which may inhabit the caecum and colon of the laboratory rat (Dix et al., 2004) and are still found in many modern laboratory animal facilities. Although usually nonpathogenic in immunocompetent rodents, pinworm infections may have untoward effects on behavior, growth, intestinal physiology, and immunology. Various diagnostic techniques for The Indian Veterinary Journal (July, 2014)