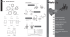egr valve and turbo charger actuator control vacuum circuit
Transcription
egr valve and turbo charger actuator control vacuum circuit
42 04 EGR VALVE AND TURBO CHARGER ACTUATOR CONTROL VACUUM CIRCUIT Vacuum Modulator The biggest difference between the vacuum circuit and layout of the HUBER EGR system after K2004 has been introduced is the location of the vacuum modulator for EGR valve control and the function of the other modulator. In case of EGR equipped vehicle (IDI Engine), it performs the role of controlling the PLA of injection pump whereas, in DI engine, it controls the turbo charger actuator. DI engine vacuum modulator 1. Turbo charger booster vacuum modulator D20DT To EGR valve From vacuum pump 2. EGR valve vacuum modulator To Turbo Charger Actuator (Gray) To EGR Valve (Black) To turbo charger actuator Vacuum pump D27DT From vacuum pump To EGR Valve To turbo charger actuator Vacuum pump 1. Vacuum modulator for EGR valve control 2. Vacuum modulator for injection pump PLA control EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN 43 Vacuum Modulator and Vacuum Hose Below figures illustrate vacuum hoses and related parts of EGR or turbo where wrong or poor connection of vacuum hose would display condition of engine irregularity and defect diagnostic codes on the scan tool. ASSY Related with EGR valve GENERAL 04 HOUSING From vacuum pump COOLING LUB EXHAUST I N T A K E EGR valve FUEL Vacuum modulator for EGR valve control SENSOR CONTROL Related with turbo charger actuator Turbo charger pressure valve Vacuum modulator for turbo charger booster control CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN From vacuum pump EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 44 04 EGR System Diagram Intercooler Exhaust manifold Intake manifold EGR valve Regulated vacuum pressure Modulator Vacuum pump Duty control Feedback EGR (Air Mass) ECU Improved target EGR Air intake signal (for EGR feedback control) Turbo charger Pedal RPM signal signal EGR valve EGR valve recirculates some of exhaust gases to intake system to reduce toxic NOx from engine according to ECU signals. 1. EGR valve opening point : -270 mmHg EGR modulator According to ECU signals, the vacuum modulator drives EGR valve by controlling vacuum pressure that is generated by vacuum pump with PWM type controls. EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN 04 45 GENERAL Operation Principle of Vacuum Modulator ASSY Vacuum pump HOUSING Output vacuum ATM EXHAUST I N T A K E Plunger COOLING LUB Connector Vacuum control FUEL Diaphragm Seat assembly Spring Atmospheric pressure SENSOR CONTROL Plunger Air flow During duty increase (B) During duty reduction (C) Vacuum is controlled according to relationship between chamber pressure (I) in rolling nipple cover and magnetic force (II) in plunger. According to ECU signals, the solenoid valve controls the vacuum pressure that is generated by vacuum pump (-900 ± 20 mbar) with PWM type control and drives the mechanical EGR valve and turbo charger. CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 46 04 Operating principle: Balance between original vacuum pressure and magnetic forcs (see aboe figure) 1. Normal state (Fig. A): Original vacuum and seat section, 3 stoppers keep sealing 2. Duty up state (Fig. B): Original vacuum pressure is connected to inside of diaphragm chamber 3. Duty down state (Fig. C): Increased diaphragm chamber pressure is connected to atmosphere to compensate the pressure. Floating plunger DUTY 50% Stroke (mm) Max. Distance 1mm Output C/V Operating principles when duty is applied from 0 to 50 % Vacuum consumption: Compared to 50 % of duty, ON/OFF periods are most unstable and vacuum consumption is most high. Flowing volume Output vacuum (-mmHg) Output characteristics EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 Up Down CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN 04 47 1. Engine is running 2. Engine RPM is within a specified range. (EGR OFF under high RPM range) 3. Engine torque is within a specified range. (EGR OFF under high torque range) 4. Vehicle speed is within a specified range. (EGR OFF under high speed range) 5. Atmospheric pressure is within a specified range. (EGR OFF under high altitude and low atmospheric pressure) HOUSING 6. Coolant temperature is within a specified range. (EGR OFF under high or low temperature) ASSY GENERAL Operating conditions EXHAUST I N T A K E 7. EGR OFF under extended period of idling. Control logic 1. Main map: EGR volume is controlled based on intake air volume 2. Auxiliary map 1) Coolant temperature (Coolant temperature sensor) 2) Engine rpm (Crankshaft position sensor) 3) Engine load (TPS): Detection of sharp acceleration 5) Atmospheric pressure (Barometric sensor): Compensation of altitude 3. Compensation value of auxiliary map will be increased/decreased based on main map then ECU calculates EGR volume finally to regulate the vacuum duty that applies to the vacuum modulator to control EGR valve openings. FUEL Shut-off conditions COOLING LUB 4) Intake air temperature (HFM): Decreases when over 60°C 1. Engine rpm: over 2,950 rpm 2. Vehicle speed: over 105 km/h CONTROL 3. Coolant temperature: over 100°C or below 10°C SENSOR 4. Idle period: over 50 seconds CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 48 04 EGR Valve and Pipe - Removal and Installation 1. Remove the vacuum hose from the EGR valve. D20DT D27DT 2. Unscrew the bolts and remove the EGR valve (2), EGR valve #1 pipe (1) and gasket. Installation Notice Tightening torque 25 ± 2.5 Nm D20DT D27DT M6 Bolt: 10 ± 1.0 Nm EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN 04 49 GENERAL 3. Remove the EGR valve #1 pipe, #2 pipe, #3 pipe and gaskets from the engine. Installation Notice 25 ± 2.5 Nm D27DT EXHAUST I N T A K E HOUSING D20DT ASSY Tightening torque LUB 4. Install in the reverse order of removal. COOLING NOTICE • Make sure to observe the specified tightening torques. • Never reuse the EGR #1 pipe (intake) and #3 pipe (exhaust) once removed (only D27DT). D27DT EGR #3 pipe (RH) EGR #3 pipe (RH) EGR #1 pipe (LH) EGR center pipe SENSOR EGR center pipe CONTROL D20DT FUEL • Replace the gaskets with new ones. EGR #1 pipe (LH) CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 50 04 Vacuum Modulator - Removal and Installation 1. Remove the vacuum hose from the vacuum modulator. D20DT D27DT 2. Remove the vacuum modulator from the bracket. Installation Notice Tightening torque 10 ± 1.0 Nm 3. Install in the reverse order of removal. NOTICE • Make sure that the vacuum hoses are connected to correct locations. D20DT EXHAUST SYSTEM KYRON SM - 2005.09 D27DT CHANGED BY EFFECTIVE DATE AFFECTED VIN