Cauliflower Ear - Avita Health System
Transcription
Cauliflower Ear - Avita Health System
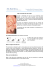
WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? Cauliflower Ear (also known as Auricular Hematoma) is a deformity of the outer ear that is caused by trauma, most commonly in wrestling, where an athlete’s head is pushed to the mat causing a shear force. Boxing is another common sport where Cauliflower Ear is seen and any type of trauma can cause it. The trauma creates hematomas that form under the skin, which are small pools of blood that clot and block blood flow. If left alone, the pools of blood will eventually harden. Without blood flow, cartilage dies and the outer ear folds in on itself without the cartilage support. The result is a bumpy or lumpy, swollen appearance of the outer ear, which resembles cauliflower. HOW CAN IT BE PREVENTED? Most of the occurrences in athletics can be prevented by wearing the appropriate head gear that is already required to participate in a competition. It is recommended that the head gear be worn during practice as well. Athletes need to make sure that their head gear is fitted properly, as a loose fit could result in the head gear coming off; a tight-fit could result in the injury itself. Sometimes Cauliflower Ear cannot be prevented with such instances of infection or accidents but early treatment can decrease the chance of deformity. TREATMENT OPTIONS Early treatment is best. The sooner the blockage is gone, the greater chance of reducing the risk of deformity. The goal is to get all the fluid out from under the skin and get the skin and the cartilage back together, restoring blood flow to the cartilage. Needle Aspiration • This can be done if it is a first time occurrence and the injury is only a few days old. If you wait too long, the blood begins to thicken • A needle may not be able to get rid of the hematoma completely • A compression bandage must be worn after aspiration to prevent more pooling of blood Incision and Drainage • A small incision can be made and the blood clots can be rinsed out using a saline solution • This is usually done when this injury has occurred more than once; there may be some scar tissue formation from the last time it occurred • Also performed if it has been too long after the injury occurred. Blood begins to thicken quickly and a needle may not be able to get all the blood out • A compression bandage must be worn after incision to prevent more pooling of blood Surgical Compression • These can be put in after drainage is completed • Surgical compression will be worn for 10-14 days • These vary in type; they could be silicon or thermoplastic splints, dental rolls or buttons that gets sewn in through the affected area of the ear • Antibiotics are prescribed to reduce the risk of infection and are usually taken for 7-10 days RETURN TO PLAY Follow the direction of your physician. Athletes are usually able to return quickly, only needing to wait 24 hours after the procedure. Take special precaution with keeping the drainage site clean to reduce the chance of infection. Make sure head gear is worn at all times, including during practice, and fits properly. CENTER FOR SPORTS HEALTH www.avitahealth.org 03-11-2014 To schedule an appointment, call 419-562-5281 Centers located in Bucyrus, Crestline, Galion, and Ontario.