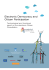Draft - Smart City Proposal Kalyan Dombivli Municipal Corporation
Transcription
Draft - Smart City Proposal Kalyan Dombivli Municipal Corporation
Draft - Smart City Proposal Kalyan Dombivli Municipal Corporation 1 1. Kalyan-Dombivli Introduction 2 Kalyan Dombivli Kalyan – Dombivli and Titwala cities form KDMC jurisdiction; Population increased from 8.2 lakh in 1991 to 15.2 lakh in 2011; Area of the city - 67 sq.km. ( 116.08 Sq. Km. Regional setting including the area under newly added 27 villages); Dormitory town – most travel for jobs outside of the city; Population growth trend and projections (in Lakhs) 12.4 15.2 16.3 19.5 22.9 8.2 1991 2001 2011 2021 2031 2041 3 2. SWOT Analysis 4 S.W.O.T. Strengths 1. Excellent rail connectivity, roughly 10 lakh daily commuters (eight stations within the city limit) 2. Low vehicular density (145 vehicles per 1000); 3. Traditionally compact, mixed use and transit oriented development; 4. 5. Identification of newly added 27 villages as a growth node by MMRDA; Weaknesses 1. Increasing congestion in station and traditional core areas; 2. Insufficient safety and traffic management measures, not pedestrian friendly; 3. Rapidly increasing vehicle ownership; 4. Lack of open and recreational green areas in the city; 5. Lack of scientific treatment and safe disposal of 650 MT solid waste generated in the city; Good water supply network coverage; 6. Affordable housing, relatively lowest property prices; 7. Ulhas creek running along the length of city; 6. 18.4 Km of open drains / nallahs; 8. Pioneering e-governance model in Maharashtra; 7. Low sewerage network coverage; 9. 91.37% literacy rate (Census 2011); 8. Above recommended levels of air and noise pollution levels, presence of open dumping site leading to foul odor in the city; 9. 35% of population living in slums; 10. 98.5% (Census 2011) access to sanitation; 11. Implementation capabilities of over 1000 Cr. of projects in last 5 years; 10. 55% of the population employed outside the city; 12. 80% cost recovery for water supply operations; 11. Lack of a super specialty hospital in the city. 13. Achieved 100% of city level reforms under JNNURM. 5 S.W.O.T. Opportunities 1. Advantageously positioned to leverage on economic opportunities Eastern freight corridor, DMIC, MMC etc.; 2. 37% of the serviced open land available for development; 3. Strong ICT and e-governance framework in KDMC can be leveraged to extend smarter interface to KDMC for proactive participation of citizens towards improving the city; 4. 7 large natural lakes and 32 Km. long water front. These have the potential of being developed into a network of public recreational areas / green spaces and for rain water harvesting at a nodal level; 5. Improvements in collection efficiency, revision of assessment values, tariff rationalization towards infrastructure services and movement to capital value based property taxation holds potential for significantly improving the financial health of the municipal corporation. Threats 1. Navi Mumbai, Thane and other cities in MMR more competitive owing to better service levels; 2. Increase in chemical industries in the vicinity and the resultant pollution. 6 3. Citizen Consultation 7 Results of round 1 citizen consultation Round 1 of the citizen consultation was conducted in order to – Identify the issues of the city Understand the aspirations of the citizens with respect to the city Frame a vision statement for the city The methods used to undertake this consultation were – Focus group discussions Interactions on Facebook and Twitter Discussions and polls on Mygov.in Door-to-door surveys Essay competitions The issues and interventions identified during this round of consultation were grouped sector wise. The results have been presented below – Mobility and mass transit 40% Sanitation 20% Parks, recreational areas & public spaces 11% Improving environment of the city 11% Safety 5% Health facilities 4% Education facilities 3% Affordable hoousing E-governance 3% 2% Emerging priority areas of intervention - mobility and environment 1 Mobility and mass transit facilities – – – 2 – Solid waste management Improving the coverage of sewerage network, Treatment and disposal of sewage Public spaces and greens – – Improvement in station areas and last mile connectivity Improving public transportation systems; Improvements in traffic management system Improved Sanitation facilities – – 3 4 Development of parks and gardens Developing water front Improving environment of the city – – Improving the aesthetic appeal of the city Reducing air pollution 9 5 Other interventions identified through citizen consultations: Safety and better law enforcement; Increase in the number of schools and colleges; Need for more and better quality government and private hospitals; Housing - Redevelopment of slums and increased availability of affordable housing Increase in the economic opportunities in the city 9 10 Results of round 2 citizen consultation Round 2 of the citizen consultation was conducted in order to prioritize an area to be developed and pan city solution to be selected under the Smart City Mission The methods used to undertake this consultation were – Focus group discussions Interactions on Facebook and Twitter Door-to-door surveys Feedback booths at railways stations The area prioritized for development by the citizens was Kalyan station area as mentioned below – Vision statement “Kalyan-Dombivli provides a convenient living habitat for its citizens with excellent transit facilities within its boundaries and provides easy access to other parts of Mumbai Metropolitan Region. The strategic positioning of the city and targeted use of large tracts of un-developed lands will make it a significant Growth Centre of Mumbai Metropolitan Region. The presence of a long beautiful waterfront, adoption of clean technologies and network of green, recreational areas will radically improve the quality of air and of life in this compact city. 12 Nodal level development – transit oriented Growth strategy 6 1 5 4 3 2 13 4. Area Based Development 14 Area based development Green field development (542 acres) Retrofitting (1512 acres) Kalyan Railway Station 15 Area based development- Components 1. Station precinct improvement – pedestrianisation, integration with MSRTC and KDMT bus transportation, increased parking and improved ease-west connectivity 2. Kalyan station redevelopment; 3. Intelligent coordinated traffic signaling and traffic management system; 4. Smart on-street parking and parking policy; 5. Network of green spaces and public areas; 6. Rain water harvesting and ground water re-charge; 7. Rehabilitation of existing solid waste dumping ground and conversion into a park / garden; 8. 10% of the demand through solar power. 9. Water demand management; 10. Sewerage network augmentation, DEWATS in green field zone, installation of bulk flow meters and SCADA at all pumping stations and STPs; 11. 5 MT Bio-methanation plant, node level MSW segregation / recycling plant and treatment and landfill site; 12. Underground power cabling and installation of smart meters; 16 5. Pan City Solution 17 PAN CITY SOLUTION • To streamline the entire process of data generation, recording, maintenance, updation and retrieval- to be able to calculate the performance indicators with known reliability and also to track the performance levels of the basic services on a regular basis • Creating a data warehouse for the city to tap the data generating at different sources, integrate them and disseminate the useful information to the specific target groups to facilitate further decision making • This would ensure • Better informed citizens participating in the development initiatives undertaken by the city • Tracking and monitoring of the performances of different services • More transparency and accountability in the processes of service delivery • Better budgeting of resources in the service provisions • The sectors to be integrated in the system include: • Water supply • Sewerage • Solid waste management • Storm water drainage • Ease of doing business (multi departments approvals) • Transport (KDMT) STRUCTURE OF THE SYSTEM Government App and Extension of the e-portal Citizens System interface Online system for data management and monitoring 6. Costing 20 Cost estimation and expense profile Capital expenditure Amount (in Rs crore) Area- based development 1360 Pan-city proposals 111 Total 1471 Components Amount (in Rs. crore) Area based development 1360 ` area development Station 311 Electricity supply- IPDS+solar 196 Improving accessibility to transit stations and green areas 259 Water demand management 36 Waste water management 59 Solid waste management 236 Development of recreational area 48 Safety 2 Rainwater harvesting through lake interlinking 200 Social infrastructure 13 Components Amount (in Rs crore) Pan city solution 111 Web-based Management Information System 10 ITS for KDMT 52.75 Intelligent Traffic Management Systems 32 ICT for Solid Waste Management 2.2 On street smart parking 13.3 21 KALYAN DOMBIVLI MUNICIPAL CORPORATION