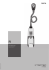Esitys
Transcription
Esitys
Kroonisen kivun ja spastisuuden lievitys neuromodulaation keinoin Mikael von und zu Fraunberg dosentti apulaisylilääkäri Neurokirurgia / KYS Neurokeskus Krooninen kipu on yleinen ja vaikea sairaus – esiintyvyys 19-48% (Suomi ja Eurooppa) – fyysinen ja psyykkinen komorbiditeetti – haitta perhe-elämälle (36%) ja sosiaalisille suhteille (27%) – kustannukset terveydenhuollolle ja yhteiskunnalle – puutteelliset resurssit ja koulutus Kroonisen kivun hoito on moniammatillista – – – – – – – – – lääkehoito fysioterapia psykologiset menetelmät sosiaalityöntekijän apu puudutukset stimulaatiohoidot radiofrekvenssihoidot muut neuromodulaatiohoidot … KYS Neuromodulaatiotyöryhmä – – – – – – – – – joka toinen maanantai klo 14-15 neurokirurgi anestesialääkäri kipulääkäri kipuhoitaja hammaslääkäri psykiatri fysiatri ortopedi Kroonisen kivun neurokirurgiset hoidot ablaatiohoidot (irreversiibeli) – – – – – – – – – central lateral thalamotomy trigeminal nucleotractotomy bulbar DREZ percutaneous cordotomy facet denervation sympathectomy for pain radiofrequency dorsal root entry zone lesion surgical dorsal root entry zone lesion … stimulaatiohoidot (reversiibeli) – – – – – selkäytimen takajuostestimulaatio okkipitaalihermon stimulaatio motorisen aivokuoren stimulaatio syväaivostimulaatio … Kivun neuromodulaatiohoidot stimulaatiohoidot – selkäytimen takajuostestimulaatio – okkipitaalihermon stimulaatio – motorisen aivokuoren stimulaatio – muu perifeerinen hermostimulaatio – syväaivostimulaatio (DBS) muu neuromodulaatio – intratekaalinen lääkehoito – radiofrekvenssihoidot (trigeminusneuralgia) Kivun neuromodulaatiohoidot stimulaatiohoidot – selkäytimen takajuostestimulaatio • lanneselkäkipu +/- radikulaatio • CRPS ja muu neuropaattinen kipu • angina pectoris – okkipitaalihermon stimulaatio – motorisen aivokuoren stimulaatio – muu perifeerinen hermostimulaatio – syväaivostimulaatio (DBS) Neuropaattinen kipu hermovauriokipu - vaurio tai toimintahäiriö kipua välittävässä hermojärjestelmässä sentraalinen – aivoverenkiertohäiriö MS-tauti selkäydinvamma perifeerinen – ääreishermon vammojen jälkitilat – kivuliaat polyneuropatiat – välilevyn pullistuman aiheuttama juurivaurio Neuropaattinen kipu jatkuva kipu ilman ulkoista ärsykettä sähköiskumainen tuikkiva kipu allodynia – normaalisti kivuttoman ärsykkeen provosoima kipu muut poikkeavat kipuaistimukset esim dysestesia Neuromodulaatio – historiallinen alku Selkäytimen takajuostestimulaatio - SCS pulssileveys (µs) amplitudi (V tai mA) pulssitaajuus (Hz) A. potilasohjain B. pulssigeneraattori C. epiduraalielektrodi SCS ja porttikontrolliteoria SCS - kipureseptorit kipuhermosäikeet kivun välittyminen selkäytimessä Melzack and Wall 1960 SCS SCS ja sentraalinen neuromodulaatio sensorinen paikantava huomio tunnesisältö motivaatio De Ridder 2016 SCS – kipualueen kattaminen SCS - lanneselkäkipu ja -radikulaatio References Study design Follow-up/ Number of patients and treatment Results and outcome measures Comments North et al. 1991 Prospective. Third party evaluation 5 years/ 50 SCS 47% of patients >50% pain relief. 10 out of 40, preoperatively disabled, returned to work Impartial evaluation Burchiel et al. 1996 Prospective. Multicenter 1 year/ 70 55% of patients >50% pain relief and significantly improved QoL measures. Analgesia consumption and work status unchanged Usage of variety of pain and functional/QoL measures Kumar et al. 2002 RCT consecutive 5 years/ 60 SCS, 44 CMM QoL improved in 27% of SCS patients and 12% CMM patients. Return to work: 15% in SCS and 0% in CMM patients SCS is cost-effective in the long term North et al. 2005 RCT 3 years/ 19 SCS, 26 reoperation SCS better pain relief (p < 0.01) and less opioid consumption (p > 0.025). Patients randomized to SCS significantly less likely to cross over The results obviate the need for reoperation in cases of recurrent radicular pain after spine surgery Kumar et al. 2007 RCT multicenter 1 year/ 52 SCS, 48 CMM 48% of SCS patients and 9% of CMM patients > 50% pain relief. Significant improvement of QoL and satisfaction in SCS patients. 32 of CMM patients crossed over to SCS after 6 months Variety of outcome measures. Still short followup Kumar et al. 2008 (followup of study from 2007) RCT multicenter 2 years/ 42 SCS, 41 CMM Significantly higher pain relief, QoL and functional status in SCS patients High level of evidence - kivun lievitys >50% 47–55% potilaista Linderoth et al 2009 SCS - CRPS ja muu neuropaattinen kipu References Study design Follow-up/ Number of patients and treatment Results and outcome measures Comments Kemler et al. 2004 RCT 2 years/ 36 SCS + PT. 18 PT 24 patients recieved permanent SCS. Intention-totreat analysis: SCS better pain relief and global effect (both p < 0.001). Health-related QoL improved only in SCS patients High level of evidence due to intention-to-treat analysis. Estimated NNT = 3.0 Kemler et al. 2008 (Followup study from 2004) RCT 5 years/ 36 SCS + PT. 18 PT Intention-to-treat analysis: Pain relief and other outcome measures were the same in both groups. Subgroup analysis of 20 SCS and 13 PT patients: SCS patients had better pain relief (p = 0.02) and global effect (p = 0.06) Despite diminishing effect of SCS, 95% of patients would repeat the treatment for the same result Grabow et al. 2003 (Including CRPS II) Systematic literature review. One RCT, 2 prospective and 12 retrospective observational studies Prospective, noncontrolled 6-40 months/ 314 (IASP criteria for CRPS) SCS. Ten studies reported trial stimulation Successful results in 54-100% of patients. Some studies reported analgesic reduction, improved QoL and global perceived effect High level of evidence for the review. Moderate level (B/C) of evidence for efficacy of SCS for CRPS 12 months/ 29 SCS + PT, all with positive response for sympathetic block 28/29 reduction of pain (VAS 4) and allodynia in all (p < 0.01). Pain disability index significantly reduced (>50%) (p < 0.01) Modest level of evidence. Biased patient selection Harke et al. 2005 Linderoth et al 2009 - CRPS-oireiden lievitys 54-100% potilaista SCS - angina pectoris References Study design Follow-up/ Number of patients and treatment Results and outcome measures Comments De Jongste et al. 1994 RCT 1 year / 8 SCS 9 awaiting SCS for 8 weeks At 8 weeks SCS patients had increased exercise capacity and time to angina, decreased signs of ischemia in ECG and decreased frequency of anginal attacks High level of evidence but few patients Hautwast et al. 1998 RCT 6 weeks / 13 SCS 12 standard treatment Same as De Jongste study. Also improved QoL High level of evidence but short follow-up Mannheimer et al. 1998 (ESBY study) RCT 6 months / 53 SCS. 51 CABG Both groups had adequate symptom relief and no difference between SCS and CABG. Intention-to-treat analysis: mortality and cerebrovascular morbity lower in SCS group High level of evidence. SCS seems preferable in patients with increased risk of surgical complication Andrell et al. 2003 (ESBY study) RCT 2 years / 48 SCS. 39 CABG SCS was less expensive than CABG and required fewer hospitalization days for the primary intervention and for cardiac events Moderately high level of evidence Ekre at al. 2003 Prospective study of SCS dysfunction 65 months / 32 with SCS battery dysfunction and after restitution of SCS function Anginal attacks and consumption of nitrates increased during dysfunction but were significantly diminished after restitution High level of evidence McNab 2006 RCT 1 year / 30 SCS. 30 PMLR No difference in angina-free exercise capacity and QoL Modest level of evidence Di Pede et al. 2003 Prospective, multicenter 13 months / 87 SCS >50% reduction anginal attacks in 73% of patients. Decreased hospital admissions and days of hospitalization Moderate level of evidence. First trial with placebo-like control Eddics et al. 2007 ”Placebo” controlled, randomized 4 weeks / 12 SCS responding patients randomized to different stimulation regimes Low intensity (placebo) stimulation resulted in reduction First blinded SCS study in walking distance, degradation of cardiovascular classification and increased frequency of angina attacks - AP-kohtausten väheneminen >50% 73% potilaista Kivun neuromodulaatiohoidot stimulaatiohoidot – selkäytimen takajuostestimulaatio – okkipitaalihermon stimulaatio • sarjoittainen (cluster) päänsärky • okkipitaalineuralgia • migreeni (?) – motorisen aivokuoren stimulaatio – muu perifeerinen hermostimulaatio – syväaivostimulaatio (DBS) Linderoth et al 2009 Okkipitaalihermon stimulaatio - ONS ONS ja sarjoittainen (cluster) päänsärky - kivun lievitys >50% 72% potilaista Magis et al Curr Opin Neur 2012 ONS ja migreeni - lisää tutkimusnäyttöä tarvitaan Freeman et al, Medical Dev 2013 Sarjoittainen päänsärky - kohtauspäiväkirja Kivun neuromodulaatiohoidot stimulaatiohoidot – selkäytimen takajuostestimulaatio – okkipitaalihermon stimulaatio – motorisen aivokuoren stimulaatio • atyyppinen kasvokipu • sentraalinen kipu – post stroke - MS - TBI – muu perifeerinen hermostimulaatio – syväaivostimulaatio (DBS) Motorisen aivokuoren stimulaatio - MCS MCS ja krooninen neuropaattinen kipu Fontaine et al J Neurosurg 2009 - kivun lievitys >50% 43% potilaista MCS pitkäaikaistulokset Fontaine et al J Neurosurg 2009 - kivun lievitys >50% yli vuoden ajan 45–60% potilaista Spastisuus – refleksikaaren yliherkkyys lihaksen epänormaalisti kohonnut tonus vastus kasvaa venytysnopeuden tai kulman lisääntyessä merkitsee refleksikaaren yliherkkyyttä liittyy ylemmän motoneuronin vaurioon on seurausta keskushermostovauriosta – – – – selkäydinvamma MS-tauti cerebral palsy … Aivohalvaus- ja dysfasialiitto ry 2005 Spastisuuden hoito ja neuromodulaatio asentohoito fysio- ja toimintaterapia omatoiminen kuntoutus botulinumtoksiini paikallishoitona baclofen (GABA reseptori) peroraalisesti intratekaaliset bolukset intratekaalinen infuusio pumpulla = ITB Intratekaalinen lääkehoito – ITB Neuromodulaatio – kehittyvä ala dorsal root ganglion (DRG) -stimulaatio burst -stimulaatio high frequency -stimulaatio (HF10) sfenopalatiiniganglion stimulaatio (SPG) langattomat elektrodit telemedisiiniset sovellukset bluetooth / langaton IPG mikrokontaktitekniikka … Kroonisen kivun ja spastisuuden lievitys neuromodulaation keinoin Mikael von und zu Fraunberg dosentti apulaisylilääkäri Neurokirurgia / KYS Neurokeskus
Similar documents
infraääniraportista - Tuulivoima
 tuhansia yhdistyksiä, joissa on satoja tuhansia jäseniä. Yksin Euroopan laajuinen EPAW
(European Platform Against Windfarms) käsittää yli 890 jäsenyhdistystä Euroopan unionin
alueella. Nämä luvut k...
tuhansia yhdistyksiä, joissa on satoja tuhansia jäseniä. Yksin Euroopan laajuinen EPAW
(European Platform Against Windfarms) käsittää yli 890 jäsenyhdistystä Euroopan unionin
alueella. Nämä luvut k...